With the success of every drug, the pharmaceutical company behind it comes to the forefront. These companies work to push the boundaries of science and healthcare, like Merck & Co. behind Keytruda.
Therefore, to survive in this innovative landscape, it is crucial to be well-versed in what the top players in the pharmaceutical industry, such as Johnson & Johnson, Pfizer, GSK, etc., are up to.
For a competitive analysis, this report includes the pharma industry’s latest trends and findings that will impact the domain.
1. Pfizer
Pfizer is a pharmaceutical giant that has had a remarkable impact on innovation and dedication in healthcare.
One of Pfizer’s most notable and recent contributions is developing the COVID-19 vaccine. Pfizer rapidly developed and distributed the first authorized mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccine with its German partner BioNTech. This achievement marked a significant milestone in the fight against the global pandemic, offering hope to millions worldwide.
Pfizer’s R&D Priorities and Strategies
Pfizer remains committed to shaping the future of healthcare with innovative approaches to tackling diseases and embracing emerging technologies. Let’s look at their latest innovation and future R&D strategies:
- Pfizer invested $11.42 billion in R&D in 2022, $1.1 billion more than the previous year.
- Breakthroughs for All™ is Pfizer’s pioneer initiative to provide fair access to innovative treatments and therapies worldwide. Through this, the company wants to reduce health disparities and ensure that present and upcoming medical advancements are accessible to everyone, regardless of socioeconomic background. The “Breakthrough for All” program improves global health outcomes and creates a more inclusive healthcare ecosystem.
- Pfizer’s Lightspeed program represents a transformative R&D approach to accelerate the process of bringing vital medicines and vaccines to patients. Fueled by the urgency of COVID-19, Pfizer challenged traditional timelines, leading to the development of an authorized vaccine in under a year and a treatment in less than 18 months.
- By 2022, under its Lightspeed program, the company had reduced the median development timeline from 9 to approximately 5 years. It achieved an impressive end-to-end success rate of 18%, nearly ten times higher than in 2010.
- Pfizer established a durable performance with the Lightspeed program by the end of 2021, with Phase 2 success rates for New Molecular Entities at 60%, much higher than the industry norm of 37%. (Source)
Pfizer Products Filed for Approval in the US/EU
| Serial No. | Year | Description |
| 1 | 2023 | Pfizer filed and got approval for PAXLOVID in the US from the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treating mild-to-moderate COVID-19 in high-risk adults. (Source) |
| 2 | 2023 | Pfizer filed the Biologics License Application (BLA) for Elranatamab. ELREXFIO received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in August 2023 under the FDA’s Accelerated Approval Program. ELREXFIO has been approved under Project Orbis in Switzerland and four other countries — Brazil, Canada, Australia, and Singapore. The UK Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) has granted ELREXFIO Innovative Medicine Designation and the Innovation Passport for treating multiple myeloma. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) Human Medicines Committee (CHMP) has recommended a conditional marketing authorization in the European Union (EU) for Elrexfio (Elranatamab). (Source) |
| 3 | 2023 | Pfizer’s Omicron XBB.1.5-adapted monovalent COVID-19 vaccine got FDA’s approval for a supplemental BLA for individuals 12 years and older. An emergency use authorization for the vaccine is granted for individuals 6 months through 11 years of age. (Source) |
| 4 | 2023 | ABRYSVO™ (Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccine) was filed and approved by the FDA to prevent lower respiratory tract disease caused by RSV in individuals 60 years and older. (Source) |
| 5 | 2022 | Pfizer filed its RSV vaccine candidate, RSVpreF or PF-06928316, in the US for FDA review. (Source) |
Popular Drugs Manufactured by Pfizer
- PAXLOVID – It is an FDA-approved co-packaged oral medication for treating COVID-19 and its variants. The paxlovid package includes nirmatrelvir and ritonavir tablets as a 5-day oral prescription treatment. It is primarily produced to treat mild-to-moderate COVID-19 in adults at high risk for progression to severe COVID-19, including hospitalization or death. It has gained widespread usage since then, with more than 11.6 million treatment courses prescribed in the US until May 2023. (Source)
- MYFEMBREE – Pfizer and Myovant Sciences’ MYFEMBREE® (relugolix, estradiol, and norethindrone acetate) is a one-pill, once-a-day therapy treatment approved by the FDA in 2022 for the management of moderate to severe pain associated with endometriosis, with a treatment duration of up to 24 months. It is a popular treatment in the women’s health field for the management of heavy menstrual bleeding associated with uterine fibroids in premenopausal women. (Source)
- Comirnaty – Pfizer manufactured the popular COVID-19 vaccine, Comirnaty, which received FDA approval. Comirnaty has been a remarkable success as it prevented COVID-19 in individuals 16 years and older. (Source)(Source)
Author’s Note: There are more drugs that Pfizer manufactures. (Source)
Pfizer Drugs That Lost Exclusivity in the Past 2 Years
- Eraxis – In 2022, Pfizer’s Eraxis (anidulafungin) lost its exclusivity. This intravenous antifungal drug was initially expected to face generic competition between early 2020 and mid-2022. (Source)
- Sutent – In 2021, Sutent by Pfizer lost its exclusivity. Sutent is a medication used for the treatment of various types of cancer, and its loss of exclusivity allowed for the introduction of generic versions of the drug into the market. (Source)
Pfizer Drugs Losing Exclusivity in the Coming 2 or 3 Years
In the coming years, Pfizer will lose exclusivity for these drugs:
- Ibrance (palbociclib) – Expected to lose patent protection in 2028. Ibrance, used in breast cancer treatment, is projected to generate substantial revenue until then.
- Xtandi (enzalutamide) – Pfizer’s revenue from Xtandi (enzalutamide), a prostate cancer drug co-developed with Astellas Pharma, faces an anticipated end by 2027. The drug will lose exclusivity in the year 2027.
- Inlyta (axitinib) – Expected to lose patent protection in 2025. Inlyta is indicated for certain forms of renal cell carcinoma. (Source)
Pfizer’s Revenue from Drug Sales
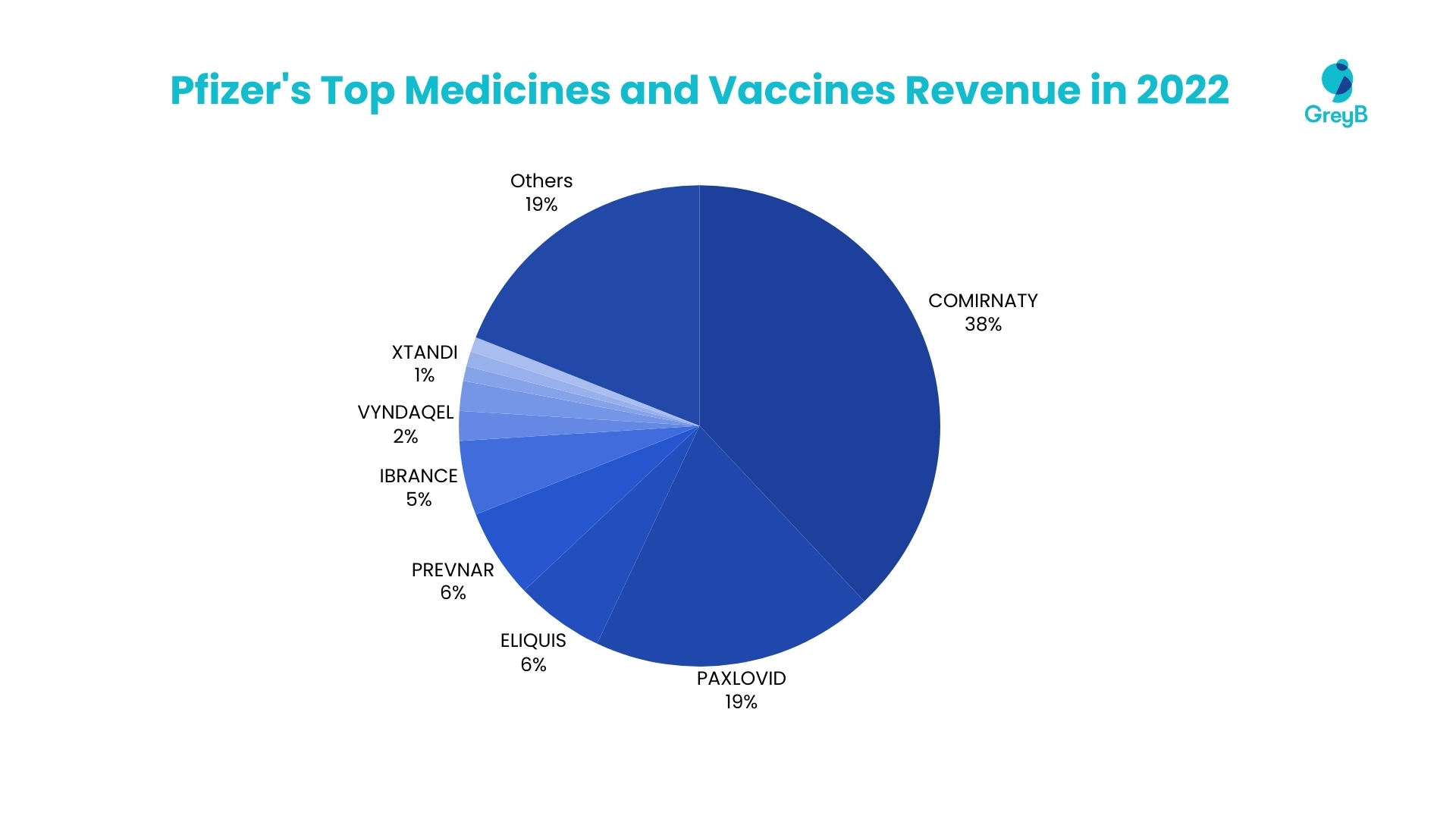
In 2022, Pfizer’s top 10 medicines and vaccines collectively contributed to 82% of the company’s total revenue. Leading the pack, COMIRNATY accounted for 38%, while PAXLOVID followed with a 19% contribution.
Other significant products like ELIQUIS, PREVNAR, IBRANCE, VYNDAQEL, XELJANZ, XTANDI, ENBREL, and INLYTA also made notable contributions. This distribution underscores the financial significance of these key medications and vaccines within Pfizer’s diverse product portfolio. (Source)
Pfizer’s Mergers And Acquisitions
- In 2023, Pfizer acquired Seagen Inc. to strengthen its position in the biotechnology sector and enhance its portfolio of transformative cancer medicines. This strategic move was designed to expand Pfizer’s presence in the field of oncology and advance the development and commercialization of groundbreaking cancer treatments. The Boards of Directors of Pfizer and Seagen approved the agreement, solidifying their commitment to this transformative transaction. (Source)
- In 2022, Pfizer acquired Arena Pharmaceuticals to maintain Pfizer’s portfolio in the field of immuno-inflammatory diseases. Arena Pharmaceuticals brought to Pfizer a promising pipeline of development-stage therapeutic candidates focusing on gastroenterology, dermatology, and cardiology. Notable among these candidates was etrasimod, an oral, selective sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) receptor modulator, which was being developed for various immuno-inflammatory conditions, including ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s Disease, atopic dermatitis, eosinophilic esophagitis, and alopecia areata. (Source)
- Pfizer completed its acquisition of Global Blood Therapeutics (GBT) in 2022 for approximately $5.4 billion. This strategic merger involved the purchase of all outstanding shares of GBT’s common stock in cash at $68.50 per share. Following the acquisition, GBT became a wholly owned subsidiary of Pfizer, and GBT’s common stock ceased trading on the NASDAQ Global Select Market. This allowed Pfizer to expand its portfolio and capabilities within the healthcare and pharmaceutical sectors. (Source)
- Pfizer successfully acquired Biohaven Pharmaceutical Holding Company Ltd. in 2022. This strategic acquisition aimed to incorporate Biohaven’s innovative dual-acting migraine therapy, NURTEC® ODT, approved for acute treatment and episodic prevention of migraines in adults, into Pfizer’s portfolio of healthcare solutions. This move was part of Pfizer’s ongoing efforts to expand its offerings and provide more comprehensive healthcare options to patients and healthcare providers. (Source)
Author’s Note: There are more mergers and acquisitions of Pfizer. (Source)
Collaborations Made by Pfizer
- In 2023, Pfizer collaborated with Flagship Pioneering, Inc. to establish a new partnership to advance innovative medicines. The collaboration involved an initial investment of $50 million from both companies to explore the development of 10 single-asset programs. This joint effort harnessed Flagship’s extensive ecosystem of over 40 human health companies and various biotechnology platforms. In this collaboration, Pfizer was committed to providing funding for and the option to acquire each selected development program. In return, Flagship and its bioplatform companies could receive up to $700 million in milestones and royalties for each successfully commercialized program. (Source)
- In 2022, Pfizer collaborated with CytoReason. This collaboration involved Pfizer using CytoReason’s artificial intelligence technology for drug development programs. During this partnership, Pfizer made a $20 million equity investment, had options to license CytoReason’s platform and disease models, and funded supplementary project support. The collaboration was aimed at leveraging innovative AI solutions to advance Pfizer’s R&D efforts, potentially amounting to a significant financial commitment of up to $110 million over five years. (Source)
- In 2022, Pfizer collaborated with Truveta to harness real-world data for advancing healthcare insights. The collaboration facilitated the delivery of real-time safety insights using extensive, verifiable, real-world data. Pfizer leveraged de-identified data from Truveta to identify, monitor, and assess potential signals in a near-real-time context. This collaborative effort allowed Pfizer to enhance risk mitigation strategies and further research endeavors while drawing from a continuously flowing stream of up-to-date U.S. health data. (Source)
- In 2021, Pfizer collaborated with Arvinas, Inc. to create and commercialize ARV-471, an investigational oral PROTAC® (PROteolysis TArgeting Chimera) estrogen receptor protein degrader. This partnership focused on addressing estrogen receptor-driven diseases, particularly breast cancer. Pfizer’s involvement included a significant upfront payment of $650 million to Arvinas and a separate $350 million equity investment.
According to John Houston, Ph.D., Chief Executive Officer at Arvinas, “We share Pfizer’s deep commitment to people with breast cancer and are thrilled to partner with them to develop this potentially best-in-class therapy. Despite advancements in oncology in recent years, considerable unmet need persists in the treatment of HR+ breast cancer. Together with Pfizer, we will deploy our PROTAC technology in an effort to help people with this devastating disease.” (Source)
2. Johnson & Johnson
Johnson & Johnson (J&J) is an American multinational corporation specializing in pharmaceuticals and medical technologies. Headquartered in New Brunswick, New Jersey, it is publicly traded on the New York Stock Exchange. Renowned globally, J&J is one of only two U.S.-based companies boasting a prestigious AAA credit rating.
J&J’s R&D Priorities and Strategies
- About 25% of J&J sales in 2022 were from new goods that came to market in the last five years. R&D received $14.6 billion in 2022, showing that management was determined to make innovations that would improve people’s lives and build value through partnerships that would improve everyone’s health.
- Johnson & Johnson (J&J) discontinued the development of bermekimab (JnJ-77474462) in eczema or Atopic Dermatitis (AD), resulting in a $610 million pretax impairment charge. While J&J initially paid $750 million for the rights to bermekimab, it was unimpressed by data from a midstage test in atopic dermatitis. The company plans to explore the drug’s potential in another skin disease, hidradenitis suppurativa (HS). (Source)
- Eric Buehlmann, the Director of R&D for Spine at DePuy Synthes, a part of Johnson & Johnson MedTech, and his team spent six years developing the Teligen™ System. The Teligen™ System is a surgical technology platform that enables surgeons to see more clearly while improving their ability to work more efficiently and safely during an operation. It received FDA clearance in 2022.
“Surgeons still operate through a tube, but a disposable camera goes inside and can be slid up and down and rotated in all directions, offering multidirectional and enhanced visualization. It’s as though the surgeon’s eyes can be placed at the very bottom of the tube for an up-close and unobstructed view.” – Eric Buehlmann, Director of R&D, Spine, DePuy Synthes, part of Johnson & Johnson MedTech. (Source) (Source)
J&J Products Filed for Approval in the US/EU
| Serial No. | Year | Description |
| 1 | 2023 | The product Talvey (talquetamab) was filed for FDA approval in the US for treating multiple myeloma after at least four prior lines of therapy. (Source) |
| 2 | 2023 | In August 2023, the FDA approved Akeega (niraparib and abiraterone acetate) for treating adult patients with BRCA-positive metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC). The European Commission granted marketing authorization for Akeega in April 2023. (Source) |
| 3 | 2023 | A supplemental New Drug Application for Balversa (erdafitinib) for treating metastatic urothelial carcinoma, was submitted to the FDA in late August 2023. Additionally, in early September, a marketing authorization application for erdafitinib was submitted to the European Medicines Agency. (Source) |
As of July 2023, Johnson & Johnson had 30 products listed in its key events pipeline for potential approvals or planned submissions in the United States and/or European Union.
Popular Drugs Manufactured by J&J
- Darzalex – In 2023, Darzalex, a medication, was developed by Johnson & Johnson for treating multiple myeloma, a form of blood cancer, providing hope for patients facing this condition. (Source)
- Stelara – In 2021, Johnson & Johnson’s Stelara treated psoriasis, Crohn’s disease, and ulcerative colitis, addressing various inflammatory conditions. (Source)
Stelara Patent to Expire
- Imbruvica – In 2021, Imbruvica, developed by Johnson & Johnson, is an essential drug in the field of oncology, contributing to the management of various cancers. (Source)
J&J Drugs That Lost Exclusivity in the Past 2 Years
- Stelara – In 2022, Stelara (ustekinumab) by Johnson & Johnson lost its exclusivity. Stelara is a biologic used for treating psoriasis and Crohn’s disease and played a significant role in the company’s revenue. (Source)
J&J Drugs Losing Exclusivity in the Coming 2 or 3 Years
- Simponi (golimumab) – In 2024, Simponi (golimumab) is projected to lose exclusivity. Simponi is employed for the management of rheumatoid arthritis. (Source)
J&J Revenue from Drug Sales
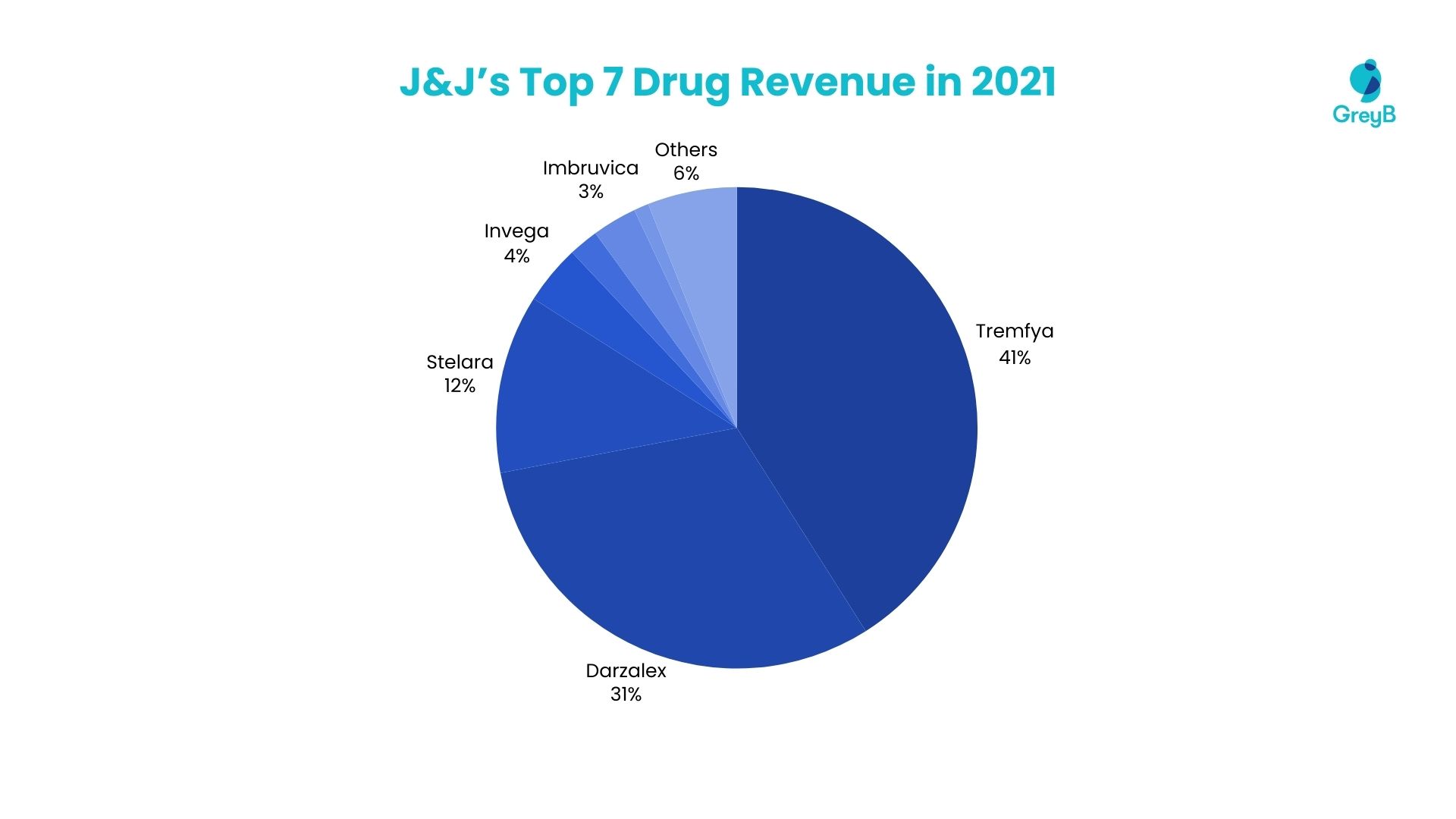
In 2021, Johnson & Johnson’s top 7 drugs significantly shaped its financial landscape. Together, these drugs generated 94% of the company’s total revenue. These high-impact pharmaceuticals, with their respective contribution percentages, include Tremfya (41%), Darzalex (31%), Stelara (12%), Invega (4%), Xarelto (2%), Imbruvica (3%), and Simponi (1%). These medications played a pivotal role in driving the company’s overall financial performance, demonstrating the critical contribution of this group of essential drugs to Johnson & Johnson’s revenue generation. (Source)
J&J Mergers And Acquisitions
- In 2023, Johnson & Johnson initiated a collaboration to launch an exchange offer, allowing its stockholders to opt for shares of its newly listed consumer health unit, Kenvue (KVUE.N). At the time, J&J held an 89.6% stake in Kenvue and intended to split off at least 80.1% of the consumer health company’s shares as part of this offering. This strategic move was a part of J&J’s broader plan to streamline its focus on its larger medical devices and pharmaceutical businesses, emphasizing its commitment to the medical device sector. (Source)
- In 2022, Johnson & Johnson completed its acquisition of Abiomed, Inc. This strategic collaboration was driven by J&J’s focus on expanding its pharmaceutical sector presence. Abiomed, a prominent player in the pharmaceutical industry, specializes in heart recovery technologies and devices. As a result of this merger, Abiomed became an integral part of Johnson & Johnson and operated as a standalone corporation within J&J’s MedTech segment. This move allowed Johnson & Johnson to diversify its portfolio of healthcare products further, particularly in advanced pharmaceutical devices aimed at improving patient care and outcomes.
According to Joaquin Duato, Chief Executive Officer of Johnson & Johnson, “This acquisition marks another important step on Johnson & Johnson’s path to accelerating growth in our MedTech business and delivering innovative medical technologies to more people around the world.” (Source)
- In 2020, Johnson & Johnson acquired Momenta Pharmaceuticals for about $6.5 billion in cash. This strategic move aimed to expand their presence in immune-mediated and autoantibody-driven diseases. The acquisition included the rights to nipocalimab, an anti-FcRn antibody, offering opportunities to address unmet medical needs in various autoimmune conditions. It aligned with Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies’ goal of achieving above-market growth in the medical device and pharmaceutical sector. (Source)
Collaborations Made by J&J
- ABHI and Johnson & Johnson Medical Devices collaborated to support SMEs in the medical device sector. Recognizing the importance of SMEs in healthcare innovation, they provided resources for growth.
According to Jonathan Williamson, Chief Commercial Officer, Emblation, “Emblation is an ambitious, innovation-led organization with market-leading technology, but from an early stage, we identified our ability to build partnerships as a core competency and a source of competitive advantage. The work program with ABHI and J&J will not only be an opportunity to improve our knowledge and skills but a catalyst for the growth of our company.” (Source)
- In 2020, Johnson & Johnson announced a significant collaboration with BARDA, a U.S. Department of Health & Human Services division, to address the urgent need for treatment solutions against COVID-19.
This collaboration aimed to leverage Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies’ expertise in pharmaceuticals and antiviral research to identify potential antiviral compounds effective against the novel coronavirus, SARS-CoV-2. It is a strategic partnership and was part of Johnson & Johnson’s broader response to the global COVID-19 pandemic. By collaborating with BARDA, Johnson & Johnson sought to contribute to the fight against COVID-19 by exploring pharmaceutical solutions, particularly in medical treatments and antiviral therapies. (Source)
3. Roche
Roche, officially known as F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG, is a renowned Swiss multinational healthcare company with a global presence. Operating through its Pharmaceuticals and Diagnostics divisions, Roche is a major player in the healthcare industry.
Headquartered in Basel and listed on the SIX Swiss Exchange, it ranks as the world’s fifth-largest pharmaceutical company by revenue. It is widely recognized as a leader in cancer treatments. Roche’s mission encompasses combating life-threatening illnesses and advancing personalized healthcare solutions.
The pharma company is dedicated to developing cutting-edge in vitro diagnostic tests for various diseases, including cancer, diabetes, COVID-19, hepatitis, and human papillomavirus, among others. (Source) (Source)
Roche’s R&D Priorities and Strategies
- Roche is a healthcare, scientific, and R&D innovator. Scientific staff at Roche Pharma Research and Early Development (pRED) are involved in the scientific community and have published in many peer-reviewed journals in oncology, infectious diseases, immunology, therapeutic modalities, and translational bioengineering. They also work in therapeutic modalities, pharmaceutical sciences, and translational bioengineering.
- Treating the disease’s cause requires first a molecular knowledge of how the disease works and then the ability to affect the target genes’ mRNA directly. The new RNAHub at Roche Pharma Research and Early Development (pRED) in Basel, launched in 2023, aims to achieve this ambitious goal.
- The RNAHub is unique in bringing together experts in RNA biology, medicinal chemistry, molecular design, drug safety, bioinformatics, data analytics, and numerous therapeutic fields. The scientists use integrated and data-centric drug discovery to improve RNA therapies and technologies’ safety and predictive validity. Roche seeks new medications, biomarkers, and targets to build transformational treatments.
- Roche Group’s research, diagnostics, pharma development, data analytics, and genetic insight teams collaborated in 17 countries on 4 continents to develop innovative medicines and diagnostics.
- It’s never been more apparent that the company is committed to new ideas. In 2022, it put a lot of money into R&D. Roche invested around CHF 14.1 billion in R&D in 2022. Their investment in a robust network of over 250 external partner organizations worldwide and the unique mix of autonomous and independent research organizations leads to groundbreaking scientific and technological advances in healthcare.
- Roche Accelerator’s building opened in 2023 in Shanghai, China. There are state-of-the-art labs, offices, and collaboration areas in the 5,000-square-meter building for entrepreneurs working in pharmaceuticals, diagnostics, and personalized healthcare (PHC), such as digital solutions and artificial intelligence (AI).
As part of Roche’s R&D organization, the Accelerator helps entrepreneurs move from an idea to a proof of concept. It uses Roche’s dedicated team, full-spectrum R&D, and commercial skills in China. (Source) (Source) (Source) (Source)
Products Filed by Roche for Approval in the US/EU
| Serial No. | Year | Description |
| 1 | 2023 | Roche planned to file a new application for the subcutaneous oncology drug Tecentriq. The application is expected to be filed with the FDA, indicating a move to secure approval in the US. The UK’s MHRA approved Tecentriq SC at the end of August 2023. It was the first approval for Tecentriq SC worldwide.(Source) |
| 2 | 2023 | Roche’s product, Mircera, was filed and licensed for commercialization in the U.S. (Source) |
| 3 | 2022 | Columvi (glofitamab) received FDA approval on June 16, 2023, for treating adult patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), offering new hope for this challenging condition. In the EU, the CHMP recommended its approval on April 26, 2023, with the European Commission’s final decision anticipated shortly. (Source) (Source) |
Popular Drugs Manufactured by Roche
In 2023, Roche manufactured a range of notable drugs:
- Rituxan – Roche continues to produce Rituxan, a medication used in cancer treatment, particularly for non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
- Herceptin – Roche manufactures Herceptin, which remains a crucial drug in treating breast cancer, especially HER2-positive breast cancer.
- Avastin – Avastin, another Roche product, is still being produced for various cancer types, including colorectal, lung, kidney, and glioblastoma.
- Actemra – Actemra is in production and produced by Roche. It serves patients with conditions such as systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis, juvenile idiopathic arthritis, and rheumatoid arthritis.
- Ocrevus – The company continues to manufacture Ocrevus, a treatment for multiple sclerosis, contributing to disease modification and symptom management.
Roche’s Drugs That Lost Exclusivity in the Past 2 Years
- Lucentis – This drug manufactured by Roche primarily treats various eye conditions, such as age-related macular degeneration. It lost exclusivity in 2021. (Source) (Source)
- Actemra – Roche’s drug Actemra/RoActemra lost exclusivity in 2021. This loss of exclusivity opens the possibility for biosimilar versions to enter the U.S. and EU markets in the second half of 2023. (Source)
Discover new drug launches, track patent expirations, and identify emerging pharma market players with pharsight. Get streamlined access to drug patent information with one click!
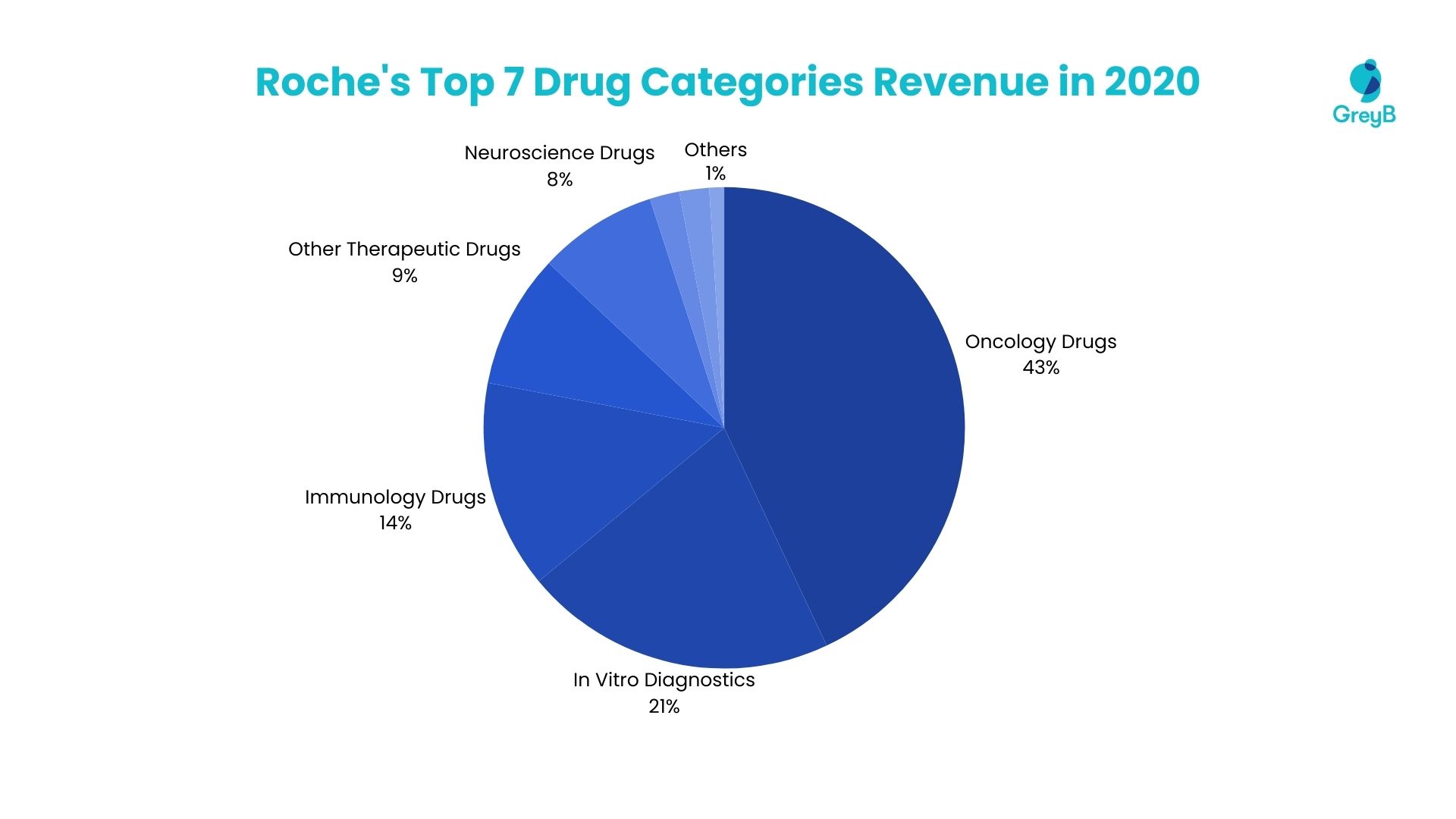
Roche’s Revenue from Drug Sales
In 2020, Roche’s top seven drugs majorly boosted its finances. Together, they made up 99% of its total revenue. These drugs were:
- Oncology Drugs: 43%
- In Vitro Diagnostics: 21%
- Immunology Drugs: 14%
- Other Therapeutic Drugs: 9%
- Neuroscience Drugs: 8%
- Ophthalmology Drugs: 2%
- Infectious Diseases Drugs: 2%
These figures show how crucial these drugs were for Roche’s financial success in different treatment areas. They were key to the company’s revenue. (Source)
Roche’s Mergers And Acquisitions
- In 2022, Roche made a strategic move by announcing its acquisition of Good Therapeutics, a Seattle-based preclinical biotech company, for $250 million. Roche’s decision to acquire Good Therapeutics was driven by the potential of Good’s lead program, which aims to enhance the effectiveness of oncology drugs targeting PD-1 proteins akin to Keytruda or Opdivo.
The acquisition aligned with Roche’s commitment to innovation in oncology therapies and strengthening its position in cancer immunotherapy. It allowed Roche to tap into Good Therapeutics’ expertise in cytokines, which is crucial in regulating the immune response against cancer cells and triggering tumor cell death. (Source)
- In 2021, Roche completed its acquisition of GenMark Diagnostics, a U.S.-based molecular diagnostic test manufacturer, in a $1.8 billion deal—this strategic acquisition aimed to enhance Roche’s portfolio of medical devices and diagnostic solutions. GenMark specializes in molecular diagnostic tests that detect multiple Pathogens from a single patient sample. The acquisition allowed Roche to expand its capabilities in molecular diagnostics, providing healthcare professionals with advanced tools for diagnosing infectious diseases and other medical conditions, reinforcing its commitment to innovation in the medical device sector.
According to Thomas Schinecker, Roche’s Chief Executive Officer, “Acquiring GenMark Diagnostics will broaden our molecular diagnostics portfolio to include solutions that can provide lifesaving information quickly to patients and their healthcare providers in the fight against infectious diseases.” (Source)
- In 2021, Roche completed its acquisition of TIB Molbiol Group, a strategic move to enhance its molecular diagnostic solutions portfolio. Through this acquisition, Roche gained access to a comprehensive range of assays for infectious diseases, including the critical capability to identify SARS-CoV-2 variants. TIB Molbiol’s extensive portfolio, consisting of over 45 CE-IVD assays and more than 100 research assays, was seamlessly integrated with Roche’s existing diagnostic systems, including the LightCycler PCR systems and MagNA Pure sample preparation systems. This acquisition strengthened Roche’s presence in the medical device sector, reinforcing its commitment to advancing diagnostic solutions for healthcare and infectious disease management. (Source)
- In 2020, Roche completed the acquisition of the Irish biotech firm Inflazome for an upfront payment of $449 million (€380 million). Roche’s decision to acquire Inflazome was driven by the potential of Inflazome’s R&D in inflammasome inhibitors. Inflazome’s focus on orally available NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitors held promise for addressing unmet medical needs in various inflammatory diseases, including Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, asthma, inflammatory bowel, and arthritis. (Source)
Collaborations Made by Roche
- In 2023, Roche announced a strategic partnership with US biopharmaceutical company Alnylam. The collaboration aimed to co-develop and co-commercialize zilebesiran, a therapy designed to treat hypertension in patients with high cardiovascular risk. The partnership allowed Roche to gain exclusive commercialization rights for the therapy outside the US, with joint commercialization rights within the country. Alnylam received an upfront payment of $310 million for the agreement. This partnership represented Roche’s commitment to addressing cardiovascular health challenges through innovative therapies and leveraging Alnylam’s expertise in the field. (Source)
- In 2023, Roche collaborated with Cardihab Pty Ltd to enhance the quality and standards of care for individuals living with cardiovascular conditions in Australia. Roche viewed this partnership as a vital step in their commitment to delivering value-based healthcare, spanning the entire patient journey from diagnosis to treatment and monitoring. By optimizing the care approach for those with cardiovascular disease, the collaboration aimed to create an improved care pathway that could reduce hospital readmission rates, lower costs, and alleviate the disease burden on patients’ quality of life. (Source)
- In 2023, Roche announced the expansion of its global business partnership agreement with Sysmex. This collaboration, ongoing for 25 years, was marked by Roche’s commitment to offering Sysmex’s hematology products, enhancing its comprehensive laboratory solutions portfolio. The partnership aimed to leverage the strengths of both companies, combining Roche’s expertise in healthcare solutions with Sysmex’s innovative hematology products to provide more effective and holistic diagnostic solutions to healthcare providers and patients.
According to Matt Sause, CEO of Roche Diagnostics, “We are delighted to expand our 25-year partnership with Sysmex in the area of hematology and in exploring more sustainable diagnostics solutions. Roche and Sysmex both have a long-standing history of delivering reliable and innovative solutions for patients, and I am very happy to see this collaboration grow.” (Source)
- In 2022, Roche collaborated with The Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis, and Malaria through its Global Access Program. This partnership was formed to address critical healthcare challenges in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) combating HIV and tuberculosis (TB). With a significant burden of TB and many undiagnosed HIV cases in LMICs, the collaboration aimed to strengthen diagnostic capacity and pandemic preparedness. The COVID-19 pandemic has disrupted healthcare programs, leading to a decline in HIV testing rates and increased TB-related deaths in these regions. Together, Roche and The Global Fund focused on building local capacity to overcome infrastructure challenges and improve diagnostic capabilities, enhancing healthcare delivery and outcomes. (Source)
4. Merck & Co.
Merck & Co., Inc., a prominent American multinational pharmaceutical company, is headquartered in Rahway, New Jersey. It shares its name with the Merck Group, founded in Germany in 1668, of which it once served as the American arm. It operates as Merck Sharp & Dohme or MSD outside the US and Canada. It is among the global top five by revenue in the pharma industry.
The pharmaceutical giant holds the 71st place on the 2022 Fortune 500 list and the 87th spot on the 2022 Forbes Global 2000 list, both based on 2021 revenues. (Source)
Merck has products (vaccines) targeting diseases such as HPV, measles-mumps-rubella, pneumococcal infections, hepatitis B, rotavirus, chickenpox, and shingles. (Source) (Source)
Merck’s R&D Priorities and Strategies
- A robust R&D program helps Merck & Co. develop new products or make new uses for old ones. Approximately 19,200 people worked for the company in various research activities as of 2022. The company is undergoing many regulatory evaluations in the United States and overseas, as well as in the late stages of clinical development. These include MK-4482 (Lagevrio), iMK-7264 (Gefapixant), MK-3475 (Keytruda), and many more. Additionally, the company is now conducting clinical trials for several other programs in Phase 3.
- In 2022, $13.5 billion was spent on R&D (R&D). The R&D costs were higher because more money was spent on clinical development, especially in cancer, cardiovascular disease, infectious diseases, and vaccines.
- In 2020, the company revealed plans for a state-of-the-art Discovery Research Centre in London. This new 220,000-square-foot hub, located in London’s “Knowledge Quarter,” will cost $1.32 billion and open in 2025. It will house 800 employees, including 120 new hires. Construction began in late 2019 after the Camden Commission approved the building permits.
- Merck and Kelun-Biotech expanded their partnership by signing a license and collaboration agreement in February 2023. As a result, Merck was given the sole right to research, develop, produce, and market up to seven investigational preclinical ADCs for cancer treatment.
- Merck stated in September 2022 that it would start a new doravirine/islatravir (MK-8591A) Phase 3 trial program to treat people who have HIV-1.
- In 2022, Merck and Royalty Pharma agreed to co-fund Merck’s Phase 2b schizophrenia trial testing of MK-8189, an investigational oral phosphodiesterase 10A (PDE10A) inhibitor. (Source) (Source) (Source)
Products Filed by Merck for Approval in the US/EU
| Serial No. | Year | Description |
| 1 | 2023 | Merck’s Keytruda (pembrolizumab) received FDA approval for treating non-small cell lung cancer patients with Stage II, IB, or IIIA disease following surgical resection and platinum-based chemotherapy in the US. (Source) |
| 2 | 2023 | The FDA accepted an application for KEYTRUDA in the US as adjuvant therapy for specific stages of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) following surgical resection with a Prescription Drug User Fee Act. (Source) |
| 3 | 2022 | Merck’s VAXNEUVANCE was approved in the US by the US FDA to prevent invasive pneumococcal disease in infants and children. (Source) |
Popular Drugs Manufactured by Merck
- Keytruda – Keytruda is a highly successful cancer drug with approvals in 38 different settings. It’s a checkpoint inhibitor that enhances the body’s immune response to fight cancer. It’s expected to contribute significantly to Merck’s revenue growth in 2023, with an estimated $3 billion in new sales. (Source)
- VAXNEUVANCE – In 2023, VAXNEUVANCE, an FDA-approved Merck’s vaccine, helps prevent invasive pneumococcal disease in infants and children. This vaccine addresses a critical health need in the prevention of pneumococcal infections. (Source)
- Januvia – This medication was developed by Merck in 2023 and is used to treat Type 2 diabetes, helping to lower blood sugar levels and manage the condition effectively. (Source)
- Singulair – Merck produces Singulair, an asthma medication crucial in controlling symptoms and improving overall respiratory function for individuals with asthma. (Source)
Merck’s Drugs That Lost Exclusivity in the Past 2 Years
- Isentress (raltegravir) – Lost Exclusivity in 2022. Isentress is used to treat HIV, but it faced declining sales due to patent expirations and competition. (Source)
Merck’s Drugs Losing Exclusivity in the Coming 2 or 3 Years
- Keytruda – Keytruda is expected to lose Exclusivity in 2028. Merck’s highly successful cancer immunotherapy, Keytruda, is scheduled to face the loss of market exclusivity in 2028, potentially impacting the company’s revenue. (Source)
Merck’s Revenue from Drug Sales
In 2022, Merck’s top 10 drugs made a significant impact, contributing to 99% of the company’s total revenue. Keytruda took the lead with 46%, followed by Gardasil at 16%, Lagevrio at 13%, Januvia at 6%, ProQuad at 4%, Janumet at 3%, Bridion at 3%, Lynparza at 4%, Lenvima at 2%, and Rota Teq at 2%. These pharmaceutical products were pivotal in maintaining Merck’s financial performance, highlighting their substantial importance in its revenue portfolio. (Source)
Top 10 Drugs Account for 99% of the Total Revenue in 2022
Merck’s Mergers And Acquisitions
- In 2023, Merck completed the acquisition of Prometheus Biosciences, Inc. This strategic move allowed Merck to enhance its portfolio and expand its presence in the healthcare industry. By acquiring Prometheus, Merck aimed to bolster its bioscience position and advance its commitment to delivering innovative healthcare solutions.
According to Robert M. Davis, Merck’s Chairman and Chief Executive Officer, “The Prometheus acquisition accelerates our growing presence in immunology, augments our diverse pipeline, and increases our ability to deliver patient value. This transaction is another example of Merck acting strategically and decisively when science and value align. Prometheus brings us a potential best-in-class candidate that creates an opportunity for us to transform treatment for patients with immune-mediated diseases. We are excited to welcome our Prometheus colleagues to Merck, and we look forward to working together, driven by our common purpose of saving and improving lives.” (Source)
- In 2022, Merck entered into a significant agreement by acquiring Imago BioSciences, Inc. for an approximate total equity value of $1.35 billion. This strategic move aimed to bolster Merck’s presence in biopharmaceuticals and expand its innovative offerings. The acquisition allowed Merck to tap into Imago’s promising pipeline of potential therapies and advance its mission of delivering cutting-edge healthcare solutions to patients worldwide. (Source)
- In 2021, Merck made a significant move by entering into a definitive agreement to acquire Acceleron Pharma Inc., a publicly traded biopharmaceutical company. The acquisition was valued at approximately $11.5 billion, with Merck acquiring Acceleron for $180 per share in cash. This strategic acquisition allowed Merck to expand its portfolio and bolster its presence in the biopharmaceutical industry, further enhancing its ability to develop and deliver innovative treatments to address critical medical needs. (Source)
- In 2021, Merck completed the acquisition of Pandion Therapeutics, Inc. Merck’s strategic focus on expanding its portfolio of innovative therapies, particularly in autoimmune diseases, driven the acquisition. By acquiring Pandion, Merck aimed to bolster its capabilities in developing novel treatments for autoimmune disorders and enhance its commitment to addressing unmet medical needs in this therapeutic area. This strategic acquisition allowed Merck to leverage Pandion’s expertise and innovative approaches to bring potential breakthrough therapies to patients worldwide. (Source)
Collaborations Made by Merck & Co., Inc.
- In 2023, Merck initiated two strategic collaborations with BenevolentAI and Exscientia, leveraging cutting-edge artificial intelligence (AI) technologies to enhance drug discovery efforts. These partnerships were established to harness the potential of AI-driven design and discovery in critical therapeutic areas such as oncology, neurology, and immunology. These collaborations aimed to accelerate drug development, focusing on generating innovative clinical candidates that could offer first-in-class and best-in-class solutions to address unmet medical needs. Merck’s decision to collaborate with these AI-driven companies underscored its commitment to advancing research and bringing new medicines to patients more efficiently. (Source)
- In 2022, Merck and Kelun-Biotech, a clinical-stage biotech company, joined forces in an exclusive license and collaboration agreement. Their collaboration aimed to develop seven investigational preclinical antibody-drug conjugates (ADC) tailored for cancer treatment. This collaboration leveraged Merck’s expertise in pharmaceuticals and Kelun-Biotech’s innovative biologic and small molecule discovery approaches, reflecting their shared commitment to advancing cancer therapies. (Source)
- In 2022, Merck collaborated with Beacon of Hope, an initiative led by Novartis and the Novartis U.S. Foundation, to foster diversity, equity, and inclusion within the R&D ecosystem. This collaboration was driven by the shared commitment to enhance diversity in clinical trials. Merck extended its clinical trials to include four Historically Black Medical School clinical trial Centers of Excellence: Morehouse School of Medicine, Howard University College of Medicine, Meharry Medical College, and Charles R. Drew University of Medicine and Science. (Source)
- In 2022, Merck partnered with Orion Corporation in a significant development and commercialization agreement. This collaboration aimed to advance Orion’s investigational candidate, ODM-208, along with other drugs targeting the cytochrome P450 11A1 (CYP11A1) enzyme, which plays a crucial role in steroid production. ODM-208, an oral, non-steroidal CYP11A1 inhibitor, underwent Phase 2 clinical trials to treat metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC). The partnership involved shared development and commercialization efforts, with Merck making an upfront payment of USD 290 million to Orion. (Source)
AI-assisted healthcare innovations
5. AbbVie
AbbVie Inc., headquartered in North Chicago, Illinois, is a leading American pharmaceutical company, ranking 6th among the world’s largest biomedical firms in revenue.
At the core of AbbVie’s portfolio is Humira (adalimumab), a groundbreaking medication that generated an impressive $21 billion in 2022 revenues and is instrumental in treating autoimmune conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn’s disease, plaque psoriasis, and ulcerative colitis. In addition to Humira, AbbVie has developed pharmaceuticals, including Skyrizi, Botox, Imbruvica, Rinvoq, Venclexta, Vraylar, and Mavyret, addressing myriad health concerns from cancer to hepatitis C.
Committed to advancing healthcare, the company continues to invest in R&D, targeting cancer, neurologic diseases, eye care, and cystic fibrosis. With a name derived from “Abbott” (its former parent company) and “vie” (reflecting life), AbbVie is dedicated to improving the quality of life worldwide. (Source)
AbbVie’s R&D Priorities and Strategies
- AbbVie invests heavily in R&D and has many chemicals and complementary devices in clinical trials, including possible therapies for complex, life-threatening conditions. In 2022, $7.1 billion was spent on R&D (R&D).
- AbbVie uses integrated discovery and development project teams, which are made up of chemists, biologists, doctors, and pharmacologists who all work together on the same compounds. These teams help the company find and create new compounds. Additionally, AbbVie works with third-party organizations, such as biotechnology companies, other drug companies, and university institutions, to find and prioritize exciting new treatments that will add to and improve AbbVie’s current offerings.
- AbbVie is developing over 90 compounds, devices, or indications individually or through collaborations and license agreements. This robust pipeline includes programs in various stages of development, from discovery to approval.
As of August 30, 2023, AbbVie’s pipeline encompasses 10 drugs in the Discovery phase, 28 in Preclinical, 1 in the IND (Investigational New Drug) stage, 72 in Phase 1, 50 in Phase 2, and 20 in Phase 3. There are 2 drugs at the NDA/BLA (New Drug Application/Biologics License Application) stage and 100 drugs that have received approval.
A significant number of drugs, totaling 370, are categorized under “Other,” which may include drugs in early development stages or those with uncertain timelines. These developments indicate a substantial increase in AbbVie’s R&D activities compared to previous years. The company’s commitment is particularly notable in mid to late-stage development programs, with over 50 programs in these advanced stages demonstrating a strong focus on bringing novel treatments to the market.
- AbbVie got the U.S. FDA approval to use Skyrizi to treat adults with active psoriatic arthritis and moderate to severe active Crohn’s disease in 2022.
- In 2021, AbbVie gained European Commission approval for Venclyxto, a hypomethylating drug for newly diagnosed AML patients ineligible for rigorous treatment.
- AbbVie got FDA approval to use Imbruvica plus rituximab to treat previously untreated chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL) patients in 2020. (Source)
Products Filed by AbbVie for Approval in the US/EU
| Serial No. | Year | Description |
| 1 | 2023 | AbbVie has presented applications for a new indication of risankizumab (SKYRIZI®) for the treatment of ulcerative colitis to both the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and the US FDA. (Source) |
| 2 | 2022 | AbbVie’s product, RINVOQ® (upadacitinib), was filed for approval in the US to treat moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in adults and children aged 12 and older. (Source) |
Popular Drugs Manufactured by AbbVie
In 2023, AbbVie manufactures the following popular drugs:
- Humira – Manufactured by AbbVie to treat conditions such as arthritis, psoriasis, and Crohn’s disease. Humira is the company’s top-selling drug. (Source)
Author’s note: Find what’s next for Humira Biosimilars as the drug’s exclusivity ends. Here
- Skyrizi – An AbbVie-developed autoimmune drug for adults with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis. (Source)
- Rinvoq – Another new autoimmune drug by AbbVie is indicated for treating rheumatoid arthritis, atopic dermatitis, and ulcerative colitis. (Source)
Other drugs manufactured by AbbVie are Venclexta, Vraylar, and Mavyret. (Source)
AbbVie’s Drugs That Lost Exclusivity in the Past 2 Years
- Restasis – Lost its exclusivity in 2022 as Viatris received FDA generic approval, potentially opening the door to generic versions of the drug for treating dry eyes. (Source)
- Combigan – Lost its exclusivity in 2022. It faced a key patent expiration in 2022, leading to potential generic competition for this drug, originally from Allergan and used to treat glaucoma and ocular hypertension. (Source)
AbbVie’s Revenue from Drug Sales
The top nine drugs which contributed significantly to AbbVie’s total revenue in 2021, along with their respective percentages, are as follows: Rinvoq (19%), Venclexta (16%), Restasis (10%), Skyrizi (11%), Vraylar (10%), Botox (10%), Creon (8%), Humira (7%), and Imbruvica (7%). Collectively, these drugs represented 98% of AbbVie’s total revenue for the year. (Source)
Top 9 Drugs Account for 98% of the Total Revenue in 2021
AbbVie’s Mergers And Acquisitions
- In 2023, AbbVie made a strategic acquisition by purchasing the discovery-stage biotechnology company Mitokinin in a deal valued at $655 million, reinforcing its focus on expanding its neuroscience pipeline. This acquisition included an initial payment of $110 million to Mitokinin’s shareholders, with the potential for future payments totaling $545 million, alongside royalty-based payments on net product sales. The decision to acquire Mitokinin was driven by the promising PINK1 activator compound developed by the company, which demonstrated the potential to selectively enhance the active form of PINK1, a key factor related to damaged mitochondria. This strategic move aligned with AbbVie’s commitment to advancing innovative treatments and strengthening its presence in neuroscience. (Source)
- In 2022, AbbVie completed the acquisition of DJS Antibodies Ltd, a UK-based biotechnology company that focused on discovering and developing antibody medicines targeting challenging disease-causing proteins, including G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). The acquisition by AbbVie helped to meet its medical needs in diseases such as Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF). DJS’s lead program, DJS-002, a novel lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) receptor 1 (LPAR1) antagonist antibody, showed promise in preclinical studies for treating IPF and other fibrotic conditions, signifying AbbVie’s dedication to advancing innovative therapies in critical areas of healthcare. (Source)
- In 2022, AbbVie made a strategic acquisition by purchasing Belgium-based company Syndesi Therapeutics for up to $1 billion. The deal commenced with an upfront payment of $130 million to Syndesi’s shareholders, accompanied by additional contingent payments of up to $870 million, depending on achieving predetermined milestones. This acquisition was a pivotal move by AbbVie, expanding its neuroscience portfolio with Syndesi’s assets, including the promising lead small molecule, SDI-118, designed to modulate synaptic vesicle protein 2A (SV2A). AbbVie’s interest in this mechanism was driven by the potential to develop treatments for cognitive impairment and various symptoms associated with neurodegenerative and neuropsychiatric conditions like Alzheimer’s disease and major depressive disorder. (Source)
- In 2020, AbbVie completed its acquisition of Allergan plc, which significantly expanded and diversified its revenue base. The acquisition was a strategic effort to enhance AbbVie’s long-term growth potential and strengthen its presence in key therapeutic areas. With a well-diversified portfolio spanning various therapeutic categories, including Immunology, Hematologic Oncology, Neuroscience, and the global aesthetics business, the merger aimed to position AbbVie as a pharmaceutical and biopharmaceutical industry leader. This strategic move was driven by providing innovative solutions to address unmet medical needs and securing a more robust financial foothold to support future R&D efforts. (Source)
Collaborations Made by AbbVie
- In 2023, AbbVie and Capsida Biotherapeutics joined forces to expand their collaboration beyond neurodegenerative conditions into the realm of eye diseases. This partnership emerged just a month after Capsida inked a substantial deal with Eli Lilly valued at up to $685 million. Building upon their 2021 collaboration focused on neurodegenerative diseases, where AbbVie committed $90 million for three CNS disease targets, this new endeavor aimed to develop three targeted genetic medicines addressing eye diseases with high unmet medical needs. It marked a significant move for Capsida into ophthalmology, broadening its scope beyond its prior exclusive focus on neurodegenerative conditions. (Source)
- In 2023, AbbVie and Coherus Biosciences successfully resolved a dispute surrounding Coherus’ collaboration with the Mark Cuban Cost Plus Drug Company, which aimed to offer the adalimumab biosimilar, Yusimry, referencing AbbVie’s Humira, to patients at reduced costs. The disagreement stemmed from AbbVie’s contention that the partnership contradicted an existing agreement that granted Coherus a nonexclusive license to commercialize Yusimry in the US. To address the dispute, both companies worked together to reach an agreement, ultimately facilitating the availability of the biosimilar to a broader patient population through this innovative partnership. (Source)
- In 2023, AbbVie and Anima Biotech formed a strategic collaboration to advance the field of mRNA biology. The collaboration focused on identifying and developing mRNA biology modulators targeting three specific areas: Oncology and Immunology. Anima’s innovative mRNA Lightning platform played a central role in this partnership, enabling the discovery of novel modulators for the designated targets. Under the agreement, AbbVie gained exclusive rights to license, further develop, and ultimately commercialize the promising programs. (Source)
- In 2022, AbbVie announced a significant collaboration with AbCellera, focusing on a multi-year, multi-target partnership. This strategic collaboration aimed to harness AbCellera’s antibody discovery and development expertise. The aim was to create optimized development candidates for up to five chosen targets across various medical indications, as selected by AbbVie. The collaboration empowered AbbVie with the right to develop and commercialize therapeutic antibodies from this partnership further. AbCellera received research payments and stood to gain downstream clinical and commercial milestone expenses and royalties on net product sales. This collaboration represented a forward-looking effort to advance therapeutic solutions. (Source)
6. Novartis
Novartis AG, headquartered in Basel, Switzerland, is a Swiss multinational pharmaceutical giant and Europe’s third most valuable pharmaceutical company, following Novo Nordisk and Roche. In 2022, it held the fourth position by revenue worldwide in the pharma industry. The company was formed through the merger of Ciba-Geigy and Sandoz in March 1996, one of the largest historic corporate mergers.
Novartis operates through two key divisions: Innovative Medicines and Sandoz (generics). It spun off the Sandoz in October 2023 as part of a restructuring effort. (Source)
Novartis’ R&D Priorities and Strategies
- Novartis’ research program is run by the Novartis Institutes for BioMedical Research (NIBR). NIBR is the company’s primary source of research and early development innovations. NIBR oversees finding new medicines for diseases that don’t have enough treatments.
- The Genomics Institute of the Novartis Research Foundation (GNF), based in San Diego, US, became part of NIBR in 2022. This makes it easier for people in NIBR to work together and gives Novartis researchers better access to biological, therapeutic, and translational tools. New technology is being developed at the NIBR San Diego site to help with drug discovery research. This includes regenerative medicine, small-interfering RNA treatment, and covalent drug discovery.
- R&D costs for the company were $10 billion in 2022, with $9.1 billion spent on core R&D and $9.5 billion in 2021.
- In 2022, they were granted 23 permits in the top four markets (the United States, the European Union, China, and Japan).
- The firm pledged to invest $250 million over five years (2021-2025) to research and develop novel medicines for malaria and neglected tropical illnesses in 2022. Additionally, the company progressed in the clinical development of next-generation malaria medications.
- Novartis spent about $59 million in 2021 on neglected disease research, which the Access to Medicine Foundation said should be a top goal for R&D. Since there aren’t any useful, well-suited, or available products for some diseases, conditions, and pathogens in these infectious disease areas, researchers, and patients in low- and middle-income countries that need R&D the most. About $30 million of this funding went to malaria. (Source) (Source)
Products Filed for Approval by Novartis in the US/EU
| Serial No. | Year | Description |
| 1 | 2023 | The product filed for approval is Pluvicto, and the filing was made to the FDA in the US. (Source) |
| 2 | 2023 | The product filed for approval is Cosentyx® (secukinumab), which was approved in EU by the European Commission. A regulatory decision from the US Food and Drug Administration is expected later in 2023. (Source) |
| 3 | 2023 | The product filed for approval was Cosentyx, and it was approved in the EU by the European Commission (EC). (Source) |
| 4 | 2022 | The product filed for approval is “Vijoice® (alpelisib),” and it was filed for approval in the US. (Source) |
| 5 | 2021 | Scemblix® (asciminib) was filed for approval and received approval in the US by the US FDA for the treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) in two distinct indications. (Source) |
Popular Drugs Manufactured by Novartis
- Cosentyx – In 2023, Novartis manufactured the drug Cosentyx® (secukinumab), which the European Commission has approved. It is used in adults with active moderate to severe hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) when conventional systemic HS therapy is inadequate. Novartis has FDA approval for Cosentyx on October 31. (Source)(Source)
- Kisqali – In 2023, Novartis manufactured Kisqali® (ribociclib), a drug used to treat epidermal growth of hormone receptor-positive/human factor receptor 2-negative (HR+/HER2-) breast cancer. It is typically administered in combination with endocrine therapy. (Source)
- Entresto – In 2021, Novartis manufactured Entresto® (sacubitril/valsartan), which reduces the chance of cardiovascular death and hospitalization for adult patients with chronic heart failure. It has the most significant benefits observed in patients with a below-normal left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF). (Source)
Novartis’ Drugs Losing Exclusivity in the Coming 2 or 3 Years
- Entresto – Entresto, a heart failure medication by Novartis, is expected to lose exclusivity in the next few years, particularly between 2024 and 2026. This loss of exclusivity is due to patent expirations and invalidations, opening the door for potential generic versions, including interest from Mylan. (Source)
Stay ahead in the dynamic pharma industry with Elixir! It offers comprehensive, context-aware tracking of patent lifecycle events globally. Say goodbye to database hopping and keep track of everything from USPTO to EPO updates in one place. Sign up or book a demo now for Elixir and ensure you never miss a critical deadline or opportunity again!
Novartis’ Revenue from Drug Sales
In 2022, Novartis generated 82% of its net sales from the Innovative Medicines division, indicating the significant contribution of its pharmaceutical products. The Sandoz division accounted for the remaining 18% of net sales, likely encompassing generics and biosimilars.
Net Sales by Divisions in 2022
In 2022, the net sales from Novartis’s Innovative Medicines division show the largest share, 40%, from Cardiovascular drugs, while Solid Tumors contributed 21%. Immunology and Hematology accounted for 7% each, addressing autoimmune and blood-related conditions. The remaining 20% came from others. (Source)
Net Sales of Innovative Medicines in 2022
In 2022, Novartis’s Sandoz division generated net sales from various franchises, with a significant % of its revenue attributed to Retail Generics at 73%. Biopharmaceuticals also played a substantial role, contributing 23% of the total net sales. While a minor component, anti-infectives accounted for 4% of Sandoz’s revenue. (Source)
Net Sales of Sandoz by Franchise in 2022
Novartis’ Mergers And Acquisitions
- In 2023, Novartis acquired DTx Pharma, a biotechnology company known for its innovative Fatty Acid Ligand Conjugated OligoNucleotide (FALCON™) platform, designed to address the challenges associated with delivering oligonucleotide therapeutics. This acquisition aimed to leverage DTx Pharma’s platform, Specifically the FALCON technology, which enhances the delivery and efficacy of small interfering RNA (siRNA) therapeutics to tissues beyond the liver, thereby improving biodistribution and cellular uptake. DTx Pharma’s lead program, focused on Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease Type 1A (CMT1A), had garnered FDA Orphan Drug Designation and represented a promising solution for a progressive neuromuscular disease. (Source)
- In 2023, Novartis completed its acquisition of Chinook Therapeutics, a biopharmaceutical company focused on precision medicines for kidney diseases. This acquisition, valued at up to USD 3.5 billion, was motivated by Chinook’s promising pipeline of assets, including late-stage candidates such as atrasentan and zigakibart for treating Immunoglobulin A Nephropathy (IgAN). In Phase 3 development, Atrasentan demonstrated significant proteinuria reduction, while zigakibart (BION-1301) entered Phase 3 development for IgAN. This strategic move aligned with Novartis’ commitment to advancing treatments for kidney diseases. (Source)
- In 2021, Novartis finalized its acquisition of Gyroscope Therapeutics, a UK-based ocular gene therapy company. This strategic move was driven by the urgent need to address geographic atrophy (GA), a severe dry age-related macular degeneration causing progressive and irreversible vision loss. With no approved treatments available for GA, Novartis aimed to bolster its capabilities in retinal diseases by harnessing Gyroscope Therapeutics’ expertise in ocular gene therapy to develop innovative solutions for this significant unmet medical need. (Source)
- In 2021, Novartis acquired Arctos Medical as part of its ongoing commitment to advancing treatments for patients with vision loss. The acquisition was driven by the potential of optogenetics-based AAV gene therapy, which offered promising prospects for innovative therapeutics in the field of ophthalmology. By adding Arctos’ pre-clinical gene therapy program and proprietary technology to its portfolio, Novartis aimed to bolster its efforts in developing solutions for individuals affected by vision-related conditions. (Source)
Author’s Note: There are more mergers and acquisitions of Novartis. (Source)
Collaborations Made by Novartis
- In 2023, Novartis Ireland collaborated with FutureNeuro, the SFI research center for rare and chronic neurological diseases, to drive advancements in healthcare research and clinical care through the DataScape project. This collaboration explored stakeholders’ attitudes, expectations, and concerns regarding using health data in healthcare improvement and research. The goal was to foster a culture of trust that would facilitate the secure and responsible utilization of health data to improve patient care. Novartis’ involvement in this project exemplified its dedication to leveraging data to enhance healthcare research and delivery. (Source)
- In 2022, Novartis expanded its research-based partnership with the University of California, Berkeley. It was a joint effort to tackle “undruggable” disease targets and discover novel therapeutic modalities. This collaboration aimed to develop cutting-edge technologies for identifying next-generation therapies, building upon the successes achieved over the previous five years. By combining the expertise of their researchers, the collaboration focused on the exploration of challenging disease targets, particularly in the realm of cancer, which had proven elusive to traditional small-molecule compounds and conventional drug discovery methods. (Source)
- In 2021, Novartis and UCB entered into a global co-development and co-commercialization agreement, focusing on UCB0599, a potential groundbreaking small molecule inhibitor targeting alpha-synuclein misfolding in Phase 2 clinical development. Additionally, upon concluding the Phase 1 program, Novartis had the option to co-develop UCB7853, an anti-alpha-synuclein antibody. This collaboration was to advance innovative treatments for Parkinson’s Disease (PD), leveraging UCB’s expertise and the potential of these novel compounds to address the unmet medical needs of PD patients. (Source)
- In 2021, Novartis entered a strategic collaboration and license agreement with BeiGene, Ltd. The collaboration aimed to harness BeiGene’s anti-PD-1 antibody, tislelizumab, for developing, manufacturing, and commercializing innovative cancer therapies across multiple countries, including the United States, Canada, and various European and Asian nations. The partnership allowed both companies to explore tislelizumab in combination with other cancer treatments through global clinical trials. Novartis assumed responsibility for regulatory submissions and commercialization upon regulatory approvals, while BeiGene retained an option to co-detail the product in North America. This collaboration represented a concerted effort to advance cancer treatment options and expand their global reach. (Source)
Author’s Note: There are more collaborations of Novartis. (Source)
7. Bristol Myers Squibb
Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, or Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS), is an American multinational pharmaceutical corporation headquartered in Princeton, New Jersey. It consistently secures a place on the prestigious Fortune 500 list of the largest U.S. corporations. In fiscal year 2022, the company achieved a total revenue of $46.2 billion.
Bristol Myers Squibb is a leading manufacturer of prescription pharmaceuticals and biologics, with a diverse portfolio spanning critical therapeutic areas such as cancer, HIV/AIDS, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, hepatitis, rheumatoid arthritis, and psychiatric disorders. (Source)
BMS’ R&D Priorities and Strategies
- The research teams of Bristol Myers Squibb have developed a robust early-stage pipeline comprising more than 50 assets. It is anticipated that more than 15-20 of these assets will advance to the proof-of-concept stage by the middle of the year 2024.
- In 2022, BMS got 18 approvals for new medicines and expanded the uses and formulations of medicines already on the market in significant markets. They also launched three first-of-their-kind medicines, including Opdualag® for metastatic melanoma, SotyktuTM for moderate to severe plaque psoriasis, and Camzyos® for obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. All of these medicines addressed severe, unmet medical needs.
- The company also improved its current products and R&D (R&D) abilities by forming strategic partnerships with Evotec, Immatics, Owkin, and others and acquiring Turning Point Therapeutics, which added to its precision oncology portfolio.
- BMS invested a total of $11.1 billion in R&D (R&D) activities in the year 2020. These activities included discovering and developing novel medicines. At the end of 2020, BMS had more than 50 medicines in research for more than 40 diseases.
- The potential of the new product portfolio is at the center of the company’s business strategy. The company has introduced around 9 new medications since 2020. Many of these medicines are either the best-in-class or the first-in-class medicines in their respective categories, and many have considerable potential for growth into additional indications.
- The diverse projects that are in the mid-stage and late-stage pipeline will provide a boost to the second wave of innovation. They have 6 different assets that are either already in Phase 3 clinical development or in the process of entering it. A next-generation anti-thrombotic called Milvexian is one of the assets, along with CELMoD medicines for treating multiple myeloma and LPA-1 for treating lung fibrosis. (Source) (Source)
Products Filed by Bristol Myers Squibb for Approval in the US/EU
| Serial No. | Year | Description |
| 1 | 2023 | Bristol Myers Squibb’s product Breyanzi (lisocabtagene maraleucel; liso-cel) was filed for approval in the EU, and it received approval from the European Commission (EC) in the European Union. (Source) |
| 2 | 2023 | Reblozyl (luspatercept-aamt) received FDA approval for expanded use in the US to treat anemia in adult MDS patients who may need regular red blood cell transfusions without prior ESA use. (Source) |
| 3 | 2022 | The product filed for approval is Sotyktu™(deucravacitinib), filed in the US. (Source) |
Popular Drugs Manufactured by Bristol Myers Squibb
In 2023, Bristol Myers Squibb manufactured the following popular drugs:
- Eliquis – Eliquis is a widely used blood thinner that helps prevent blood clots.
- Pomalyst – Pomalyst is another blood cancer drug that has contributed significantly to the company’s product portfolio. (Source)
BMS’ Drugs Losing Exclusivity in the Coming 2 or 3 Years
- Yervoy – Yervoy of Bristol-Myers Squibb is anticipated to lose its exclusivity in 2024, affecting its market position.
- Sprycel – Another drug of Bristol-Myers Squibb, Sprycel, is poised to lose exclusivity in 2024, opening the door to potential generic competition. (Source)
- Revlimid – Revlimid, the top-selling drug for Bristol-Myers Squibb, will gradually lose exclusivity. The company granted volume-limited licenses for generic versions in the US in March, and competition will increase until 2026 when the market fully opens. This is expected to result in declining sales for Revlimid through 2026, potentially impacting the company’s revenue in the coming years.
- Eliquis – Eliquis, a drug by Bristol-Myers Squibb, is expected to lose its exclusivity by 2026.
- Pomalyst – Pomalyst, another drug from Bristol-Myers Squibb, is also set to lose its exclusivity by 2026. (Source)
BMS’ Revenue from Drug Sales
In 2021, Bristol Myers Squibb generated a substantial portion of its total revenue from a select group of top-selling drugs, collectively accounting for 65% of the company’s total revenue. These drugs include Yervoy at 20%, Eliquis at 17%, Pomalyst at 9%, Opdivo at 8%, Revlimid at 6% and Orencia at 5%. These top six drugs played a crucial role in contributing to Bristol Myers Squibb’s financial success and solidified their positions as key revenue drivers for the company in that year. (Source)
Top 8 Drugs Account for 65% of the Total Revenue in 2021
BMS’ Mergers And Acquisitions
- In 2023, Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS) strategically acquired Mirati Therapeutics for an equity value of $4.8 billion. This acquisition aimed to strengthen BMS’s presence in the oncology sector and expand its portfolio of cancer treatments. The decision was unanimous and well-received by both companies’ boards of directors, highlighting the mutual recognition of the potential value this collaboration would bring to the field of oncology therapeutics. (Source)
- In 2022, Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS) announced its acquisition of Turning Point Therapeutics, signifying its strategic move to bolster its position in precision oncology. This acquisition was motivated by BMS’s commitment to advancing innovative therapies for cancer patients. Turning Point Therapeutics held a promising pipeline of investigational medicines designed to target prevalent mutations involved in cancer development. The highlight of this acquisition was Turning Point Therapeutics’ lead asset, repotrectinib, a next-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor with Breakthrough Therapy Designations from the FDA. (Source)
- In 2020, Bristol Myers Squibb (BMY) announced the acquisition of MyoKardia, Inc. (MYOK) for $13.1 billion in cash, marking a strategic move in the pharmaceutical industry. This merger was motivated by Bristol Myers Squibb’s interest in MyoKardia’s innovative cardiovascular therapies, particularly mavacamten, aimed at treating obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), a severe and debilitating heart disease. The acquisition allowed Bristol Myers Squibb to expand its cardiovascular medicine portfolio and gain access to mavacamten’s potential as a groundbreaking therapy. With the NDA submission for mavacamten and plans to explore its application in additional indications, the acquisition of MyoKardia has reinforced Bristol Myers Squibb’s commitment to addressing critical cardiovascular conditions and advancing novel therapeutic options. (Source)
- In 2020, Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS) finalized its acquisition of Forbius, a strategic move aimed at bolstering BMS’s portfolio with their TGF-beta program, notably including the lead investigational asset, AVID200, which was in Phase 1 trials for oncology and fibrosis. This acquisition aligned with BMS’s commitment to expanding its presence in oncology and fibrotic diseases, providing opportunities for developing inventive therapies to address critical unmet medical needs in these areas. (Source)
Collaborations Made by Bristol Myers Squibb
- In 2023, Bristol Myers Squibb, in collaboration with Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (a Janssen Pharmaceutical Company of Johnson & Johnson), initiated the Phase 3 Librexia program, marking a significant collaboration aimed at advancing the development of milvexian, an investigational oral factor XIa (FXIa) inhibitor with antithrombotic potential. This collaboration was driven by the need to address critical medical conditions, such as stroke prevention, acute coronary syndromes, and atrial fibrillation, for which Milvexian could hold promise. The extensive Librexia program, spanning multiple indication-seeking studies involving nearly 50,000 patients, was launched to generate essential clinical data and pave the way for potential therapeutic advancements in antithrombotics. (Source)
- In 2022, Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS) and Century Therapeutics entered into a research collaboration and license agreement, marking a strategic partnership in the development and commercialization of induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) derived, engineered natural killer cells (iNK) and T cell (iT) programs targeting hematologic malignancies and solid tumors. This collaboration brought Century’s expertise in iPSC technology and cellular immunotherapies together with BMS’s deep experience in oncology. The partnership aimed to harness the potential of these innovative cell therapies to address critical unmet medical needs in the field of cancer treatment, with a priority on acute myeloid leukemia and multiple myeloma, with the potential for further expansion into additional programs. (Source)
- In 2022, Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS) and Immatics N.V. forged an expanded strategic alliance to jointly pursue the development of multiple allogeneic off-the-shelf TCR-T and CAR-T programs, marking a significant collaboration in cancer immunotherapies. This collaboration aimed to leverage the strengths and expertise of both companies, with Immatics contributing its proprietary gamma delta T cell-derived, allogeneic Adoptive Cell Therapy (ACT) platform, ACTallo®, and Bristol Myers Squibb bringing a suite of next-generation technologies to the table. The partnership sought to accelerate the development of cutting-edge therapies for cancer treatment, underlining the growing importance of immuno-oncology and the quest for innovative solutions in the fight against cancer. (Source)
- In 2021, Bristol-Myers Squibb (BMS) and Eisai forged an exclusive global strategic collaboration to co-develop and co-commercialise MORAb-202, an antibody-drug conjugate (ADC). Using an enzyme cleavable linker, MORAb-202 marked Eisai’s entry into the ADC field, combining their proprietary anti-folate receptor alpha (FRα) antibody with eribulin, an anticancer agent. This collaboration reflected BMS’s strategy to expand its oncology portfolio and advance innovative treatments. MORAb-202 showed promising single-agent activity in patients with advanced solid tumors, particularly in FRα-positive cancers. With plans to progress into the registrational stage, this partnership showcased both companies’ commitment to developing potentially groundbreaking therapies for patients with challenging-to-treat solid tumors. (Source)
8. Sanofi
Sanofi S.A., headquartered in Paris, France, is a distinguished French multinational pharmaceutical and healthcare company since 1973. The company merged with Synthélabo in 1999 to become Sanofi-Synthélabo and later merged with Aventis in 2004, adopting the name Sanofi-Aventis. In May 2011, it returned to its original name, Sanofi. It is a constituent of the Euro Stoxx 50 stock market index.
Sanofi specializes in researching, developing, manufacturing, and marketing pharmaceutical products, primarily in the prescription market, while also producing over-the-counter medications. The company’s focus spans seven major therapeutic areas: cardiovascular, central nervous system, diabetes, internal medicine, oncology, thrombosis, and vaccines. Sanofi Pasteur, its subsidiary, is the world’s largest vaccine producer. (Source)
Sanofi’s R&D Priorities and Strategies
- Sanofi does early-stage research and early and late development stages to offer a stable and well-balanced range of products. It spent €6,706 million (15.6% of its net sales) on R&D in 2022.
The company aims to develop an R&D pipeline that will produce first-in-class or distinctive best-in-class medicines, with two-thirds of the biological substances and two-thirds of the pipeline directly deriving from Sanofi’s internal research. In 2022, efforts were made to reshape and consolidate the R&D portfolio in oncology and immune diseases.
- The company is involved in many R&D activities, and it markets some of its products through partnerships with other biotechnology and pharmaceutical businesses. It presently has a global strategic collaboration on monoclonal antibodies for the development and commercialization of Kevzara® (sarilumab), Dupixent®, and SAR440340 (REGN3500- itepekimab), among other monoclonal antibody products.
- Sanofi’s “Play to Win” plan has been executed to encourage growth and new ideas so the company can find breakthroughs with the most promising medicines to meet critical patient needs. Five therapies that could make a big difference for patients were chosen as part of a strategic framework. These are Fitusiran and Efanesoctocog alfa for hemophilia, Amlitelimab for immunology and inflammation, tolebrutinib for multiple sclerosis, and Nirsevimab for preventing respiratory syncytial virus.
- The US National Institute of Health (NIH) and Sanofi have a Cooperative R&D Agreement (CRADA) to make a live attenuated RSV vaccine for babies 6 months and older. In September 2020, Phase I/II research in the United States began to determine the safety and efficacy of two doses of an intranasal delivery device in newborns. This was done with the end objective of extending the immunity provided by Nirsevimab to additional RSV seasons. The results of this investigation were found to be encouraging during the fourth quarter of 2022.
- In 2022, Sanofi and Exscientia stated they would be working together on research and licensing up to 15 new small molecule candidates for use in oncology and immunology using Exscientia’s AI-driven platform and actual patient samples.
- Sanofi and the US Department of Health and Human Services decided to extend their R&D agreement in 2020. The purpose of this extension was to capitalize on Sanofi’s prior development work on a SARS vaccine to find a more practical way to move forward with creating a COVID-19 vaccine. (Source)
Products Filed by Sanofi for Approval in the US/EU
| Serial No. | Year | Description |
| 1 | 2023 | The product filed for approval is Dupixent® (dupilumab), and the application was filed in the US. (Source) |
| 2 | 2023 | The product filed for approval is Nirsevimab, and it was filed in the US. (Source) |
| 3 | 2023 | The product filed for approval is Beyfortus™ (nirsevimab-alip), and it was filed for approval in the US. (Source) |
| 4 | 2023 | The product filed for approval is ALTUVIIIO™ (Antihemophilic Factor Recombinant, Fc-VWF-XTEN Fusion Protein-ehtl), and it was filed for approval in the US. (Source) |
Popular Drugs Manufactured by Sanofi
- Lantus – In 2022, Sanofi manufactured Lantus, a long-acting insulin for diabetes type I and II. (Source)
- Dupixent – Used for treating eczema and dermatitis, it generated $4,341 million in sales in 2020.
Sanofi’s Drugs That Lost Exclusivity in the Past 2 Years
- Lantus – Lantus, Sanofi’s flagship drug, lost market exclusivity in 2019. It contributed to the company’s shrinking sales and profit before 2019. (Source)
Sanofi’s Drugs Losing Exclusivity in the Coming 2 or 3 Years
- Aubagio – Sanofi will be facing the loss of exclusivity in the next few years in Aubagio, which is expected to lose its exclusivity by 2030. (Source)
Sanofi’s Revenue from Drug Sales
In 2020, Sanofi’s total revenue was significantly driven by a select group of top-performing drugs, with the top 8 pharmaceuticals contributing to an impressive 98% of the company’s earnings. The standout performers in Sanofi’s revenue portfolio included Dupixent, accounting for 29%, Influenza Vaccines at 18%, Pentacel with 13%, Aubagio with a substantial 12%, Toujeo at 8%, Myozyme/Lumizyme with 7%, Fabrazyme also at 7% and Lovenox, contributing 4% to the company’s total revenue. (Source)
Top 8 Drugs Account for 98% of the Total Revenue in 2020
Sanofi’s Mergers And Acquisitions
- In 2023, Sanofi, a Paris-based pharmaceutical company, was reportedly exploring a potential acquisition of Mirati Therapeutics, a cancer drugmaker. The acquisition discussions were ongoing, though there was no guarantee of a final agreement. Notably, Mirati had garnered attention for its lung cancer drug, Krazati, which had received approval from the US health regulator in December to treat advanced lung cancer in adults. However, it’s essential to mention that the specific rationale or details surrounding the acquisition, if it did indeed occur, were not disclosed in the provided information. (Source)
- In 2023, Sanofi completed the acquisition of Qunol®, a prominent brand in the health and wellness industry based in the United States. This strategic move was aimed at reinforcing Sanofi’s Consumer Healthcare’s (CHC) Vitamin, Mineral, and Supplements (VMS) category, particularly within the actively sought-after “healthy aging” segment. Qunol’s CoQ10 for heart health and Turmeric for joint health complement Sanofi’s US portfolio by adding a trusted and highly profitable brand, aligning with the increasing consumer demand for chronic condition management. (Source)
- In 2023, Sanofi completed its acquisition of Provention Bio, a significant move aimed at expanding its portfolio to include Tzield, the first FDA-approved disease-modifying therapy for slowing the onset of type 1 diabetes (T1D). By acquiring Provention Bio, Sanofi positioned itself as a global pharmaceutical leader with access to groundbreaking therapies. This strategic acquisition underscores the potential of such therapies and signifies the company’s commitment to making life-changing treatments, including Tzield, more accessible to a broader population more swiftly. (Source)
- In 2021, Sanofi made a strategic move by acquiring Amunix Pharmaceuticals, Inc., an immuno-oncology company focused on developing cutting-edge T-cell engagers (TCE) and cytokine therapies for cancer patients. The acquisition aimed to harness Amunix’s proprietary XTEN® and Pro-XTEN™ masking technologies, which had been clinically validated. This acquisition provided Sanofi access to Amunix’s promising pipeline, including lead candidate AMX-818, a HER2-directed TCE. By making this significant investment of approximately $1 billion upfront, with potential additional payments upon reaching specific development milestones, Sanofi aimed to maintain its commitment to advancing innovative oncology treatments, given its active involvement in developing around 20 molecules in this therapeutic area. (Source)
Author’s Note: There are more mergers and acquisitions of Sanofi. (Source)
Collaborations Made by Sanofi
- In 2022, Sanofi and pharmaceutical giants GSK and Takeda joined forces in a collaborative effort to advance biologic manufacturing in Singapore. This partnership was established under the Biologics Pharma Innovation Programme Singapore (BioPIPS), initiated by A*STAR with support from the Singapore Economic Development Board. The primary objective of this collaboration was to harness the power of research and innovation to enhance biologics manufacturing capabilities in Singapore. This encompassed the production of recombinant therapeutic proteins and vaccines, aligning with the shared commitment to bolstering the pharmaceutical landscape and addressing global healthcare needs. (Source)
- In 2022, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. announced its acquisition of Sanofi’s stake in the collaboration concerning Libtayo® (cemiplimab). This strategic move allowed Regeneron to gain exclusive worldwide rights for the development, commercialization, and manufacturing of Libtayo. The collaboration’s original intent was to jointly advance and promote this medicine, reflecting a common goal between the two pharmaceutical giants. The transaction marked a shift in the partnership dynamics, with Regeneron poised to assume complete control over the Libtayo program, enhancing its commitment to the therapy’s future development and commercialization. (Source)
- In 2022, the French multinational pharmaceutical and healthcare company Sanofi forged a significant partnership with New York-based TrialSpark, which specialises in technology-driven drug development. The collaboration stemmed from a shared vision to streamline drug development processes, focusing on more efficient trial design, faster trial completion, and the generation of higher-quality trial data. This alliance was established to identify and develop clinical-stage Phase II and III drug candidates that address unmet patient needs. Over three years, the partnership aimed to facilitate six transactions, and it also sought to explore innovative clinical development models, particularly in domains such as behavioral intervention and digital technologies. (Source)
- In 2020, Sanofi and GSK embarked on a collaborative effort to combat the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. This partnership aimed to develop an adjuvanted vaccine for COVID-19, leveraging the innovative technologies offered by both companies. Sanofi contributed its S-protein COVID-19 antigen, which was developed through recombinant DNA technology. This approach created a precise genetic match to the virus’s surface proteins, further enhancing the potential for an effective vaccine. The collaboration responded to the urgent global need for COVID-19 vaccines and was a testament to the pharmaceutical industry’s dedication to addressing public health crises through cooperative R&D efforts. (Source)
9. AstraZeneca
AstraZeneca plc is a renowned Anglo-Swedish multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company headquartered at the Cambridge Biomedical Campus in Cambridge, England. Established in 1999 through the merger of Sweden’s Astra AB and the UK’s Zeneca Group, AstraZeneca has emerged as one of the world’s largest pharmaceutical entities. The company boasts a diverse portfolio encompassing critical therapeutic areas like oncology, cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, infection, neuroscience, respiratory, and inflammation.
The company has expanded its influence through strategic acquisitions, including Cambridge Antibody Technology, MedImmune, Spirogen, and Definiens. AstraZeneca holds one of the highest market capitalizations among pharmaceutical companies worldwide.
AstraZeneca’s R&D Priorities and Strategies
- AstraZeneca delivers a pipeline of life-changing drugs by using its unique scientific skills. This includes emphasizing science and new ideas, from discovery to creation and life-cycle management, to get better results and productivity.
- In 2022, the company’s pipeline continued to deliver overwhelmingly positive results for patients, consisting of 72 regulatory events, such as submissions or approvals for medicines in major countries. Two of these were NME’s first approvals. A healthy pipeline of high-potential medicines supports the company’s ability to achieve long-term, sustainable growth. There have been 29 pipeline progression events, which include either NME Phase II starts or Phase III investment decisions.
- AstraZeneca does R&D in over 60 countries around the world. It has key R&D centers such as the Discovery Centre (DISC) in Cambridge, UK, and a new center was announced in Kendall Square in Boston, MA.
- The Discovery Centre (DISC) was publicly disclosed in Cambridge, UK, in 2021. The DISC, located in the middle of the Cambridge Biomedical Campus, is meant to be a key part of the company’s goal of offering patients medicines that change their lives. It will be the company’s most extensive R&D center in the UK. When fully staffed, over 2,000 people will work there in therapy areas and drug discovery and development.
- The new R&D center will be in Kendall Square, Cambridge, Massachusetts, which is in the middle of the greater Boston life science ecosystem. It will include about 1,500 R&D, commercial, and corporate employees. The site, which is scheduled to be finished in 2026, will bring together the AstraZeneca and Alexion teams in the Boston area and help reach the goal of connecting its networks. It is set up so that it can be used for both internal and external collaborations.
- The amount spent on R&D in 2022 was $9,762 million. In 2022, more investment was made into late-stage assets in Oncology and BioPharmaceuticals. To take advantage of new tools, such as cell therapy, more money was put into discovery.
- AstraZeneca released pre-clinical research in Nature Cell Biology in 2022 that showed how human ventricular progenitor cells help make new heart tissue after a heart attack. The company also formed a strategic research partnership with Illumina, a gene sequencing company, to combine their strengths in genomic analysis methods to find new drug targets faster and more effectively. (Source) (Source) (Source) (Source)
Products Filed by AstraZeneca for Approval in the US/EU
| Serial No. | Year | Description |
| 1 | 2023 | The product filed for approval was Tezspire (tezepelumab-ekko), and the approval was granted in the US. (Source) |
| 2 | 2023 | The product filed for approval was trastuzumab deruxtecan, and it was filed in the US and more than 40 countries, including the EU. (Source) |
| 3 | 2023 | The product filed for approval is nirsevimab, and it was filed in the US. (Source) |
Popular Drugs Manufactured by AstraZeneca
- Farxiga – Farxiga, manufactured in 2023, is an AstraZeneca-developed medication used to treat type 2 diabetes by helping control blood sugar levels. (Source)
- Nexium – In 2022, Nexium was manufactured by AstraZeneca. It is a proton pump inhibitor used to reduce stomach acid production. It is primarily used to treat gastrointestinal reflux conditions, ulcers, and heartburn. (Source)
- Symbicort – In 2021, Symbicort was manufactured by AstraZeneca in China to treat mild, intermediate, and severe asthma. It is taken as needed as an anti-inflammatory reliever for patients aged 12 years and older. (Source)
- Crestor – In 2020, AstraZeneca manufactured Crestor (rosuvastatin), a statin for treating dyslipidaemia and hypercholesterolemia. Crestor is one of their notable drugs, and it was sold to Grünenthal GmbH in over 30 European countries, except the UK and Spain. (Source)
AstraZeneca’s Drugs Losing Exclusivity in the Coming 2 or 3 Years
Farxiga – AstraZeneca’s “Farxiga” will lose its exclusivity in 2026, potentially leading to increased competition in the Type 2 diabetes drug market. (Source)
AstraZeneca’s Revenue from Drug Sales
In 2021, AstraZeneca’s financial success was notably driven by its top seven drugs, with Farxiga leading at 35%, followed by Pulmicort at 21%, Oncology at 18%, CVRM at 11%, Tagrisso at 8%, and Imfinzi and Lynparza collectively contributing 3% and R&I at 2%. These essential pharmaceutical products played a pivotal role, collectively accounting for 98% of AstraZeneca’s total revenue, emphasizing their significant contribution to its financial performance. (Source)
Top 7 Drugs Account for 98% of the Total Revenue in 2021
AstraZeneca’s Mergers And Acquisitions
- In 2023, AstraZeneca completed the acquisition of CinCor Pharma, Inc., a US-based clinical-stage biopharmaceutical company. This acquisition aimed to strengthen AstraZeneca’s cardiorenal pipeline by adding baxdrostat (CIN-107), an aldosterone synthase inhibitor, to address the challenges of treatment-resistant hypertension and chronic kidney disease. The strategic move allowed AstraZeneca to expand its portfolio and advance its efforts in developing innovative solutions for these critical health conditions. (Source)
- In 2022, AstraZeneca completed the acquisition of Neogene Therapeutics Inc., a clinical-stage biotechnology company specializing in T-cell receptor therapies (TCR-Ts). The acquisition aimed to bolster AstraZeneca’s position in next-generation therapies. AstraZeneca’s investment included an initial payment of $200 million, with the potential for additional payments totaling up to $120 million, based on future milestones and considerations. This strategic move expanded AstraZeneca’s capabilities in innovative therapies and furthered its commitment to advancing healthcare solutions. (Source)
- In 2022, AstraZeneca made the strategic decision to acquire TeneoTwo, Inc., including its Phase I clinical-stage CD19/CD3 T-cell engager, TNB-486, which was being evaluated for relapsed and refractory B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. This acquisition was driven by AstraZeneca’s goal to expedite the development of potential new medicines for B-cell haematologic malignancies, mainly diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and follicular lymphoma. By adding TNB-486 to its portfolio, AstraZeneca aimed to enhance its haematology pipeline, complementing its existing therapies, such as Calquence (acalabrutinib), and expanding its capabilities to address a wide range of blood cancers. (Source)
- In 2021, AstraZeneca’s subsidiary, Alexion, exercised its option to acquire the remaining equity in Caelum Biosciences for CAEL-101, a potentially groundbreaking fibril-reactive monoclonal antibody for treating light chain (AL) amyloidosis. This strategic acquisition aimed to address a rare and life-threatening disease characterized by the accumulation of misfolded amyloid proteins in vital organs, leading to organ damage and failure. By adding CAEL-101 to its portfolio, AstraZeneca aimed to advance the development of novel treatments for this challenging condition and expand its commitment to enhancing the lives of patients with rare diseases. (Source)
Author’s Note: There are more mergers and acquisitions of AstraZeneca. (Source)
Collaborations Made by AstraZeneca
- In 2021, AstraZeneca developed a significant partnership with the Royal Academy of Engineering to facilitate connections between African healthcare innovators and its A.Catalyst Network, comprising over 20 global health innovation hubs. This collaborative effort was established to foster the development of engineering solutions geared towards addressing local challenges, with a specific focus on health technology. Through this annual award, the Academy provided essential support for entrepreneurs and innovators throughout sub-Saharan Africa, ultimately nurturing a community of over 100 alumni who have made valuable contributions to the region’s innovation landscape. (Source)
- In 2020, AstraZeneca established a global development and commercialization partnership with Daiichi Sankyo to advance DS-1062, a trophoblast cell-surface antigen 2 (TROP2)-directed antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) with promising potential for treating various cancer types. DS-1062 focused on tumor types, notably non-small cell lung cancers and breast cancers, where TROP2 overexpression was prevalent. This collaboration exemplified AstraZeneca’s strategic investment in ADCs, capitalizing on innovative technology and building upon the successful prior partnership with Daiichi Sankyo—the initiative aimed to further AstraZeneca’s commitment to developing transformative therapies in oncology. (Source)
- In 2020, AstraZeneca partnered with the University of Oxford to collaborate on the global development and distribution of a promising recombinant adenovirus vaccine intended to combat COVID-19 caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus. This collaboration aimed to advance the potential vaccine, ChAdOx1 nCoV-19, which was in development at the Jenner Institute and Oxford Vaccine Group. Under the partnership, AstraZeneca assumed responsibility for the vaccine’s development and its worldwide manufacturing and distribution. The collaboration emerged as a crucial response to the urgent need for effective COVID-19 vaccines, leveraging AstraZeneca’s resources and expertise to accelerate vaccine development and global access. (Source)
- In 2019, AstraZeneca and BenevolentAI initiated a substantial collaborative effort, harnessing the power of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning to accelerate the finding and evolution of treatments for chronic kidney disease (CKD) and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). This collaboration aimed to leverage AstraZeneca’s extensive genomics, chemistry, and clinical information datasets with BenevolentAI’s cutting-edge target identification platform and biomedical knowledge graph. The two organizations sought to unlock innovative solutions and potentially life-changing therapies for these challenging medical conditions by combining their expertise and resources. (Source)
10. GSK
GSK plc, formerly GlaxoSmithKline plc, is a British multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company headquartered in London. With a market capitalization of £70 billion as of August 2022, GSK was the eighth-largest listing on the London Stock Exchange.
GSK has a history of pioneering healthcare solutions, including developing the first malaria vaccine, RTS, S (with the PATH vaccines initiative and the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation). It manufactures medications for various diseases, including asthma, cancer, infections, diabetes, and mental health. Some medicines initially developed by GSK and its legacy companies are now sold as generics, including antibiotics like amoxicillin, antivirals like valacyclovir, antiparasitic albendazole, and treatments for conditions like epilepsy, depression, and leukemia. Several of these medications, such as albendazole, amoxicillin, and zidovudine, are recognized as essential medicines by the WHO, highlighting their importance in global healthcare.
GSK’s R&D Priorities and Strategies
- GSK spent £5.5 billion on R&D in 2022, 9% more than in 2021. This was done to improve its vaccines and drugs and help the world fight disease.
- The company has 69 possible vaccines and drugs in different stages of development, out of which 18 are in the late stage. More than 70% work by changing the immune system, and more than 70% have been tested on humans genetically. In 2022, it began 16 Phase I programs, moved nine individuals to Phase II, and began five Phase III programs.
- In 2022, GSK stated that it would spend £1 billion over 10 years to speed up R&D (R&D) on infectious diseases that affect low-income countries. This study is mainly about developing new and different vaccines and medicines to stop and treat diseases such as tuberculosis, malaria, HIV (through ViiV Healthcare), neglected tropical diseases (NTDs), and anti-microbial resistance (AMR).
- GSK and Tempus formed a 3-year collaboration arrangement to provide GSK access to Tempus’ AI-enabled platform in 2022. This access includes Tempus’ library of patient data that has been de-identified. GSK is cooperating with Tempus to improve clinical trial design, accelerate enrollment, and find therapeutic targets leveraging its leading Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning (AI/ML) capacity. This collaboration contributes to GSK’s R&D success rate and provides patients with faster access to more personalized medication. The partnership extends an existing relationship between the two companies, which dates back to 2020 and focuses on getting people with certain types of cancer into clinical trials.
- Late in the year 2021, the FDA granted GSK permission for the drug Apretude (cabotegravir), which is the first and only long-acting injectable pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) alternative. It is used to lower the risk of contracting sexually acquired HIV-1. (Source) (Source) (Source)
Products Filed by GSK for Approval in the US/EU
| Serial No. | Year | Description |
| 1 | 2023 | The supplemental Biologics License Application (sBLA) for Jemperli (dostarlimab) was filed for approval in the US. (Source) |
| 2 | 2023 | The product filed for approval is Ojjaara (momelotinib), and it was approved by the US FDA in the US. (Source) |
| 3 | 2022 | The product filed for approval is momelotinib in the US, and the application was accepted by the US FDA. (Source) |
| 4 | 2021 | The product filed for approval is JEMPERLI (dostarlimab-gxly), and the approval was obtained from the US FDA in the US. (Source) |
| 5 | 2020 | The product Trelegy Ellipta was filed for approval in the US to expand its indication for the treatment of asthma in patients aged 18 years and older. (Source) |
Popular Drugs Manufactured by GSK
- Shingrix – In 2023, GSK manufactured Shingrix (Recombinant Zoster Vaccine or RZV) for the prevention of shingles in adults aged 50 and over. (Source)
- Triumeq – In 2022, Triumeq was manufactured for the treatment of children with HIV-1 who weigh 25kgs or more (previously 40kgs). (Source)
- Tivicay – In 2020, Tivicay was manufactured by GSK. It is used in the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection in both pediatric and adult patients. (Source)
GSK’s Drugs That Lost Exclusivity in the Past 2 Years
Requip PD – Requip PD from GSK lost its exclusivity in 2021, and it was indicated for Parkinson’s disease. (Source)
GSK’s Drugs Losing Exclusivity in the Coming 2 or 3 Years
Dolutegravir – GSK anticipated the loss of exclusivity of dolutegravir by the year 2028 or 2029. (Source)
GSK’s Revenue from Drug Sales
The top four drugs, including Trelegy at 49%, Benlysta at 22%, Nucala at 15%, and Breo Ellipta at 5%, collectively accounted for 91% of GSK’s total revenue in 2021. These essential pharmaceutical products played a pivotal role in contributing to the company’s overall financial performance, underscoring their importance within GSK’s revenue structure. (Source)
Top 4 Drugs Account for 91% of the Total Revenue in 2021
GSK’s Mergers And Acquisitions
- In 2022, GSK completed the demerger of its Consumer Healthcare business to form the Haleon Group, with shares of Haleon plc documented on the New York Stock Exchange as well as the London Stock Exchange. This strategic move allowed GSK to sharpen its focus on pharmaceuticals and vaccines, streamlining its business operations for greater efficiency and growth. (Source)
- In 2022, Unilever Plc’s Indian arm, Hindustan Unilever Ltd (HUL), completed the merger with GSK Consumer Healthcare Limited (GSKCH) in India. This strategic acquisition provided HUL access to a portfolio of popular health food drink brands, including Horlicks, Boost, and Maltova. The merger aimed to expand Unilever’s presence in the health and nutrition segment in India, capitalizing on the strong market position of these trusted brands. (Source)
- In 2022, Hindustan Unilever Ltd (HUL) completed the merger of GSK Consumer Healthcare Limited (GSKCH) with itself, a deal initially valued at INR 31,700 crore when first announced. As part of this merger, HUL also exercised its option to acquire the Horlicks brand for India from GSK for an additional INR 3,045 crore, per the terms of the original agreement between Unilever and GSK. This strategic move allowed HUL to strengthen its presence in the Indian consumer healthcare market and expand its product portfolio. (Source)
- In 2020, Hindustan Unilever Limited (HUL) completed the merger of GSK Consumer Healthcare Limited (GSKCH) with HUL. This merger marked one of the significant deals in the fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) sector. The acquisition aimed to create substantial value for all stakeholders involved, consolidate HUL’s position as India’s enormous FMCG company, and expand its product portfolio to serve consumers in the region better. (Source)
Collaborations Made by GSK
- In 2023, GSK and Save the Children renewed their partnership for another five years, further solidifying their collaboration to improve child vaccination rates. GSK committed £15 million to this initiative, aiming to reduce the number of ‘zero dose’ children, those who have never received any routine vaccinations, in Ethiopia and Nigeria. With a strong presence in Gavi’s Phase 5 strategy and the World Health Organization’s Immunization Agenda 2030, this collaboration leveraged their combined expertise and a decade of working together to develop and implement tailored strategies to reach these underserved children in various settings. (Source)
- In 2023, GSK announced an exclusive partnership with Chongqing Zhifei Biological Products, Ltd. (Zhifei) to co-promote GSK’s shingles vaccine, Shingrix, in China. This collaboration aimed to leverage Zhifei’s established presence in the Chinese vaccine market to expand access to Shingrix and explore additional potential indications for the vaccine. By combining the strengths and expertise of both companies, the partnership sought to facilitate broader patient access to Shingrix and enhance its availability in China, ultimately addressing the unmet healthcare needs in the region. (Source)
- In 2022, GSK collaborated with Tempus, a US-based precision medicine company, in a three-year partnership. This collaboration aimed to leverage Tempus’ AI-enabled platform and de-identified patient data library. GSK utilized Tempus’ Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning capabilities to enhance clinical trial design, accelerate patient enrollment, and identify potential drug targets. This collaboration was driven by the goal of improving GSK’s R&D success rates and delivering more personalized treatments to patients, ultimately advancing the field of precision medicine. (Source)
- In 2021, GSK and iTeos Therapeutics entered a collaboration agreement to co-develop and co-commercialize EOS-448, an anti-TIGIT monoclonal antibody, in phase I development for potential cancer treatment. The promising potential of TIGIT drove this collaboration as a target in immuno-oncology therapies, supported by compelling preclinical data and a phase II randomized clinical trial. It provided GSK with a unique position, granting access to antibodies that simultaneously target all three recognized CD226 checkpoints, namely TIGIT, CD96, and PVRIG, to advance innovative treatments for cancer patients. (Source)
Future Outlook
While the pharmaceutical sector faces increased scrutiny in terms of pricing, accessibility, and sustainability, it is also poised to benefit from breakthroughs in drug development, personalized medicine, and biotechnology. The industry’s continued growth and evolution are driven by technological advancements, demographic shifts, and global health crises.
For example, the pharmaceutical industry’s ongoing digital transformation is impacting where the research and development efforts are concentrated. By integrating artificial intelligence and big data analytics, these processes are streamlined, clinical trials are accelerated, and patient outcomes are improved.
While this report outlines the past and present plans of the major players in the pharmaceutical industry., the key to your success is to predict their next move before it becomes public knowledge.
Competitive analysis and technological landscape studies are the most effective routes to achieve this.
Contact the industry experts and plan your next business move.
How Can We Help You?
We support industry-leading R&D and Innovation professionals through complex problems. Describe your challenge, and let us bring clarity and expertise.