Consumers love the idea of dairy-free yogurt—until they take a bite and find it’s too watery, chalky, or just tastes “off.” At the same time, shoppers are getting increasingly aware of labels. They want yogurt with natural ingredients, no artificial preservatives, stabilizers, or chemicals they can’t pronounce.
While appealing to eco-conscious buyers, sustainable packaging further accelerates spoilage. The result? Yogurts that spoil too fast or lose their benefits before they even reach the customer.
To make matters worse, manufacturing complexity drives up costs.
Innovation trends in the yogurt industry are turning these challenges into opportunities. Microbial fermentation improves the texture and nutrition of plant-based yogurts, and novel whey protein technologies enhance consistency while eliminating lactose.
Functional yogurts with specialized probiotics target health benefits, from gut health to immunity. Sustainable production methods reduce environmental impact while delivering superior products.
This report highlights the trends in yogurt innovation and the leading companies shaping the future of this food sector.
Using Microbial Fermentation for Sustainable, Plant-Based Yogurts
Emerging innovations in fermentation are replicating conventional dairy products’ sensory and nutritional qualities. Fermentation cultures include using mycelium liquid extract and mycoprotein-based ingredients.
These advancements enhance plant-based yogurt’s texture, flavor, and nutritional profiles, offering viable alternatives that meet consumer expectations for sustainability and taste.
Combining Lactic Acid Bacteria with Other Ingredients to Enhance Fermentation.
Traditional lactic acid bacteria (LAB) struggle to effectively ferment non-dairy substrates, limiting the quality of plant-based dairy products.
To solve this, Re-Milk has developed a method of combining yeast-derived ingredients and LAB to improve the fermentation of plant-based dairy alternatives significantly. This method enhances texture, mouthfeel, and flavor, enabling plant-based products to resemble traditional dairy more closely in sensory and nutritional profiles.
Re-Milk has paused its previous plan to build a 750,000-square-foot facility in Denmark and has partnered with an existing production facility in Western Europe. This strategy allows Re-Milk to focus on scaling up production more rapidly.
The company has also brought executives from industry giants like Danone, PepsiCo, and Nestlé to its board, further strengthening its industry connections and expertise. Re-Milk already has the infrastructure to make dairy-free products at scale, and the above methodology can be easily integrated into its production.
Creating Dairy-Free Yogurt Production Using Mycelium Extract
Many dairy-free alternatives lack essential nutritional properties or pose other health concerns, like digestive discomfort. Mycorena, now under Naplasol, has a viable solution to these issues.
Their innovation uses mycelium as a dairy-free ingredient in yogurt. The process creates a mycelium liquid extract rich in native fungal proteins, avoiding the conventional harsh chemicals and high-temperature treatments. This method preserves the proteins’ native structure, resulting in a product with enhanced solubility and functionality.
The end product is a protein-rich, allergen-free, and eco-friendly alternative to dairy that maintains a desirable taste and mouthfeel.
Naplasol, a member of the VEOS Group, acquired Mycorena for its flagship product, Promyc®. The company plans to produce Promyc® at its state-of-the-art facility in Bree, Belgium, enabling large-scale manufacturing. The above processing method will easily integrate into making their existing products.
These insights were derived from analyzing thousands of patents filed by these companies. Reading through the patents manually and understanding the innovation requires much time. Advanced AI scouting tools, like Slate, simplify finding these Innovation trends in yogurt.
You can search “What are some new innovation trends in yogurt?” and get precise search results from patents, research papers, and other relevant sources!

Try this yourself by filling out the form below.
Using Fungal Biomass for More Sustainable Yogurt Production
Current plant-based yogurts rely heavily on conventional binders, stabilizers, and thickening agents, which are often derived from animal or synthetic sources. Innovation with these materials may not align with the rising consumer preference trends for sustainable, eco-friendly yogurt ingredients. Many of these alternatives also lack the desired texture and consistency of traditional dairy yogurt.
NoshBIO has created a solution using specific fungal biomass to create versatile food ingredients for yogurt. Filamentous fungi produce a product that is a binder, stabilizer, and thickener. It also offers textures and consistency similar to conventional yogurt.
This ingredient is an environmentally friendly, vegan alternative to chemical additives. It addresses the demand for sustainable yogurt while preserving essential proteins, dietary fibers, and hydrocolloid properties.
Analyst comments:
Combining mycelium and mycoprotein-based ingredients enhances yogurt’s texture, mouthfeel, and nutritional value, creating a more appealing option for health-conscious and environmentally aware consumers.
NEXTY Award winner Nature’s Fynd is also actively working on this. Furthermore, by utilizing renewable resources like fungi, these innovations reduce reliance on resource-intensive agriculture and align with the growing need for eco-friendly food solutions.
Regulatory challenges to foresee in this trend
Labeling and Marketing Compliance:
Dairy-related terminology, such as “yogurt,” for non-dairy products, is heavily regulated. Claims about the sensory attributes (taste, texture, and nutritional profile) of these products need to be carefully worded to avoid misleading consumers, especially regarding claims of “dairy-like” or “natural.” Regulatory bodies may restrict such claims unless clear, substantiated evidence is provided.
Novel Food Approval & Ingredient Classification:
Innovation trends in yogurt, like using mycelium liquid extracts, yeast-derived ingredients, and fungal biomass, will likely be classified as novel foods under EU and FDA regulations. To secure pre-market approval, these ingredients must undergo extensive safety assessments, including allergenicity testing and human consumption trials.
GMO and Genetic Engineering Regulations:
If genetically modified organisms (GMOs) are involved in the fermentation processes or the creation of novel ingredients, these products will face rigorous scrutiny. Specific GMO labeling, safety testing, and compliance with local GMO regulations (e.g., the EU’s strict policies on GMOs) will be essential.
Food Additives and Functional Ingredients:
Integrating nontraditional ingredients such as fungal biomass and novel proteins into production may trigger scrutiny under food additive regulations. These ingredients may need to be evaluated separately for their safety, efficacy, and potential for allergic reactions.
Sustainability Claims and Environmental Impact:
As these products are marketed as more sustainable alternatives to dairy, companies must substantiate their eco-friendly claims through verified environmental assessments (e.g., Life Cycle Analysis). The EU Green Claims Directive and similar global standards are increasingly strict about the evidence required to make such sustainability claims.
Production Facility and Compliance:
Scaling up production in new facilities, such as transitioning from a planned facility in Denmark to an existing plant in Western Europe (as seen with Re-Milk), means aligning with local food safety standards, hygiene regulations, and traceability protocols. These regulations ensure the production processes comply with national and international food safety laws.
Improving the Taste and Nutritional Value of Yogurt with Whey Protein
The yogurt industry is witnessing new trends in microbial and protein-based formulation innovation, including heat-stable whey proteins and optimized production processes.
These innovations improve texture and protein retention and address consumer demand for high-protein, lactose-free, and sustainable yogurt products. As these trends evolve, manufacturers adapt to new technologies that enhance yogurt’s functional properties and sensory attributes while reducing production complexity and operational costs.
Fonterra made Heat-stable whey for texture enhancement in yogurts
Traditional whey protein formulations can be unstable during processing, which causes sedimentation and changes in texture. They also develop a gritty mouthfeel and are not heat-stable, limiting their use in products like yogurt that are processed with heat.
Fonterra has found a way to produce heat-stable, denatured whey protein compositions that address these challenges. These compositions contain tiny particles that create a smooth, homogeneous texture and exceptional stability in yogurt. This process also enhances the functional properties of whey proteins, making them ideal for high-protein applications in yogurt without compromising sensory attributes.
The company has already invested in state-of-the-art manufacturing facilities, such as its plant in Sri Lanka. This facility’s high-tech equipment, like the form-fill-seal (FFS) machine, enables efficient and hygienic production of yogurt cups. This facility allows Fonterra to produce 10 million servings of yogurt monthly. This new yogurt enhancement technique could fit into their Anchor product brand.
Newer, Simplified Processes for Whey-enriched Yogurt
Lactose intolerance is widespread, driving the demand for lactose-free dairy products. Traditional Greek yogurt production involves filtering whey, which complicates the process and leads to resource wastage. The current methods struggle to meet this demand while ensuring product consistency and quality.
A patented invention from Namyang Dairy Products addresses this issue. It’s a production method that integrates whey protein concentrate (WPC) to enhance the nutritional profile of lactose-free Greek yogurt. It also provides a creamy, thick texture while maintaining the lactose-free attribute.
This method optimizes the ingredient ratios for the desired protein content and consistency. It also simplifies the production process by eliminating the need for whey separation. It combines lactose hydrolysis and fermentation in a single streamlined step, increasing efficiency.
Namyang has been a household name in South Korea’s dairy industry for decades. The company already makes various yogurt products, such as its popular “Io” yogurt, which is known for its quality and taste. The company has multiple high-tech factories across South Korea, including a key facility in Sejong City. It’s well-equipped to use this new process to enhance its yogurt products.
Enhancing Whey Protein Retention in Yogurt Production
The problem in yogurt production lies in optimizing the retention of whey proteins while maintaining high product yield and quality. Traditional methods involve adding phospholipase enzymes directly to milk, which results in residual enzymes in the whey. This leads to challenges in processing, as the presence of these residual enzymes can interfere with both the quality of the yogurt and the nutritional value of the whey. Additionally, excess enzymes can affect the texture and stability of the final yogurt product.
CHR Hansen‘s innovative method involves adding phospholipase enzymes to cream or whey cream instead of directly adding them to milk. This method helps keep more fat and protein in dairy products, like yogurt, while making the leftover liquid (whey) high-quality. Adding enzymes to the cream or whey cream (instead of the main dairy mix) leaves fewer traces of the enzymes in the final product. This means the proteins in the whey are preserved better and don’t break down as much.
This process boosts the amount of yogurt made. It includes a second heating process (pasteurization) to break down leftover enzymes, improving the yogurt’s texture and enhancing its nutritional value.
CHR Hansen constantly innovates in such aspects and patents most of its work. The company currently holds 1239 granted patents among 2972 global ones. Insights by GreyB have details on their filing trends, dominant markets, and how many competitors’ inventions were shut down due to CHR Hansen’s patents. Find out more here.
Regulatory challenges to foresee in this trend
Novel Ingredient Approval & Classification:
These innovations may fall under novel food or food additive categories in many regions, including the EU and the FDA. These ingredients and processes require safety assessments, efficacy testing, and approval before marketing.
GMO and Enzyme Regulations:
Using genetically modified whey proteins or enzyme-based treatments (such as CHR Hansen’s method) may trigger scrutiny under GMO regulations, especially in markets with strict laws like the EU. This involves additional testing, labeling, and consumer notifications related to GMOs and enzymes.
Lactose-Free Claims & Allergen Testing: Given the widespread lactose intolerance and demand for lactose-free products, manufacturers must ensure their claims meet regulatory standards. In addition, whey protein-based yogurt products may face allergenicity concerns due to the presence of dairy proteins, requiring comprehensive testing and appropriate labeling to avoid allergen risks.
Labeling and Marketing Restrictions:
According to regulatory standards, “high-protein” or “lactose-free” terms must be carefully substantiated. For instance, high-protein claims must meet minimum protein content thresholds established by regional food authorities (e.g., EFSA or FDA). Moreover, the use of dairy-related terms (e.g., “yogurt”) for products with significant alterations in their composition (like heat-stable or enzymatically treated whey) could be restricted under labeling regulations.
Phospholipase Enzyme Use and Residuals:
CHR Hansen’s method of adding enzymes to cream to improve protein retention can trigger regulatory review regarding residual enzyme presence in the final yogurt product. The safety of residual enzymes will need to be validated through testing to ensure consumer safety and compliance with food safety regulations.
Functional Yogurts with New Microbial Compositions
New yogurt formulations focus on gut health, mental well-being, and immunity enhancement. Companies leverage these innovation trends to position yogurt as a superfood by incorporating specific microbial strains and functional ingredients. These advancements address rising consumer concerns around chronic conditions, stress, and immune support and offer non-pharmaceutical alternatives for well-being.
Enhancing Gut Health With Microbe-Enhanced Yogurt
With the rising prevalence of chronic conditions linked to gut health, such as leaky gut syndrome, consumers seek natural dietary solutions. However, traditional probiotics face challenges in surviving the gastric passage and colonizing the gut effectively, limiting their impact on gut health.
Meiji Co. addresses these issues by incorporating compounds like kojibiose, a form of glucose, into yogurt. These functional sugars significantly enhance the growth of beneficial gut bacteria, improving probiotic efficacy. Beyond supporting bacterial colonization, this composition enhances mineral absorption and intestinal regulation.
Meiji is a powerful player in the yogurt industry in Japan, with a 35.8% market share. Its products, like the Meiji Bulgaria Yogurt, are available in countries like Thailand, China, and Singapore, showcasing its ability to adapt to diverse markets. The company has over 70 years of research in lactic acid bacteria, with a library of over 6,000 strains. This new invention will most definitely boost customer perception of their flagship products.
Boosting Immunity Through Microbe-based Yogurt.
Preventive measures like hand hygiene are insufficient for complete viral protection. Dietary interventions that enhance immunity naturally are needed, particularly for vulnerable populations like the elderly.
Meiji Co. has created a yogurt enriched with a specific strain that causes Immunoglobulin A (IgA) production in your saliva. Salivary IgA is an important antibody that protects your mouth and throat from harmful bacteria and viruses. This bolsters mucosal immunity and fills the gap in immune support strategies.
In addition to enhanced yogurt, more trends are changing the future of probiotics in the food industry. Industry leaders like Danone, Nestle, and Yakult are developing new probiotic formulations and overcoming scientific and production challenges.
You can access the full report immediately using the form below.

Probiotic Research Trends Report
Read The ReportRegulatory challenges to foresee in this trend
Gut Health with Microbe-Enhanced Yogurt:
Functional sugars that enhance gut bacteria growth must comply with novel food regulations and be tested for safety. Claims about improving gut health may be scrutinized unless substantiated by robust clinical trials and evidence.
Stress Reduction with Specific Probiotics:
Probiotic claims related to mental health need to be carefully managed. The connection between gut health and mental well-being is still evolving, so regulatory bodies may require solid scientific backing before allowing such claims on product labels.
Immunity Boosting Through Microbes:
Claims about boosting immunity through specific microbes (e.g., Immunoglobulin A production) must be supported by clinical research. Immunity-related claims are heavily regulated, and companies must comply with local health and safety standards.
Making Yogurt Production Sustainable and Customizable
Yogurt production has traditionally been labor-intensive, requiring careful temperature management during boiling and fermentation. While homemade yogurt remains popular, modern consumers increasingly seek convenience, consistency, and sustainability in yogurt-making solutions. Innovation trends in yogurt are addressing these needs, offering advanced technologies and sustainable practices that cater to consumer preferences.
Advanced Temperature Control Mechanisms to Improve Consistency
Traditional yogurt production at home demands meticulous attention to boiling and fermenting temperatures. This makes the process time-intensive and challenging for consumers. Inconsistent temperature control can lead to uneven quality and texture.
Automatic yogurt makers have simplified home yogurt production with features like heating, cooling, maintaining warmth, timers, and automatic shut-off. Arcelik’s innovative yogurt maker further addresses these challenges by incorporating a dual heating-cooling mechanism.
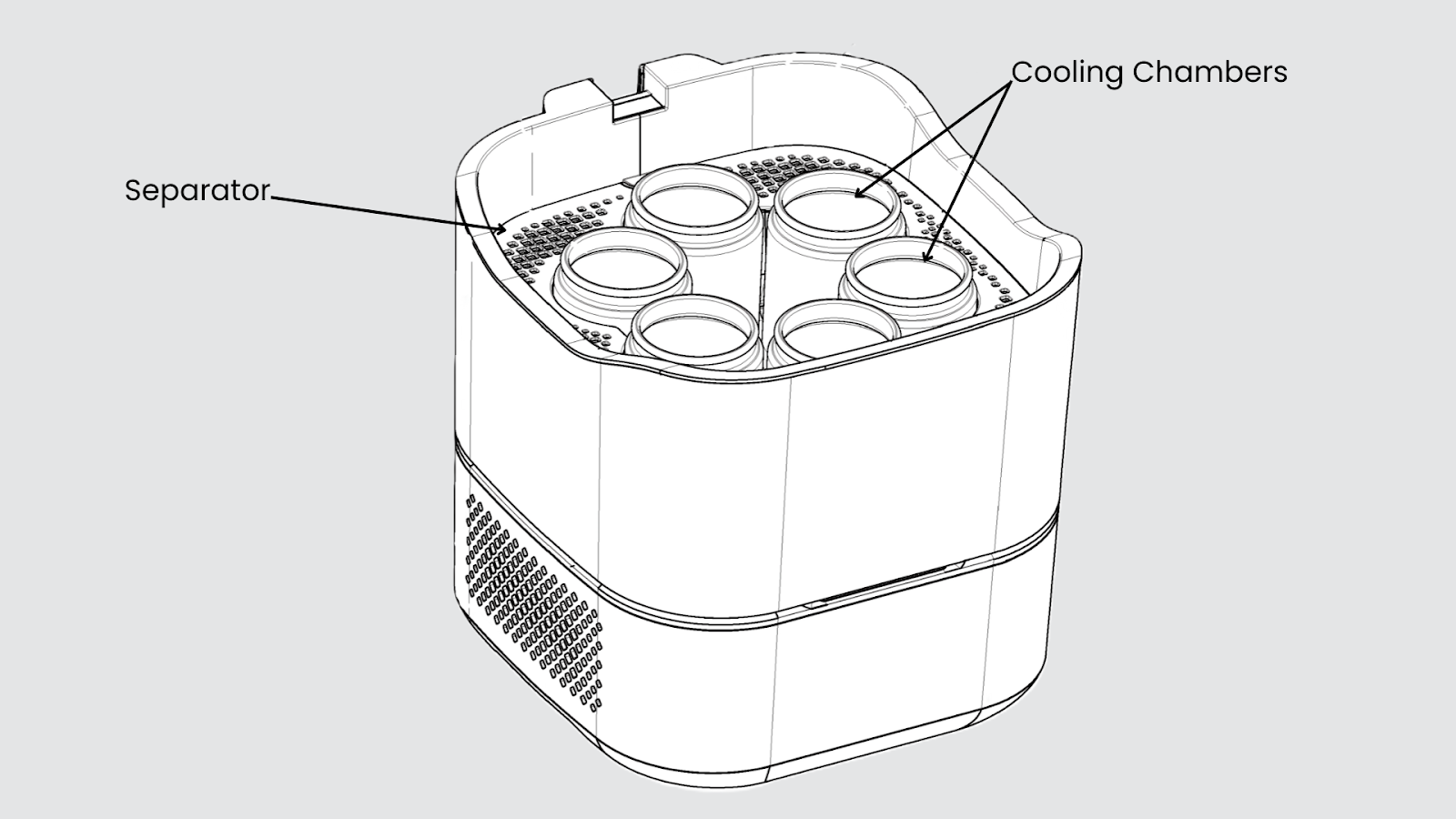
This technology helps evenly distribute heat across multiple containers, ensuring all items maintain the same temperature. The key part is a separator made from a non-heat-conducting material. Because of this, there’s no unwanted heating or cooling interference between the containers, which helps keep the contents consistent in quality.
Making Customizable Plant-Based Yogurts Using Fungal Cells
Plant-based yogurt often lacks complete proteins and essential nutrients, requiring artificial thickeners to achieve a desirable texture and mouthfeel.
Fynder Group’s process of cultivating layers of fungal cells, called bio mats, offers a promising alternative. These bio mats are enriched with essential nutrients like vitamin D2. This makes them a sustainable, protein-rich source, addressing the nutritional gaps in plant-based diets.
This innovation naturally improves yogurt texture and consistency, eliminating the need for artificial additives and supporting customization for diverse dietary preferences, advancing the plant-based yogurt market.
Non-Electric Yogurt Makers with Pressure Mechanisms
Electric yogurt makers consume significant energy, posing sustainability challenges and limiting utility in regions with unreliable electricity.
The Wellness Co. developed a yogurt maker with a mechanical spring-loaded pressing system. This system produces thick, creamy yogurt without any electricity. It efficiently separates whey while maintaining product quality. This durable, energy-efficient setup is ideal for sustainable living practices and regions with limited electricity access.
Regulatory challenges to foresee in this trend
Ensuring Safety and Consistency with Advanced Temperature Control:
While automatic yogurt makers simplify production, regulations around product safety and electrical standards must be met. The dual heating-cooling mechanism, in particular, will require approval for its use in food products, ensuring it does not interfere with food safety or quality.
Novel Food and Nutritional Claims for Plant-Based Yogurts Using Fungal Cells:
Fungal bio mats enriched with nutrients like vitamin D2 must undergo safety and novel food evaluations. The nutritional claims must be substantiated with evidence to avoid misleading consumers, especially regarding their suitability as protein-rich alternatives in plant-based diets.
Compliance with Safety and Durability Standards for Non-Electric Yogurt Makers:
Mechanical yogurt makers must meet safety standards for consumer products, especially those designed for non-electric use. Regulations regarding the safety and durability of non-electric systems and claims around energy efficiency and sustainability will be necessary.
Controlled Fermentation Processes to Enhance Yogurt Production
The yogurt industry continues to evolve as manufacturers address flavor degradation, texture, and digestibility challenges. Innovation trends in yogurt focus on improving its quality by controlling fermentation, reducing sourness, enhancing texture, and ensuring consistent flavor profiles.
New techniques are being implemented to meet consumer demand for healthier, more digestible, and flavorful yogurt options. These include controlled fermentation with specific bacteria strains, sweeteners, and multi-stage fermentations. These advancements improve the product’s sensory attributes and align with evolving market trends in health-conscious and sustainable food choices.
Reducing Gas Formation in Yogurts to Preserve Natural Flavor
Traditional yogurt often suffers from flavor degradation and gas formation during storage. This happens primarily due to citric acid turning into acetic acid. These challenges are amplified by unreliable cold chain logistics in regions with limited refrigeration, leading to inconsistent product quality. Additionally, consumers demand healthier products with reduced sugars and consistent flavor profiles.
CHR Hansen addresses these problems by using specific sweeteners, such as erythritol and xylitol, to delay the conversion of citric acid to acetic acid. It also uses lactose-deficient lactic acid bacteria strains for controlled fermentation, which reduces excessive acid formation.
This process ensures flavor stability, unlike prior methods that relied on post-fermentation corrections. It reduces gas buildup, producing palatable and stable yogurt over time while aligning with consumer preferences for reduced sugars.
No posts found.Refined Fermentation Processes to Control Sourness and Sticky Texture
Traditional yogurt often has a sticky texture, overwhelming sourness, and a lingering aftertaste, making it unappealing to many consumers. These characteristics can deter individuals who prefer a more pleasant, refreshing yogurt experience without the intense sour flavor.
Yuda Milk has a solution in the form of a refined fermentation process. This method improves the quality of yogurt by blending fresh cream with raw milk at different temperatures and carefully managing the acidity. By monitoring the pH levels throughout fermentation, the yogurt avoids becoming too sour while retaining its pleasant aroma.
The method also uses a ventilated fermentation system, ensuring that heat is distributed evenly. This encourages the activity of lactic acid bacteria, which improves the texture, making it firmer and more enjoyable to eat. Overall, this technique ensures a high-quality product with enhanced taste and consistency.
Varying Temperatures to Control the Fermentation Process
Traditional yogurt, particularly Greek yogurt, often suffers from excessive sourness and may not be gentle on the stomach and intestines, limiting its appeal to sensitive consumers.
This patent showcases an interesting multi-stage fermentation process designed to enhance the yogurt’s taste and texture while maintaining its health benefits. The process involves a controlled fermentation sequence at three specific temperature stages:
- 40°C for 3 hours,
- 33 to 37°C for 3 hours,
- Finally, at 30°C for 2 hours.
This gradual temperature adjustment prevents excessive sourness while promoting nutty and soft flavor profiles. After fermentation, the yogurt undergoes a maturation stage at refrigerated temperatures for 24 hours, further refining the texture and preventing additional sourness. This method reduces sourness and improves the overall flavor and texture of the yogurt, providing a balanced and gentler option for consumers looking for a healthier, more digestible yogurt.
Regulatory challenges to foresee in this trend
Safety and Ingredient Approval for Gas Formation Reduction:
Specific sweeteners like erythritol and xylitol, as well as lactose-deficient lactic acid bacteria strains, may require approval as novel ingredients. These ingredients must meet food safety standards and undergo testing to ensure they don’t pose risks to consumers, especially when used in controlled fermentation processes.
Novel Fermentation Methods for Flavor and Texture Control:
Yuda Milk’s refined fermentation process and CHR Hansen’s controlled fermentation techniques must comply with food safety regulations. Claims related to improved texture and reduced sourness need to be backed by data showing the methods’ consistency and effectiveness across different production batches.
Temperature-Controlled Fermentation Compliance:
The multi-stage fermentation process involving specific temperature stages may need validation to ensure it meets food production standards. Additionally, using temperature control methods in fermentation must meet food safety and hygiene regulations to prevent bacterial contamination or product degradation.
Conclusion
The yogurt market is evolving rapidly due to innovation trends in fermentation, plant-based alternatives, and functional ingredients. New technologies, like fungal biomass and mycoprotein, enhance plant-based yogurts’ texture and nutritional value, addressing the demand for allergen-free and sustainable options.
Probiotics and immunity-boosting ingredients are gaining popularity, especially among health-conscious consumers. Industry leaders must adopt sustainable production practices and innovative technologies, leading to personalized, health-focused yogurts that meet diverse wellness needs.
However, finding promising inventions like the ones above for commercial use is difficult. Using standard search engines on the internet, industry leaders must cut through a lot of market noise to identify actual innovations with proven potential. Technology scouting tools, like Slate, will speed up this process.
Find patent-backed inventions from leading companies and startups in a single dashboard, reducing time spent browsing scattered sources. Try Slate by filling out the form below and see where the innovation trends in the yogurt industry are headed!