The unfolding story of 6G has expanded well beyond telecom companies and chipmakers. Companies such as Google, Meta, and Toyota, often considered peripheral to wireless communication, are now actively shaping the 6G technology landscape. Through patent filings, proposal submissions to 3GPP, and R&D collaborations, they’re aligning 6G’s development across sectors as varied as healthcare, aerospace, automotive, and enterprise software.
They no longer want to sit back and enjoy the ride; they want to take the wheel and drive 6G forward. But why now?
Because 6G promises capabilities that go far beyond faster connectivity. It introduces a platform for intelligent, adaptive systems that meet the latency, positioning, and power requirements of next-gen applications. For instance:
The technologies that 5G laid the groundwork for, such as autonomous systems, industrial IoT, and smart healthcare, 6G will enhance them further. Here’s what gives 6G a one-up:
- Latency under 0.1 milliseconds– enabling real-time responsiveness critical for scenarios like remote surgery. Imagine a surgeon in New York feeling the tissue they’re working with using robotic arms in Nairobi with zero delay.
- Near-perfect positioning (millimeter-level)- Picture self-driving cars gliding through a busy city, knowing exactly where the roadblocks and curbs are, down to the millimeter.
- Built-in AI that adapts in real time– Think of a network that predicts traffic before it forms and reroutes to avoid congestion.
- 100x energy efficiency compared to 5G– Imagine a smart city where sensors run for years without battery swaps, utilizing technologies such as Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (RIS) and AI-driven energy management.
Together, these innovations signal a shift from networks built for “connection” to those designed for “cognition,” where sensing, learning, and reacting are part of the infrastructure.
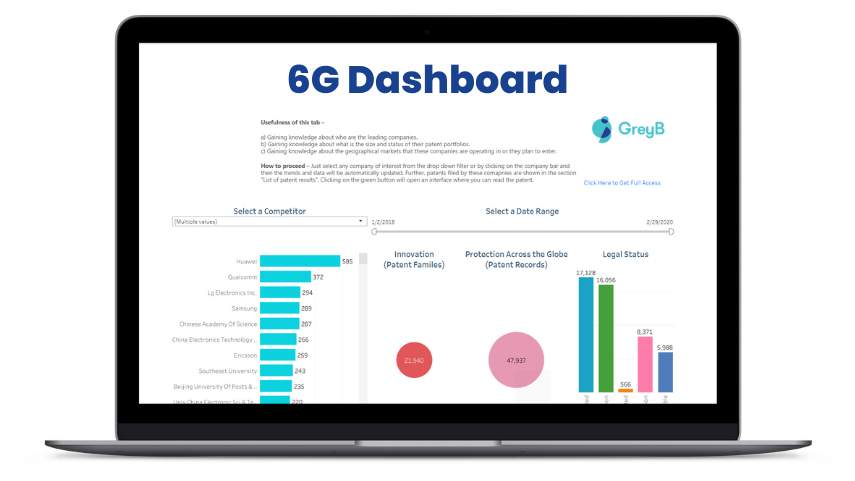
This article discusses how non-telecom industries are becoming core to 6G development. It also highlights the challenges they aim to solve and the steps organizations can take today to gain an edge in the 6G era.
1. Behind the Wheels: How Toyota, Kia, and Others Are Shaping 6G Standards
According to IoT Analytics research, “Connected Public Transport” and “Traffic Monitoring and Management” are the top two use cases in smart city initiatives. 6G integration into automotives, traffic management infrastructure, and communication networks is the key to achieving these scenarios.
With 6G capabilities, vehicles will better sense, interpret, and respond to their environments. They will have precise, real-time spatial awareness that surpasses the limitations of conventional radar and lidar systems. Overall, road safety and traffic efficiency will increase.
To illustrate 6G’s potential, NXP and Ericsson are jointly researching integrated Joint Communication and Sensing (JCAS) technologies. Their collaboration indicates how leveraging sub-terahertz frequencies and mmWave beamforming technology within 6G networks can proactively detect obstacles and vulnerable road users. This technology will help with real-time warnings at complex intersections and prevent accidents.
Automotive sector leaders such as Toyota and Hyundai (Kia) also understand the potential of 6G to change vehicle mobility. They are actively researching 6G features like terahertz signals, low latency, and native AI integration to create responsive vehicle ecosystems.
Based on their research, these automotive industry giants are making strategic 3GPP proposal submissions and patents. The aim is to influence the reference models and technical assumptions that 6G will be built upon, particularly how cars will “sense” through networks.
For instance, Toyota has submitted over 10 proposals to 3GPP, focusing on integrated sensing and communication (ISAC). Two examples include:
- R1-2400932 – Channel modeling for Integrated Sensing and Communication (ISAC), which will define how 6G can interpret and transmit spatial data.
- R1-2404914 – Deployment scenarios for vehicle-centric networks, likely informing how V2X setups will interact with fixed infrastructure under 6G.
Similarly, Kia’s patent activity in video compression and data transmission has surged by ~50% compared to non-automotive companies. These technologies are critical for immersive in-car experiences and AI-assisted safety. Its increased involvement in 3GPP working groups suggests a growing interest in owning a stake in connectivity standards that will power next-gen vehicles.
Read more about Kia's 6G Activities:
Government-Led 6G Advancements for Automotive
In Europe, BMW and Bosch are core partners in Germany’s 6G-ANNA initiative, a government-funded project aiming to define 6G architectures with automotive-grade requirements. Their work includes XR-assisted driving, over-the-air diagnostics, and smart surface antennas for vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) links.
What This Means for the Industry:
Connectivity, or precisely cognition, will be a game-changer for the automotive industry. It will be the core of everything from self-driving technologies to seamless vehicle-to-cloud services.
As 6G takes shape, its advanced capabilities like ISAC will fuel automotive innovations and unlock new possibilities in transportation safety and in-vehicle experience. It will be the key enabler for real-time environmental modeling, smart automated driving systems, and immersive vehicle experiences, as the 5G Automotive Association (5GAA) highlighted.
Given this strategic significance, automotive companies that proactively develop expertise and build robust 6G patent portfolios will gain an influential voice in automotive standards (and telecom) for smart transportation.
Conversely, companies delaying involvement risk potential licensing conflicts or vendor lock-in, which could significantly hinder their competitive advantage in the 6G era.
2. 6G will make remote medicine faster and more precise with AI
The healthcare industry faces challenges like rising costs, complex administrative processes, and a shortage of medical specialists.
With their low-latency and sensing capabilities, 6G networks will help improve areas like telemedicine and remote surgeries. It will also make continuous patient monitoring more precise and uninterrupted by collecting and analyzing data from various IoT devices, health records (EHRs), and diagnostic tools.
Another use case of 6G technology in the healthcare industry is to improve communication between hospitals, clinics, insurance providers, and regulatory bodies by enabling real-time data sharing.
With 6G expanded band frequencies and low latency, healthcare providers can instantly transmit patient data to insurance companies and regulatory bodies. This eliminates the need for human interventions, reduces the time spent on paperwork, and minimizes errors.
Automated systems, with 6G’s native AI capabilities, can verify patient information, process claims, and handle billing in real time. As a result, the entire administrative (treatment suggestions, approvals, reimbursements) workflow becomes more efficient. This will allow healthcare providers to focus more on patient care than on administrative tasks.
Recommended Case Study
A practical example is the joint research by the University of Kaiserslautern-Landau (RPTU) and the German Research Center for Artificial Intelligence (DFKI). It is a part of Open6GHub and 6G Health initiatives. Researchers are developing a functional demonstrator that aggregates biomedical data from wearable sensors through 6G mobile networks.
According to Jan Herbst, a researcher involved in the project, “With rapid advancements, especially in human-machine communication, 6G technology opens numerous groundbreaking applications in medicine. Focusing on effective preventive healthcare, we aim to enable doctors to monitor their patients’ health more efficiently and detect critical conditions and risks early.”
The demonstrator uses interoperable sensor networks with specially designed printed circuit boards (PCBs) arranged in a resilient closed-loop configuration. This results in efficient and reliable data transmission with minimal latency.
Meanwhile, global industry giants like Google and Zanni XR Inc. are actively filing patents and establishing technical foundations on 6G’s potential in healthcare.
1. Zanni XR Inc. AR platform making remote surgeries and telemedicine accurate with 6G
Zanni XR Inc.’s AR platform (patent) uses 6G to support remote surgeries and telemedicine. This AR platform overlays digital content onto live video in real time, powered by 6G’s ultra-low latency. Thanks to high-speed data transmission and real-time positioning, surgeons can perform accurate remote surgeries with enhanced precision.
The technology also improves and expands the reach of telemedicine services, where medical experts can guide local practitioners using AR-enhanced views. This will help provide specialized care even in remote or underserved locations.
2. Google’s prenatal monitoring system that uses 6G and AI Sensing
Google filed a patent (WO2024196370A1) for a prenatal monitoring system that utilizes 6G sensing and AI. This system continuously tracks fetal activity using smart sensors, transmitting data in real-time for immediate analysis. With AI analytics and 6G-enabled sensors, doctors can detect abnormalities instantly and act quickly, enabling timely interventions.
This system eliminates monitoring delays and allows earlier diagnosis of complications. It will improve maternal-fetal care through remote pregnancy monitoring and proactive interventions.
3. Guangzhobu 6G-based health system for physiotherapy cabins
Guangzhobu Vision Optical Technology filed a patent (CN117860211A) for a health data collection and analysis system used in graphene quantum physiotherapy cabins. During each treatment session, the system captures real-time physiological data like heart rate, skin temperature, and muscle activity.
Using machine learning algorithms, the system analyzes this data to track patient response and treatment effectiveness. It allows doctors to:
- Personalize treatment based on each patient’s unique data
- Adjust therapy in real-time for better results
- Reduce trial-and-error in physiotherapy care
With 6G technology enabling fast and secure data sharing, this system can bring intelligent, responsive care into wellness and rehabilitation settings.
4. 6G will enhance IoT-enabled Digital Enterprise solutions
6G technologies will significantly amplify the effectiveness and integration capabilities of advanced healthcare IoT platforms like Philips’ Health Suite Digital Platform. These platforms will be able to process and transmit large-scale, high-resolution medical data in real-time with 6G’s ultra-high-speed connectivity and low latency.
For Philips, 6G’s capabilities enable faster aggregation and analysis of diverse patient data from different sources like wearables, imaging devices, and EHRs. This will improve diagnostic precision and personalized patient interventions.
Similarly, Siemens’ IoT-enabled Digital Enterprise solutions will benefit from 6G-enabled edge computing technology. Their real-time data processing at the network’s edge will be optimized, and so will their emergency response times and continuous patient monitoring.
Moreover, the inherent security enhancements and AI-native architecture of 6G networks reinforce data privacy, regulatory compliance, and cybersecurity. These are crucial for these IoT ecosystems to safeguard sensitive healthcare data of patients.
6G with its Native AI and IoT devices will revolutionize healthcare by enabling real-time data sharing and remote interventions. This will make healthcare delivery faster and more precise.
What This Means for the Industry:
Medical device manufacturers must ensure their products are 6G-ready to make this shift happen. This includes remote surgery tools, diagnostic platforms, wellness monitoring systems, and wearables like smartwatches.
Additionally, the 6G-powered healthcare ecosystem will require the development of industry standards that ensure the privacy and security of sensitive patient data. These standards are particularly essential for applications like prenatal care and telemedicine.
Discover what’s next in the 6G industry precisely with our AI-powered research tool SLATE. Simply ask a question, “What’s next in 6G?” and get yourself a mini tech landscape in just a few minutes!

Source: Slate
3. 6G will make Immersive Media & XR more real with all senses involved
The bottlenecks currently limiting immersive experiences, such as lag, poor video quality, and buffering, will be eradicated with 6G. The new network will enable smooth and dynamic content delivery previously unattainable by networks.
To make this vision a reality, Meta, Google, and Dolby have already been involved in shaping the future of XR on next-generation networks. They have contributed over 200 proposals to 3GPP to define the framework for 6G-powered XR and tackle different aspects of this ecosystem:
- Meta’s proposal (R2-2407277) focuses on multimodality in XR. It aims to create fully immersive environments where users can interact across multiple sensory channels—visual, auditory, and haptic—creating more lifelike and interactive virtual experiences. This aligns with 6G’s capabilities to support ultra-fast, synchronized data exchange across these modalities.
- Google is working to build seamless Android and mobile XR experiences. The aim is to ensure the smooth operation of the next generation of smartphones, wearables, and other XR devices on 6G networks. In its proposal, Google focused on providing faster, lag-free connections for real-time mobile XR and enhanced gaming and social interactions on mobile devices.
- Dolby is developing 6G-powered Spatial Audio, which will enhance immersive entertainment by providing directional sound and dynamic audio environments. This technology will revolutionize how we experience interactive media, from gaming to virtual concerts, by bringing more realistic, fully immersive soundscapes integral to XR experiences.
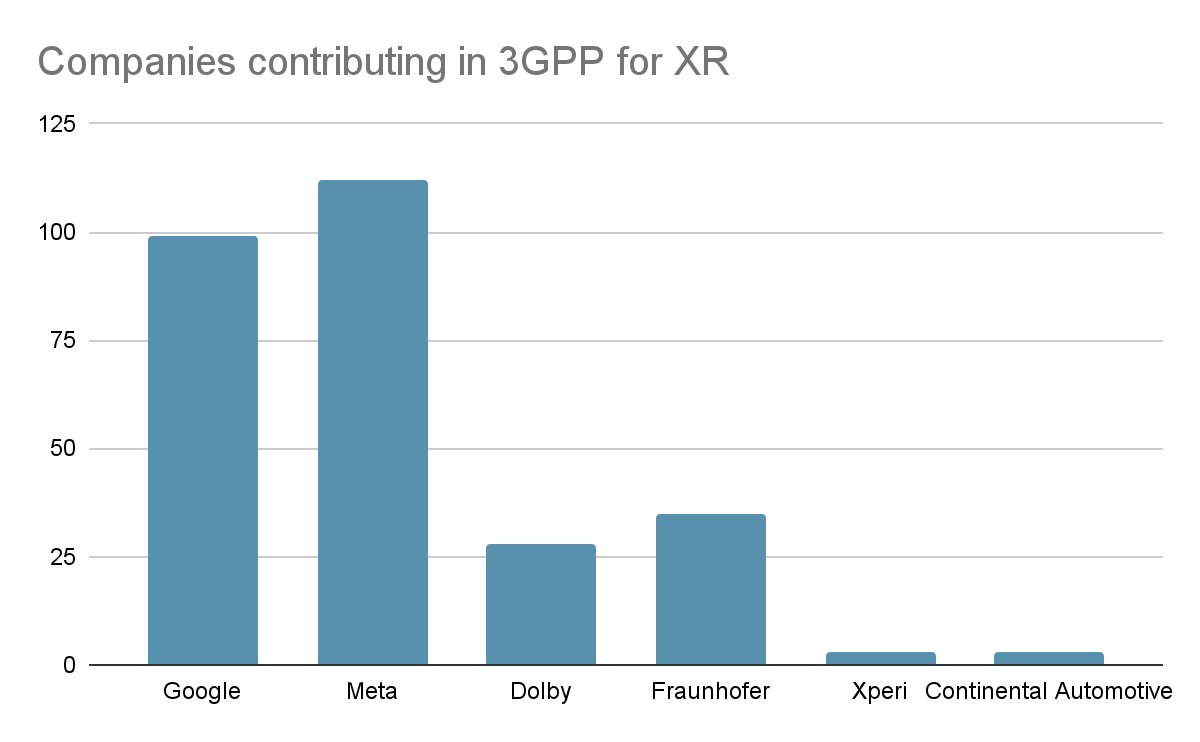
In addition, the 6G-XR Project in Europe, funded by the EU’s Horizon Europe program, is developing an experimental infrastructure to enable next-generation XR services. This initiative focuses on cloud-native multimedia functions, edge-to-cloud computing, and AI-driven orchestration to support holographic communications, immersive gaming, and metaverse experiences.
At the same time, Ericsson’s partnership with the University of Texas at Austin focuses on enhancing multiplayer mixed reality gaming and ultra-realistic interactive sports experiences using 6G’s high data rates and low latency.
What This Means for the Industry:
As 6G technology advances, XR experiences will become interactive, high-resolution, and buffer-free. This will open gates for new levels of engagement in gaming, virtual collaboration, and entertainment.
Social media companies will leverage 6G to create immersive virtual collaboration spaces. Users will be able to interact in real-time without latency issues, perfect for remote working and global social interactions.
Media companies and content creators will play a major role in this industry shift. They will have to develop 6G-compatible production tools and content to make consumers’ experiences engaging and interactive. It is also important for them to utilize 6G’s network capabilities, deliver VR/AR content in real time with high fidelity and minimal delay, and stay relevant in the industry.
Read about core companies working on 6G
4. Native AI will drive Software Development with 6G
6G introduces an AI-native, cloud-friendly architecture for intelligent, adaptive software development across hybrid cloud environments. With 1 Tbps data speed and milliseconds latency, 6G will significantly speed up the software model training, testing, and deployment. This will result in faster development cycles and real-time updates.
Mavenir, a cloud-native telecom software provider, is a notable player working on maximizing 6G’s impact on the software industry. The company has submitted a 3GPP proposal (R1-2305688) focusing on integrating machine learning into 6G radio networks. Its objective is to automate network management through AI, enhancing network optimization and reducing operational costs.
Similar research to revolutionize the software industry is happening in Finland under the “Liquid AI for 6G Software” project. This project is coordinated by the University of Jyväskylä and funded by Business Finland to create ‘liquid’ IoT system architectures. In this context, ‘Liquid AI’ refers to software and applications that seamlessly flow between devices, adapting to various hardware and network configurations. This fluidity is crucial for managing the vast, heterogeneous networks anticipated in the 6G era.
The project aims to use a unified set of technologies across all systems to run consistent code on different devices. This approach is particularly beneficial for AI subsystems, allowing for efficient deployment and maintenance of intelligent functions throughout the network. The project also addresses challenges associated with massive data volumes generated by IoT devices by bringing computing closer to data sources.
What This Means for the Industry:
With 6G’s AI-native capabilities, software developers will be able to move towards microservices architectures. They will be able to break down big software applications into modular, reusable components that can be developed, tested, and deployed independently. This type of software architecture is essential for accelerating and scaling AI-powered software applications.
Moreover, 6G’s hybrid cloud support will allow the industry to seamlessly deploy software models across different environments, optimizing cost, performance, and scalability.
5. 6G will provide uninterrupted connectivity in flights or remote areas
6G’s Non-Terrestrial Networks (NTNs) will change how we stay connected across the globe. Using satellites and drones (UAVs), these networks will make low-delay, always-on communication possible to places traditional networks can’t reach, like planes in the sky or remote villages.
Companies like Thales and Airbus are already developing 6G-enabled aviation networks (NTNs) to make in-flight Wi-Fi and seamless connectivity a reality.
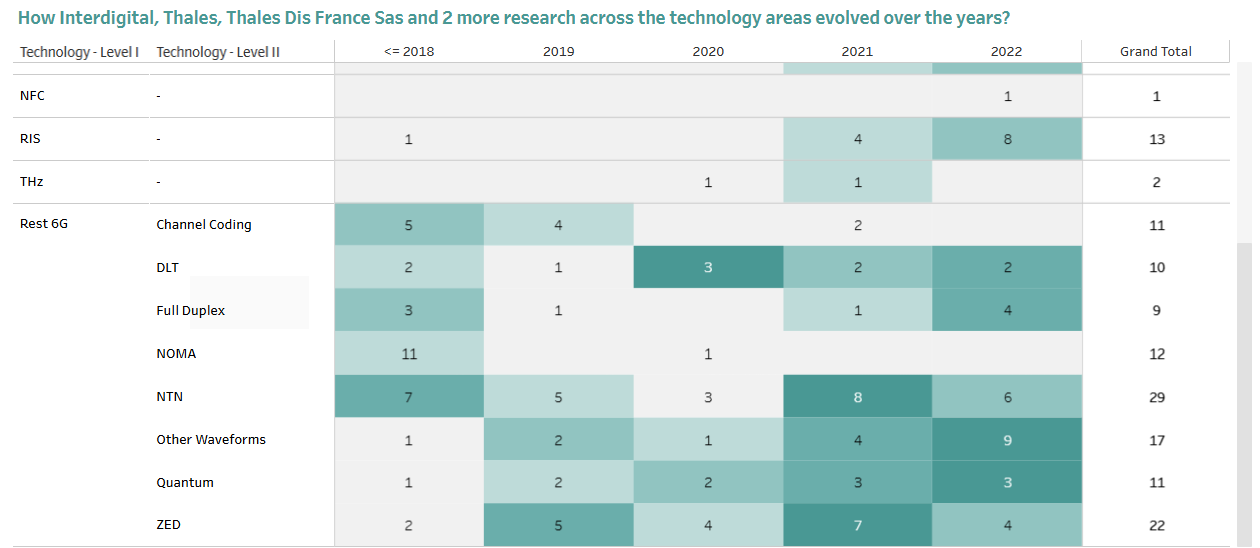
At the same time, satellite providers such as Globalstar, Inmarsat, Eutelsat, Viasat, and Hughes/Echostar (Dish) are helping shape 6G standards. They’ve submitted important proposals—like R4-2304331 and R4-2300302—to help define how 6G can work smoothly with satellites and support future global connectivity.
- R4-2304331 outlines the performance requirements for 6G systems using low-frequency bands for reliable and efficient satellite-based networks.
- R4-2300302 reviews current 5G standards to see if they work for satellite use and suggests changes needed for better 6G support in space-based communication.
What This Means for the Industry:
Deploying Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites will bridge connectivity gaps for both consumer and commercial use. In-flight connectivity will become more efficient and seamless, enabling real-time passenger communication and enhancing airline operations. Satellite operators will be tasked with developing 6G-compatible solutions supporting global coverage, ensuring reliable and continuous connectivity across land, sea, and air.
6. The Nervous System of Tomorrow’s Smart Cities
6G will act as the central nervous system of future smart cities. Its ultra-low latency, 1 Tbps data speeds, and integrated sensing capabilities will revolutionize various aspects of smart cities:
- Integrated Sensing and Communication (ISAC): 6G networks seamlessly merge communication and sensing. This will allow infrastructure to monitor environmental conditions, traffic flow, and public safety in real-time.
- Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communication (URLLC): Critical services like emergency response and autonomous transportation will benefit from near-instantaneous data transmission, enhancing safety and efficiency.
- Massive Machine-Type Communication (mMTC): Supporting a vast number of IoT devices, 6G will facilitate comprehensive monitoring and automation in sectors such as energy management, waste disposal, and water treatment.
Several initiatives are at the forefront of integrating 6G into smart city frameworks:
1. ARCHITECOGROUP CO LTD’s IoT-Driven Air Quality Monitoring
ARCHITECOGROUP CO LTD has developed an IoT-based system (Patent KR102565319B1) designed for ESG-compliant green construction. This system utilizes AI and IoT sensors to monitor air quality and optimize energy consumption in buildings. With 6G’s capabilities, such systems can achieve real-time data collection and predictive control, enhancing indoor environmental quality and energy efficiency.
2. European Smart City Trials
The 6G Smart Networks and Services Industry Association (6G-IA) has documented various smart city trials across Europe, focusing on:
- Mobility and Transportation: Implementing 6G improves traffic management and enables autonomous vehicle communication.
- Energy and Utilities: Developing smart grids for efficient energy distribution.
- Public Safety: Enhancing surveillance and emergency response systems through real-time data transmission.
- Environmental Monitoring: Deploying sensors for air quality and pollution tracking.
These projects involve collaborations among city governments, research institutions, and industry stakeholders to validate 6G applications in real-world settings.
3. MultiX Project: Advancing 6G for Urban Applications
The MultiX project aims to transform 6G networks into active environmental observers by integrating multisensory perception into 6G radio access networks. This initiative focuses on real-time urban monitoring, contactless patient care, and industrial automation. Universidad Carlos III de Madrid coordinates it, and 17 partners from seven countries are involved under the Horizon Europe program.
4. University of Málaga’s 6G Research Initiatives
Keysight Technologies, Inc. and the University of Málaga have established two new facilities dedicated to 6G research: the 6G Keysight-UMA Lab and the Red Victoria Network. These centers are part of the 6G-SANDBOX project, aiming to position Málaga as a hub for 6G innovation. They are working on 6G applications in autonomous driving, public safety, and smart agriculture.
5. NVIDIA’s Cloud-Based 6G Research Platform
NVIDIA has launched an AI-powered, cloud-based platform facilitating 6G research and testing. This platform enables the simulation of various communication environments, from individual cell towers to entire cities. It allows researchers to test 6G network performance in real-time scenarios. Early adopters include companies like Nokia, Samsung, and SoftBank Corp and academic institutions such as Northeastern University.
What This Means for the Industry:
The integration of 6G technology into smart cities presents significant opportunities and considerations:
- Urban Planners and Policymakers must proactively invest in 6G-ready infrastructure to meet sustainability and efficiency goals.
- Technology Developers should focus on creating interoperable solutions that leverage 6G’s real-time data processing and automation capabilities.
- Industry Collaborations and cross-sector partnerships are essential to drive innovation and standardization in 6G applications.
Key Takeaways: Preparing for 6G Beyond Telecom
The arrival of 6G is expected around 2030. However, key work items defining 6G’s core technologies will be finalized by the end of 2025. Just as LTE paved the way for 5G, the upcoming generation will build on recent 5G advancements from Releases 17, 18, and 19. These include Non-Terrestrial Networks (NTN), AI/ML integration, Massive MIMO, Ambient IoT, and Reduced Capability (RedCap) devices.
While these technologies aim to improve connectivity, their true impact lies in the industries they will transform. As 6G development accelerates, non-telecom organizations exploring its potential can now influence emerging standards, secure high-value patents, and prepare future-ready products and services. Waiting means playing catch-up in a space that rewards early innovation.
So, how can you get involved early?
By identifying use-cases in your domain, contributing to standard bodies, filing strategic patents, and partnering with early movers in research. But to do this effectively, you need the right intelligence at the right time. This includes,
- Spotting early trends and industry-specific 6G use-cases
- Identifying competitors and newcomers filing patents in your domain.
- Tracking standard-essential activities and IP positioning.
- Discovering startups and researchers working on frontier 6G technologies.
GreyB can help you map the 6G opportunity before your competitors do.
Fill the form to talk to our experts
Here’s how GreyB helped an industry expert gain early insights into key 6G technologies and map innovations that would become central to the 6G standard: