In Apr 2024, the Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard (FMVSS) No. 127 issued a mandate to implement Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB) systems on all new passenger vehicles by September 2029.
This regulation, while presenting monumental challenges for automakers, also offers strategic opportunities for forward-thinking manufacturers.
This article will discuss the new standards, market impact, technical challenges, compliance, and competitive insights for automotive companies.
Regulatory Landscape and New Standards
The NHTSA’s finalized rule establishes stringent performance requirements that fundamentally reshape expectations for automotive safety. The regulation requires AEB systems to prevent collisions with stationary objects at speeds of up to 62 mph, while automatically applying brakes at speeds of up to 90 mph when a collision with a lead vehicle is imminent.
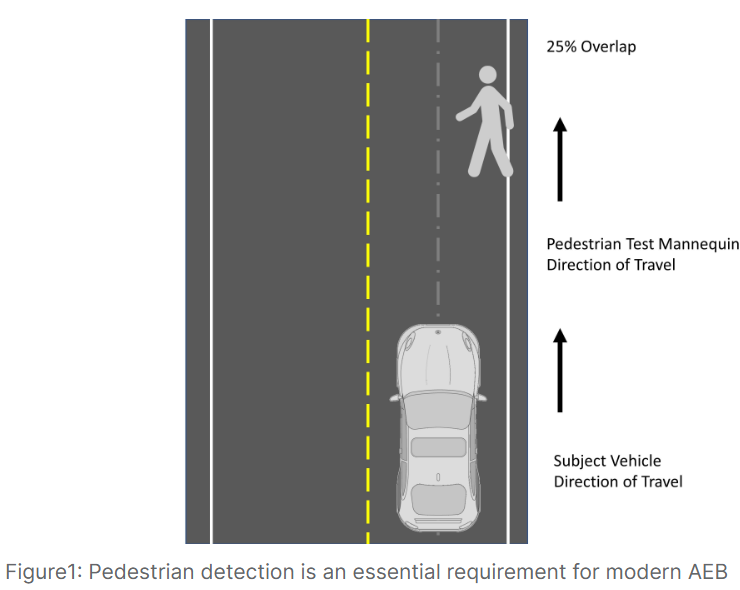
Perhaps most challenging, these systems must detect pedestrians effectively in both daylight and darkness conditions, with automatic braking capability up to 45 mph for pedestrian scenarios.
Recent preliminary testing reveals the magnitude of the challenge: only one out of 13 tested 2023 vehicle models passed NHTSA’s requirements, and even that vehicle engaged harsh braking that could be uncomfortable for passengers and potentially dangerous at higher speeds.
The Insurance Institute for Highway Safety’s updated testing shows similarly concerning results, with only 17% of 2023 model year vehicles entirely avoiding pedestrian mannequins in daytime conditions, dropping to just 11% during nighttime testing.
The regulatory framework deliberately avoids technology-specific mandates, instead establishing performance-based standards that enable manufacturers to choose optimal sensor combinations while meeting effectiveness thresholds. This approach creates opportunities for innovative solutions while ensuring consistent safety outcomes across all vehicle platforms.
Market Dynamics and Financial Implications
The AEB market represents a rapidly expanding sector valued at approximately $70 billion in 2024, with projections reaching $134 billion by 2034, with a CAGR exceeding 6.7%. This growth trajectory is driven not only by regulatory mandates but also by an increasing consumer awareness of safety and the insurance industry’s recognition of AEB effectiveness.
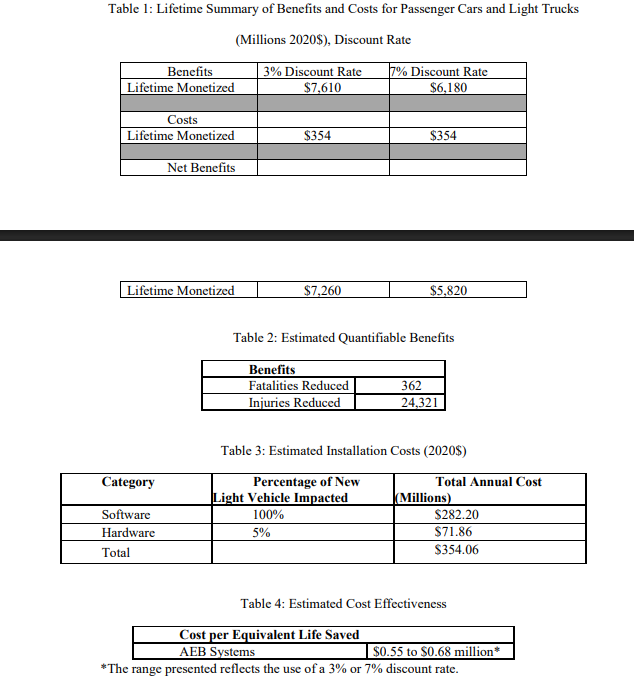
Cost estimates for compliance reveal significant industry debate. The NHTSA projects annual costs of $354 million across all manufacturers, estimating an implementation cost of approximately $82 per vehicle.
However, the Alliance for Automotive Innovation argues that meeting new requirements could cost over $430 million per original equipment manufacturer (OEM), citing the need for upgraded sensors, more powerful Electronic Control Units (ECUs), and additional hardware integration.
The economic justification remains compelling despite implementation costs. NHTSA’s analysis projects lifetime net benefits of $5.24 to $6.52 billion, with the regulation expected to save at least 360 lives annually and prevent over 24,000 injuries.
These benefits translate to measurable insurance premium reductions, with companies like Liberty Mutual offering discounts to Volvo owners with advanced safety features.
Technical Challenges and Industry Response
The most significant technical challenge lies in achieving high-speed performance and detecting stationary objects. According to NHTSA data, an estimated 42,915 people died in motor vehicle crashes in 2021, with speeding being a factor in nearly one-third of fatalities.
High-profile incidents involving systems like Tesla’s Autopilot and Ford’s BlueCruise have demonstrated how current sensors struggle to reliably recognize static hazards such as stalled vehicles or road debris.
Traditional AEB systems are often designed to ignore stationary objects to prevent “phantom braking” from false detections. However, this design choice can lead to severe outcomes when vehicles encounter legitimate stationary hazards. The industry currently faces millions of vehicles under investigation for phantom braking issues, with Toyota, Subaru, Ford, Honda, and GM vehicles subject to recalls for unexpected AEB activation.
The regulatory requirements significantly exceed international standards, creating additional complexity for global manufacturers. European regulations under the General Safety Regulation set AEB operation speeds between 12.4 mph and 37.3 mph, while NHTSA mandates capability up to 60 mph. This disparity complicates global platform strategies and increases development costs for manufacturers seeking regulatory harmonization.
The Overlooked Blind Spot: Sustainability
Behind the headlines about safety lies a quieter cost: sustainability.
Every radar module, every lidar unit, every GPU, and camera array adds not only safety but also material weight, rare earth demand, and future e-waste.
In 2022, the world generated 62 million tonnes of e-waste; less than a quarter was recycled correctly. The demand for rare earths is forecasted to triple by 2030.
What happens when millions of vehicles are required to incorporate dense electronics?
Unless addressed, AEB hardware risks becoming another environmental liability; an ironic trade-off where solving one crisis (road safety) worsens another (e-waste).
Regulators haven’t yet connected these dots.
But investors, ESG committees, and activists will. Just as the EU has tightened rules on batteries and supply chain traceability, similar frameworks will be introduced for electronics.
Strategic Solutions and Technology Pathways
Successfully navigating the AEB mandate requires a multifaceted approach that combines advanced sensor fusion, artificial intelligence integration, and strategic technology partnerships to achieve optimal results. The most promising solutions focus on software-defined approaches that enhance existing sensor performance rather than requiring complete hardware overhauls.
Sensor Fusion Optimization: Advanced radar technology enhanced with AI capabilities addresses traditional limitations in stationary object detection. High-precision object classification enables systems to filter irrelevant objects while quickly identifying actual hazards, solving the fundamental problem of stationary object blindness that affects many current systems.
Software-Defined Solutions: Implementing software-defined approaches allows continuous upgrades to meet evolving safety benchmarks. This strategy provides cost-effective compliance while maintaining flexibility for future regulatory changes and performance improvements.
Integrated Development Platforms: Establishing comprehensive testing protocols that mirror NHTSA’s standardized procedures ensures reliable compliance verification. These platforms must accommodate both daytime and nighttime testing scenarios across a range of speeds and various object types.
Regional Compliance and Global Harmonization
The global regulatory landscape presents both challenges and opportunities for manufacturers operating across multiple markets. Japan has implemented mandatory AEB requirements for new passenger cars from November 2021, with existing models required to comply by December 2025. The European Union mandated AEB systems on new vehicle models from May 2022, with all new vehicles required to comply by May 2024.
India’s automotive industry is also advancing toward AEB mandates, with the government proposing mandatory Advanced Emergency Braking Systems (AEBS) for large passenger vehicles from April 2026. These developments create opportunities for manufacturers to leverage standard technology platforms across multiple regulatory environments while addressing region-specific requirements.
Implementation Timeline and Strategic Planning
The September 2029 deadline provides a critical five-year window for strategic planning and system development. However, the Trump administration’s regulatory review has introduced potential timeline adjustments, with NHTSA postponing implementation to March 20, 2025, to allow additional assessment time.
Manufacturers should prioritize early compliance strategies that position them advantageously in the market. Current voluntary AEB adoption already covers approximately 90% of new passenger vehicles in the United States, creating a foundation for enhancing system capabilities rather than implementing new ones entirely.
The phased approach should focus on making immediate improvements to existing systems while developing next-generation platforms that can exceed regulatory requirements. This strategy enables manufacturers to capture early market advantages while ensuring robust compliance with final regulations.
Competitive Advantages and Market Positioning
Organizations that successfully navigate the AEB mandate will establish significant competitive advantages in an increasingly safety-conscious market.
Euro NCAP’s updated 2026 protocols introduce enhanced AEB testing scenarios, including junction collision avoidance and cyclist detection capabilities. Manufacturers achieving maximum safety ratings through advanced sensor integration will command premium market positioning.
Consumer demand is increasingly driving purchasing decisions beyond regulatory minimums, creating market premiums for vehicles that achieve top-tier safety ratings. The Insurance Institute for Highway Safety’s advocacy for stringent AEB regulations reflects consumer awareness of current system limitations, particularly in dark conditions.
Premium vehicle segments particularly benefit from advanced safety technology differentiation, with manufacturers like Volvo leveraging City Safety technology to demonstrate measurable benefits in crash reduction. The NCAP roadmap extending through 2033 ensures continuous technology evolution requirements, rewarding ongoing innovation investments.
Conclusion
The AEB mandate represents a transformative moment for the automotive industry, requiring strategic vision, technical innovation, and operational excellence. Organizations that approach this challenge as an opportunity to advance safety leadership while optimizing cost structures will emerge as industry leaders in the next decade of automotive evolution.
Success demands immediate action combined with long-term strategic planning. The companies that begin comprehensive AEB development programs today will not only meet regulatory requirements but will establish the foundation for continued safety innovation and market leadership in an increasingly autonomous future.
How Can We Help You?
We support industry-leading R&D and Innovation professionals through complex problems. Describe your challenge, and let us bring clarity and expertise.














