The first article covered the features that distinguish 5G from its predecessors, as well as the new technologies it incorporates. In the second article, its application areas in various domains have been discussed. Given its extensive application areas, one wonders: Which companies are conducting research on 5G?
Recognizing a shared interest, the team delved deeper into the topic, their curiosity piqued by the sheer volume of data on 5G research. Anticipating similar inquiries and aiming to save valuable time, they meticulously compiled a summary of research activity, partnerships, agreements, and mergers and acquisitions (M&As) undertaken by key players in the field. This comprehensive resource eliminates the need for days of independent research.

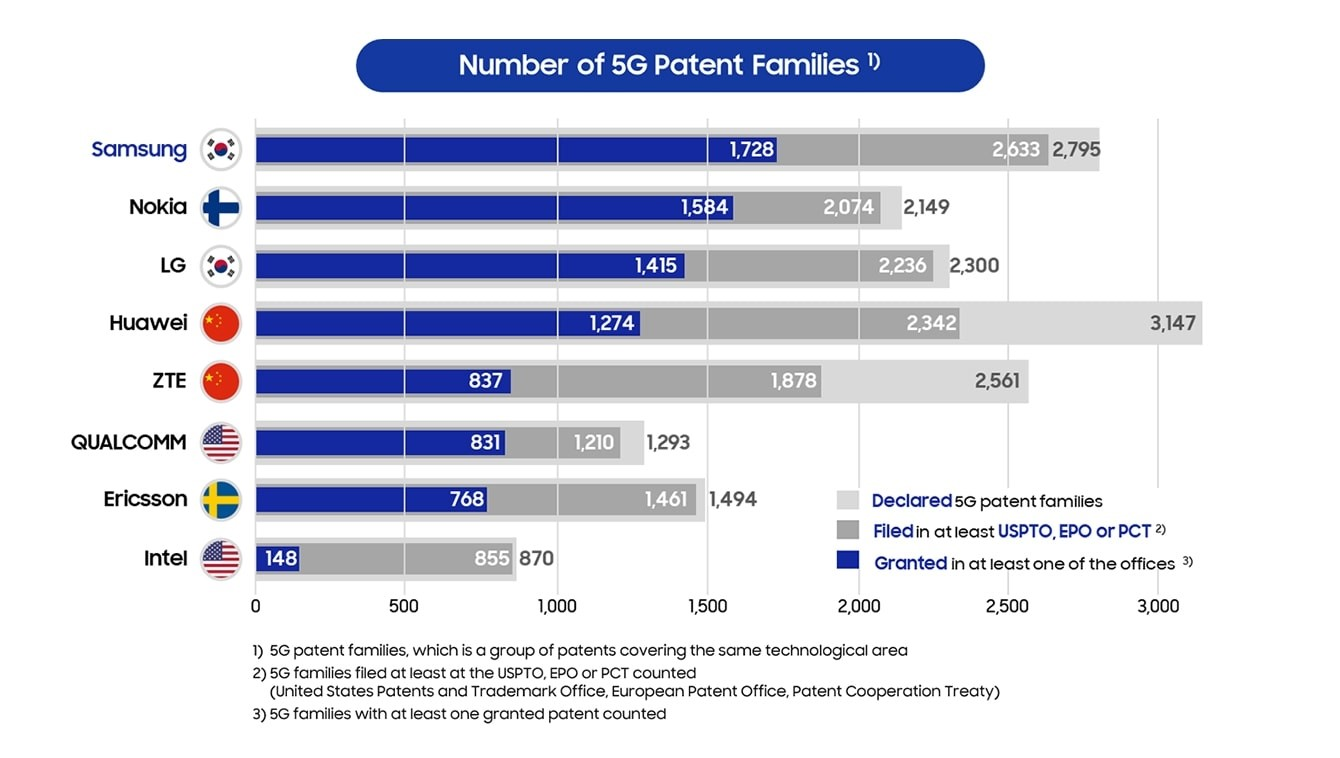
The top 5G companies leading the research are Samsung, Huawei, Nokia, LG, Ericsson, and Qualcomm. Other players that are providing 5G solutions to industries and individuals.
1. Samsung Electronics (South Korea)
Samsung started researching 5G technology in 2011. In 2013, Samsung successfully developed the world’s first adaptive array transceiver technology operating in the millimeter-wave Ka bands for cellular communications.
The new technology sits at the core of the 5G mobile communications system, providing data transmission several hundred times faster than current 4G networks. The company has achieved significant advancements in next-generation technology and can now be considered a leader in the 5G domain.
Here is the journey of Samsung’s achievements in 5G technology and its collaborations to be the top 5G player.
2016
- In March 2016, Samsung demonstrated the World’s first mmWave Multi-cell handover. A vehicle traveling 25 kilometers per hour could move between three transmitters, maintaining a gigabit data transmission. Samsung’s approach to 5G uses adaptive beamforming technology to tightly focus the radio waves into a beam targeted at each user’s device.
- In June 2016, Samsung announced the development of breakthrough 5G-ready antenna and power amplifier technologies, enabling smaller and more energy-efficient 5G equipment and devices. The new technologies were intended to be applied to 5G base stations and end-user devices using the 28 GHz mmWave spectrum.
- In September 2016, Samsung Electronics successfully conducted a 5G trial in China and also received certification from the China Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) based on its successful completion of phase 1 of the 5G Technology R&D Trial executed by the IMT-2020 (5G) Promotion Group at PT/EXPO CHINA 2016.
- In November 2016, Samsung Electronics successfully conducted a 5G prototype trial in conjunction with the China Mobile Research Institute (CMRI), marking a significant milestone in the cooperation between the two companies, which began when Samsung joined the China Mobile 5G Innovation Center in June 2016.
2017
- In February 2017, Samsung announced the new RFIC at a 5G mobile technology workshop held at the Korean Institute of Science and Technology Information. The company presented details on the development and strengths of the chip, outlining its role in the roadmap to commercial 5G products. The RFIC itself is designed to greatly strengthen the overall performance of 5G access units (the 5G ‘base station’). Samsung strongly emphasizes designing for low cost, high efficiency, and compact form factors.
- In February 2017, at a press conference at the Palau de Congressos de Catalunya, Samsung Electronics unveiled its end-to-end portfolio of 5G mobile network products and solutions for 2017. Showcased products included consumer devices for fixed wireless access connectivity, a 5G Radio Base Station (5G Access Unit), Next-Generation Core Network infrastructure, and more.
- In June 2017, SK Telecom and Samsung successfully completed a trial to deliver a 5G end-to-end connection based on 5G New Radio (NR) technology. The trial represented the successful case of a 5G end-to-end connection, using the 3.5GHz spectrum, through virtualized core, radio, and device based on 5G NR technology. The event took place at Samsung’s R&D center in Suwon, featuring Samsung’s 5G virtualized core.
2018
- On January 3, 2018, Verizon announced they selected Samsung Electronics America to supply the telco with commercial 5G Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) network solutions. The two companies planned to launch commercial 5G services in Sacramento, California, in the second half of 2018.
- In February 2018, Samsung developed the world’s first complete commercial 5G FWA solutions, which include: commercial form-factor 5G home routers (CPEs) for both indoors and outdoors, a 5G Radio Access Network (RAN) comprised of a radio access unit and virtualized RAN, a next-generation core, as well as AI-powered 3D radio frequency planning tools and services.
- On February 26, 2018, Samsung Electronics America, Inc. announced at Mobile World Congress that Sprint has purchased 5G-ready massive MIMO solutions from them, which include the deployment of Samsung’s latest MIMO technology solutions on Sprint’s 2.5GHz TDD-LTE network.
- In March 2018, KDDI and Samsung announced the successful completion of a 5G field trial held in Okinawa Cellular Stadium, a 30,000-person capacity baseball stadium in Japan. Using Samsung’s 5G end-to-end solutions spanning virtualized core, virtualized RAN, one of the smallest 5G access units, and multiple prototype 5G tablet devices, the trial showcased a live feed of 4K video contents downloaded. It streamed simultaneously on 5G tablets supporting the millimeter-wave spectrum. This was the first time 5G performance was tested using multiple 5G devices in Japan.
- In July 2018, Samsung and Cisco successfully completed a friendly-user trial and series of 5G demonstrations with Orange in Floresti, Cluj, Romania. The trial used Samsung’s 5G solutions, including the virtualized RAN, one of the smallest 5G access units, multiple indoor and outdoor 5G routers (CPE), and Cisco’s Meraki Z3 WiFi Router and Ultra Gateway Platform.
- In July 2018, Samsung and Mobile TeleSystems (MTS), Russia’s largest telecommunications operator and digital services provider, used Samsung’s 5G network and devices to successfully demonstrate a series of 5G scenarios, including HD video calls, ultra-low latency video games, and high-definition video streaming. The demonstration zone was set up in the Popov Central Museum of Radio Communications exhibition hall, one of the world’s oldest science and technology museums in St. Petersburg.
- In July 2018, Samsung and SK Telecom successfully demonstrated their 5G Next-Generation Core (5G NC) based on 3GPP Release-15 standards. The 5G NC developed by the two companies operates independently of an LTE network, enabling previously unavailable features.
- In September 2018, AT&T announced that it had selected Samsung Electronics America and CommScope to supply the company with its first 5G-ready Citizens Broadband Radio Service(CBRS) network solution. Samsung would provide CBRS-compliant radios and base station equipment, while CommScope was selected as the Spectrum Access System (SAS) provider.
- In September 2018, Samsung Electronics America, Inc. announced that their 5G-ready massive MIMO solutions on Sprint’s 2.5 GHz TDD-LTE network are now in commercial service. As part of Sprint’s network, Samsung’s massive MIMO solutions deliver improved 4G LTE throughput and capacity to Sprint’s subscribers.
- On Sept. 12, 2018, Verizon and Samsung announced the world’s first successful data transmission using 800 MHz bandwidth of 28 GHz frequency, resulting in a maximum throughput of close to 4Gbps. The test took place in Samsung’s Dallas, TX lab.
- In September 2018, Samsung Electronics America, Inc. announced its support of Verizon’s 5G Home service, which will provide 5G broadband Internet service to consumers in Los Angeles, Sacramento, Houston, and Indianapolis. Verizon’s 5G broadband Internet service is the world’s first 5G commercial network. Samsung’s FCC-certified 5G solutions supported the service.
- On September 17, 2018, Samsung Electronics announced that SK Telecom had selected it to supply the company with 5G solutions, including core and RAN, compliant with the 5G New Radio (NR) standard based on 3GPP Release 15.
- In December 2018, Samsung Electronics America, Inc., Qualcomm Technologies, and Verizon announced a successful 5G New Radio (NR) data connection using 400 MHz of bandwidth in the 28 GHz spectrum, resulting in maximum throughput of more than 1.7 Gbps. The data connection demonstrated the delivery of multi-gigabit 5G speeds to a smartphone form-factor mobile test device, focusing on how users can experience a virtually seamless, uninterrupted data transmission using 3GPP 5G NR specification and dual connectivity (known as EN-DC).
2019
- In January 2019, Samsung and KDDI announced they had successfully completed a 5G test with real-time transmission of 4K ultra-high-definition (UHD) surveillance video on a train platform, the first in Japan.
- On February 22, 2019, Samsung successfully completed the development of its cutting-edge mmWave Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits (RFICs) and Digital/Analog Front End (DAFE) ASICs, supporting 28 GHz and 39 GHz bands. Using the new RF chipsets, Samsung is reducing the size, weight, and power consumption of its 5G base stations by approximately 25 percent while continuing to lead the industry. As of February 2019, Samsung has shipped over 36,000 5G base stations.
- On February 24, 2019, For the first time ever on display, Samsung showed its new Galaxy S10 5G mobile phone, designed with the best hardware and software to take advantage of the full 5G experience. Also on display is a full spectrum of equipment that enables wide-scale 5G deployment.
- On February 25, 2019, Samsung, Cisco, and Orange unveiled two promising industrial 5G applications – a drone and an industrial robot- at the MWC 19 in Barcelona. This was the first time the three companies demonstrated the 5G-equipped devices at the exhibition. These companies have stepped up their 5G efforts by piloting drones and industrial robots, leveraging the low latency and high speed that 5G offers.
- On September 4, 2019, Samsung Electronics announced its latest mobile processor, the Exynos 980. The new chipset combines best-in-class connectivity with an integrated 5G modem and intelligent processing performance in a single chip.
- On Oct 22, 2019, Samsung Electronics announced its new 5G New Radio Access Unit supporting the 28GHz spectrum. This new AU combines radio, antenna, and digital units into one compact box, making it the industry’s first integrated radio for mmWave spectrum, compliant with the 3GPP NR standard.
- On November 15, 2019, Samsung Electronics announced the successful integration of a cloud-native 5G standalone (SA) Core with Hewlett-Packard Enterprise (HPE) and Openet. It represents a significant milestone and demonstrates substantial progress toward 5G SA.
2020
- On Feb 15, 2020, Samsung said it is pouring resources into its telecom network equipment business, aiming to capitalize on the security fears hobbling China’s Huawei. As per Samsung, potential companies have started noticing Samsung’s efforts to reinvent itself as a top-tier supplier of 5G networks and close a big gap with 5G leaders such as Huawei, Ericsson, and Nokia.
- On Mar 20, 2020, Zhilabs announced the introduction of NetLiner, a new product providing mobile operators with real-time end-to-end network insights to take customer experiences to the next level and enable automated network operations in 5G networks.
- On April 14, 2020, Samsung Electronics announced that it had achieved the industry’s fastest 5G speeds in a demo by combining 800 MHz of mmWave spectrum with Multi-User MIMO technology. In two mobile devices, it achieved appx. 4.3Gbps speeds on each, with an industry peak speed of 8.5Gbps on both devices.
- On Apr 16, 2020, Samsung announced that it would use Xilinx, Inc., the leader in adaptive and intelligent computing, Versal™ adaptive compute acceleration platform (ACAP) for worldwide 5G commercial deployments. Xilinx Versal ACAPs provide a universal, flexible, and scalable platform that can address multiple operator requirements across multiple geographies.
- On May 18, 2020, Samsung said that the Galaxy A Quantum would have the world’s first 5G smartphone with a quantum random number generator (QRNG) chipset. The new chipset is developed by SK Telecom’s subsidiary ID Quantique which ensures better mobile communication security by generating random numbers based on quantum crypto technology, which creates strong keys that are not biased and cannot be predicted.
2021
- In 2021, Samsung introduced the C-Band/CBRS Dual-band 16T16R Massive MIMO Radio. The new radio is the first to support C-Band and Citizens Broadband Radio Service (CBRS) frequencies in one device. This gives mobile operators a ‘one-box’ solution and makes it easier to support two mid-band spectrums crucial to network evolution and 5G expansion.
- In 2021, Samsung, along with KT Corporation, established Korea’s first commercial 5G SA network. Since the successful launch, Samsung and KT have tested 5G SA in KT’s key offices and metropolitan locations. For this commercial launch, Samsung offered KT end-to-end 5G network solutions from Radio Access Network (RAN) to Core.
- In 2021, Samsung launched its new chipsets, which make 5G networks perform faster and use less power. They were also helpful in the reduction of the overall size of the next-generation 5G RAN (Radio Access Network) solutions. The chipsets included a second-generation 5G modem SoC, a third-generation mmWave RFIC (Radio Frequency Integrated Circuit), and a DFE-RFIC (Digital Front End-Radio Frequency Integrated Circuit). Samsung’s 5G network infrastructure such as Massive MIMO radios, baseband units, and 5G Compact Macro, uses these chips. The new chips satisfied the 3GPP’s Release 16 standards.
Partnerships and Collaborations
2015 – 2019
- In June 2015, Samsung partnered with Korean telecommunications operator LG U+ to jointly develop 5G technology to strengthen both companies. The agreement also enhanced Korea’s global leadership in 5G research and helped drive the creation of standards for the next major phase of innovation in mobile telecommunications.
- In Nov 2015, Samsung signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) to develop common views on next-generation 5G technologies with Japanese telecommunications operator, KDDI.
- In Feb 2016, Samsung Electronics and Deutsche Telekom showcased the world’s first end-to-end 5G demonstration at Mobile World Congress 2016. During the live demonstration, Samsung, one of Deutsche Telekom’s 5G partners, introduced its 60GHz mmWave small cell solution and handheld smartphones. The 4K UHD video contents were transmitted over the air without any delay by the Ultra High Mobile broadband (U-MBB) service using Samsung’s 60 GHz radio access technology.
- In September 2016, Samsung Electronics America announced its collaboration with T-Mobile US on new demonstrations and lab tests designed to bring the power of 5G mobile networks to the masses. Through this collaboration, the companies assess next-generation network development in real-world mobile use cases and applications and conduct lab and field trials demonstrating various innovative 5G-driven capabilities.
- In February 2017, Samsung and Verizon completed the deployment of 5G systems in five U.S. cities in preparation for beginning customer trials of 5G technology.
- In February 2017, KDDI, a Japanese telecommunications company, and Samsung Electronics successfully completed a 5G handover trial. It’s Japan’s first-ever 5G multi-cell handover test using the 28 GHz spectrum to be conducted in a real outdoor environment on Tokyo’s metropolitan expressway amongst towering skyscrapers.
- In February 2017, Samsung Electronics and Arqiva, a leading UK communications infrastructure, announced an agreement to conduct the United Kingdom’s first 5G trials focusing on Fixed Wireless Access. The trial deployment demonstrated the potential for 5G to serve as a compelling alternative to fiber deployment for delivering fast broadband services as a lead-in to future 5G enhanced mobile broadband services.
- In February 2017, Samsung and Keysight Technologies, Inc announced their technology partnership on 5G development and testing. Samsung and Keysight entered into a technology collaboration to enable the design and deployment of 5G devices to support early operator trials. The initial focus of the partnership is on 5GTF specifications (www.5gtf.org ).
- On February 27, 2017, Samsung and Deutsche Telekom successfully showcased 5G Guaranteed Latency (GLA) as an end-to-end network slice at Mobile World Congress (MWC) 2017. GLA is one of the key differentiators that clearly distinguishes 5G technology from the previous 4G. It is viewed as highly critical for the 5G era, as it enables latency control, low and stable, according to the requirements of specific use cases.
- In September 2017, Samsung Electronics America, Inc. and Charter Communications, Inc. announced a collaboration on 5G and 4G LTE wireless networks lab and field trials at various locations in the U.S. The 5G trial evaluated fixed use cases using Samsung’s pre-commercial 28 GHz (mmWave) system and devices. The 4G trials were performed at 3.5 GHz (CBRS), utilizing Samsung’s combined 4G LTE small cell technology in an outdoor environment to evaluate mobile use cases.
- In February 2018, KT, Verizon, and Samsung joined to demonstrate Samsung 5G solutions and use cases, including a prototype 5G tablet device and a successful live video call conducted over 5G between Minneapolis and Seoul during a sponsored sports event.
- In February 2018, Orange, Samsung, and Cisco announced a collaboration on a 5G millimeter wave trial across multiple homes in Romania. The trial marked Orange as the first operator to conduct a multi-vendor 5G fixed wireless access (FWA) customer trial in Europe.
- In September 2018, Telefónica Deutschland and Samsung Electronics agreed to run 20 Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) trials in Germany. Samsung will support the set-up of the trial with a complete end-to-end millimeter wave (26 GHz) solution. The combination of newly developed hardware technology with special software enables fast transfer rates of several Gigabits per second across the so-called “last mile.”
- On October 24, 2018, NEC Corporation and Samsung announced a partnership of joint effort to strengthen their next-generation business portfolio, including 5G. The partnership combines the best-in-class technology and expertise in 5G, merging NEC and Samsung’s leadership in 5G and IT solutions.
- On December 6, 2018, Samsung Electronics announced that it had signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the Korea Transportation Safety Authority (KOTSA) to collaborate on next-generation telecommunication technology to enable autonomous driving innovation across the country. Through the partnership, both entities will build 4G LTE, 5G, and Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) telecommunication networks and related IT infrastructures at K-City, a testbed for autonomous driving technology in Korea.
- On February 19, 2019, Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) and Samsung Electronics announced a collaboration to jointly provide solutions that help communications service providers (CSPs) accelerate 5G deployment. With this collaboration, HPE and Samsung will combine their strengths in edge-to-core infrastructure, data management, and radio networks to provide end-to-end solutions that enable a fast and smooth 5G transition.
- On February 22, 2019, Samsung and Fastweb announced an agreement to conduct Italy’s first 5G Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) trial on the commercial spectrum. Companies are trialing to demonstrate how 5G FWA networks could serve as a compelling alternative to FTTH (Fiber-to-the-Home) to deliver ultra-broadband connectivity and gigabit experience to end-users.
- On October 30, 2019, Samsung Electronics announced a collaboration with IBM leveraging IBM’s Cloud and AI capabilities and Samsung’s mobile devices. “The mobile industry is undergoing a dramatic transformation and opening up new ways of business by bringing innovative technologies like 5G, AI, and IoT to enterprises,” said DJ Koh, President and CEO of the IT & Mobile Communications Division, Samsung Electronics.
2020 – 2022
- On 13 January 2020 – At CES 2020, Samsung announced a partnership with BMW to showcase new approaches to create future mobility experiences with the world’s first commercialized 5G TCU (Telematics Control Unit). BMW announced that 2021’s BMW iNEXT would be the first car in the world to be equipped with 5G technology from Samsung and HARMAN.
- On Feb 21, 2020, Samsung announced a commercial agreement with U.S. Cellular for 5G and 4G LTE network solutions. The new agreement establishes terms under which U.S. Cellular can purchase Samsung’s commercially-proven network solutions, including 5G New Radio (NR) technology, to help U.S. Cellular deliver next-generation service.
- On Mar 3, 2020, Samsung Electronics announced that it is extending its collaboration with Marvell to encompass infrastructure innovations across additional Radio Access Network segments (RAN) segments. Marvell and Samsung have worked closely to deliver multiple generations of market-leading baseband and transport processing solutions for base stations based on Marvell’s OCTEON® and OCTEON Fusion® processors.
- On Mar 4, 2020, Samsung announced an agreement with Spark, New Zealand’s largest mobile carrier, to build Spark’s 5G networks in 2020. Spark has been doing 5G trials with Samsung since 2019 that used Samsung’s 5G end-to-end solutions to test and verify the potential of next-gen network technology.
- On April 21, 2020, Samsung announced a partnership with Xilinx to optimize the functionality of the latter’s new 5G gear. Samsung will utilize Xilinx’s Versal adaptive compute acceleration platform (ACAP) to improve the signal processing quality of its 5G mobile data network equipment.
- In 2021, Samsung Electronics and Ciena® teamed up to market 5G network solutions. With this agreement, Samsung will be able to combine its 5G technologies with Ciena’s xHaul solutions aiding the next generation of high-bandwidth applications and services that will be needed as 5G networks grow.
- In 2022, Samsung Electronics America, Inc. and Kajeet announced a partnership where Kajeet’s Smart Private 5G™ Platform and Samsung’s Citizens Broadband Radio Service (CBRS) technologies will be deployed together. This deal made Kajeet a U.S. Samsung private RAN distributor. Both firms will work together to rapidly deliver novel and adaptable 5G-ready solutions bringing next-gen solutions to a range of companies and government agencies.
- In 2022, Samsung Electronics America and Amdocs collaborated to offer U.S. companies 4G and 5G private network solutions. This will assist companies in major industry sectors such as education, utilities, manufacturing, logistics, transportation, and retail use of next-gen communications applications and services. The collaboration calls for Samsung to offer its full set of private network solutions to support private network and Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) use cases.
Acquisitions
On October 17, 2018, Samsung Electronics announced its acquisition of Zhilabs, known for its Artificial Intelligence (AI)-based network and service analytics, to enhance its 5G capabilities further. The acquisition lays the foundation for Samsung to foster its 5G offerings of automation and network analytics to fine-tune the customer experiences in the 5G era.
Government Deals
In 2022, Samsung announced that it would partner with three key Korean government organizations to deliver a wide range of solutions for private 5G networks.
- Korea Electric Power Corporation – To improve workplace safety and efficiency, Korea Electric Power Corporation will adopt smart grid technology and develop digital twins. The digital twin will remotely monitor and assess the workplace to enhance worker safety. Wearable cameras and autonomous robots powered by 5G will also facilitate easier control and monitoring of various sites.
- Korea Industrial Complex Corporation – The Korea Industrial Complex Corporation will put a digital safety platform powered by 5G at different work sites. They will receive assistance from Samsung to establish a robust, AI-based smart monitoring system that detects fire threats and other security concerns in real-time.
- Korea Water Resources Corporation – Korea Water Resources Corporation will develop digital twins to accurately display water flow and anticipate floods. Water purification facilities’ digital twins will simulate the process using AI, enhancing water management and prediction.
Patent Analytic
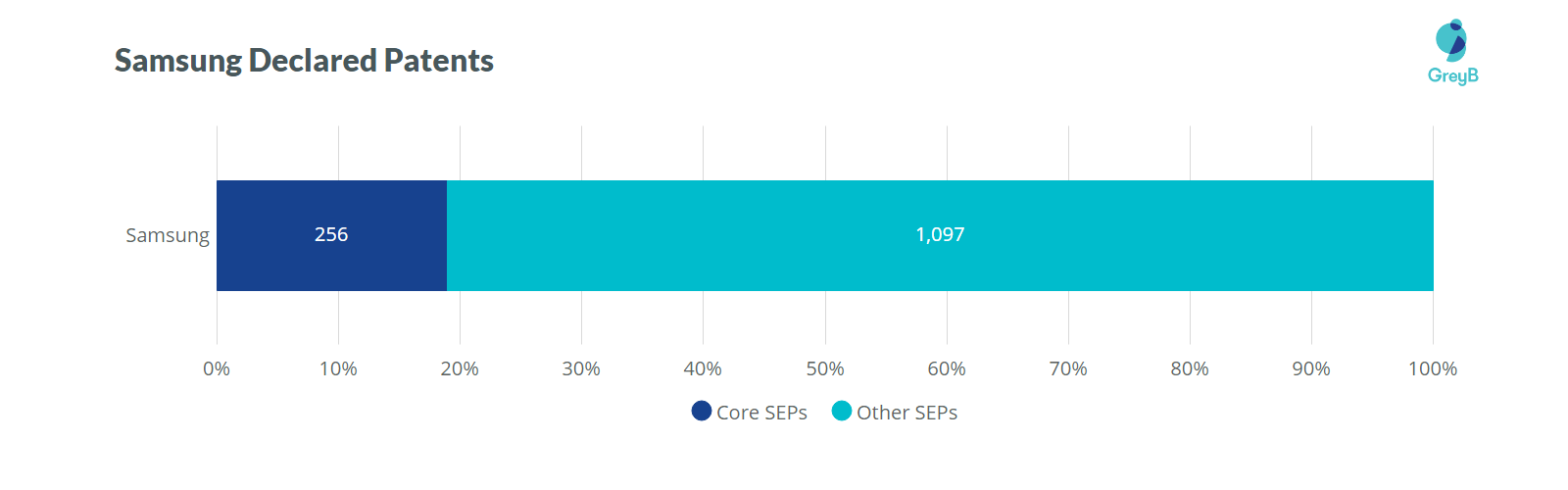
As per Iplytic, Samsung is leading the race for the most declared 5G granted patent families.
Further, Samsung holds the second position in the Core 5G SEPs count, as per the GreyB 5G SEP Report. As of March 31, 2019, out of 1,353 declared patent families, Samsung has 256 Core 5G SEP in its portfolio. However, the 5G declared patents share is just 25% out of 1353 families.
2. Huawei Technologies (China)
Huawei has been investing heavily in researching 5G wireless networks and patenting key technologies. The company has hired experts abroad to decide the technical standards for the next-generation wireless communication technology.
Below are some of Huawei’s major activities in the 5G domain.
2017
- As of early 2017, 10% of 1450 patents essential for 5G networks were in Chinese hands, with the majority belonging to Huawei and ZTE.
- Huawei spent around $12 billion on R&D in 2017, three times the amount Ericsson spent, $4.1 billion. In 2018, it planned to spend $800 million on 5G research and development alone.
- The company aims to integrate AI into 5G, which, according to them, is a more integral element of Huawei’s 5G strategy. The company also plans to launch a full range of Huawei commercial equipment, including wireless access networks, core networks, and devices.
- Huawei has also revealed its hopes to launch smartphones ready to support 5G networks by 2019 and start selling in mid-2019. The company is also said to be working on developing a brand-new chipset for 5G services.
2018
- In February 2018, Huawei and Vodafone made the world’s first 5G call using a non-standalone 3GPP 5G-NR standard and sub-6 GHz spectrum. The two companies constructed a 5G NR end-to-end test network for the trial, utilizing a 3.7 GHz spectrum. They also used Huawei Radio Access Network and core network equipment to support the test with microservice-centric architecture, control plane/user plane separation, and unified access and network slicing technology.
- Huawei also started manufacturing products that provide 5G services. At the 2018 Mobile World Congress, Huawei launched its 5G customer-premises equipment (CPE), the world’s first commercial terminal device supporting the 3GPP standard for 5G. Huawei used its self-developed chipset Balong 5G01 – the world’s first commercial chipset supporting the 3GPP standard for 5G, with a downlink speed of up to 2.3 Gbps.
2019
- In Jan 2019, Huawei completed the 5G NR (New Radio) test at 2.6GHz spectrum in the 5G trial organized by the IMT-2020 (5G) Promotion Group. To date, Huawei officially completed the third phase of the China 5G Technology R&D (Research and Development) Trial, including laboratory and field testing in NSA (Non-Stand Alone) and SA (Stand Alone) scenarios.
- Bell and Huawei have collaborated to provide fiber-like mobile home broadband service across Canada. They are trying to connect dozens of communities and polar tribes in the north with 1.9 million square kilometers through Wireless Fiber 5G technology.
- In Jan 2019, Huawei launched its TianGang chip designed for 5G base stations. The TianGang chip supports all network standards and all 5G bands, including 3.2 and 3.5GHz, and C-bands used by commercial satellites. This chip also supports the integration of active power amplifiers and passive antenna arrays into very small antennas, one of the key building blocks of 5G base stations.
- In Feb 2019, Thailand joined hands with Huawei for the 5G testbed. Despite sustained pressure from the US for not using Huawei equipment, Thailand is doing the exact opposite. It will be the Chinese company’s first testing in Southeast Asia.
- At Mobile World Congress 2019, Huawei introduced the company’s first 5G-enabled foldable smartphone – Mate X, and new Matebooks.
- The company also showcased the HUAWEI 5G CPE Pro, the CPE (Customer Premise Equipment) that provides ultra-high-speed broadband and intelligent Dual-Link features. Huawei 5G CPE Pro supports HUAWEI HiLink protocol – a smart home interconnection platform that offers interconnection and interworking solutions between all types of smart devices.
- Rain teased its 5G ambitions in late 2018, but the company’s CEO, William Roos, officially announced its intentions at Huawei’s MWC 2019 booth on Tuesday. Initially, only those in select areas across Johannesburg can benefit from the network. But Rain and Huawei promise that the network will be rolled out to more metro areas in South Africa as more base stations are built. It will utilize the 3.6GHz spectrum.
- At Mobile World Congress (MWC) 2019, Huawei finally unveiled World’s first 5G foldable smartphone, the Huawei Mate X. The flexible display Android smartphone features the ‘Falcon Wing Mechanical Hinge’ and outward folding screen design, which unfolds to make an 8-inch tablet.
- On Feb 25, 2019, Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd. noted that Saudi Arabia would fully embrace its next-generation 5G infrastructure technology, giving it some rare good news after several months of defending itself against accusations that its gear poses national security risks.
- As reported by ET Tech, Huawei has reportedly said that India can potentially become the second-largest 5G market in the next ten years. Huawei and other partner telecom companies are awaiting the Indian government’s approval on spectrum allotment. This spectrum (3.5 GHz spectrum) band is expected to be the first band to be globally accepted for 5G deployment.
- On March 3, 2019, battling a wave of opposition to its 5G trials from the US and other countries, Huawei, installed three 5G stations in Tibet. The 5G stations are being installed in different parts of China as part of Huawei’s plans to lead the 5G trials.
- On June 7, 2019, Huawei signed a deal to bring super-fast 5G wireless networks to Russia by reaching an agreement with Russia’s top mobile network, MTS. The move signals that the Chinese tech giant isn’t letting its blacklist status in the U.S. bring down its global business.
- On September 6, 2019, Huawei unveiled a new 5G processor for its mobile devices, the Kirin 990 5G chip. The new chipset is directly aimed at competitors like Qualcomm. Huawei said the processor would power its upcoming flagship smartphone called the Mate 30, which will be released later this month in a bid to rival Apple’s expected new iPhones.
- On Dec 2, 2019, Huawei founder Ren Zhengfei shared his wish to build a new factory capacity in Europe to make 5G equipment. The Chinese tech giant also plans to shift research to Canada from the United States, citing an interview with Ren.
2020
- On Apr 28, 2020, Huawei said it is working with chip supplier STMicroelectronics to develop silicon for its mobile and automotive products. The company said it is part of an effort to protect it from broader US trade restrictions.
- On May 15, 2020, Huawei announced that it established an alliance with 18 automakers to build a 5G-enabled automobile ecosphere. The company aimed to accelerate the commercial use of 5G technologies in the industry. According to Huawei, the alliance’s first batch of 18 automakers include First Automobile Group, Chang’an Automobile, Dongfeng Motor Corporation, SAIC Motor Corporation, Guangzhou Automobile Group, BYD Auto, Great Wall Motors, Chery Holdings, and JAC Motors.
- On May 20, 2020, Gan Bin, the Vice President of the Huawei Wireless Product line, revealed that the company apparently built over 200,000 5G base stations in its home countries. He also expects 800,000 bases to be in place by the year-end, covering 340 different cities. The speeds of the data transfer rates are showcasing a tenfold increase of 5G over the previous-gen 4G.
2022
- In 2022, Huawei launched 5GtoX Suite as part of the i-series solution. The solution improves the functionality of toC, toH, and toB services, making it possible to roll out services with more agility while maintaining more consistent quality. It also boosts coverage and network accuracy by 80%.
- In 2022, Huawei and China Unicom Beijing launched the 64T64R MetaAAU in a prototype urban residential neighborhood in Tongzhou District. The 64T64R MetaAAU increased user-perceived rates significantly. This revolutionary solution overcomes deep residential area coverage issues, making building gigabit, high-quality 5G networks easier everywhere.
- In 2022, Huawei and Etisalat UAE, part of e&, successfully tested the cloud-native “5G Edge Computing platform”. Both parties aspire to enable the most creative digital services in UAE. These cutting-edge 5G services support Etisalat UAE’s efforts to speed up 5G monetization and increase consumer value.
Partnerships and Collaborations
- Huawei planned to research 5G-Cloud Applications for Mobile Root Systems. To make it possible, the company joined hands with Festo Didactic Research to remove the challenges in the field of mobile robotics.
- In February 2018, Huawei joined hands with Qualcomm and successfully completed 5G NR Interoperability and Development Testing (IODT) based on the 3GPP global standard.
- In April 2018, Huawei joined hands with China Unicom to develop 5G network slicing technologies.
- In May 2018, Huawei and MTN launched the first 5G trial in South Africa using Huawei’s commercial 5G terminal in conjunction with an existing tower.
- VEON Ltd., formerly known as VimpelCom, also agreed upon a partnership with Huawei for pilot testing and integration of 4.5G and 5G solutions along with IoT.
- Huawei also signed up with an agreement with the University Politecnica de Madrid (UPM) in May 2018 to create HUAWEI-UPM5G Chair, which aims to promote closer ties between the university and the Chinese telecommunications giant.
- In Dec 2018, Migu joined hands with Shanghai Mobile and Huawei to Complete the World’s First Real 4K UHD Live Broadcasting Through 5G Network Slicing. Shanghai Mobile and Huawei set up a 5G network infrastructure and provided slice services to build dedicated channels that feature ultra-high bandwidths and ultra-low latency: a guaranteed experience for 4K UHD video playback.
- Huawei and China Unicom implemented the world’s first remote operation using 5G surgery in Fujian China Unicom Southeast Research Institute. The operation was placed at the China Southeast Research Institute, and the operation signal was transmitted in real-time through 5G technology to perform remote hepatic lobectomy on the experimental animals 50 km away.
- In February 2019, Huawei partnered with China Mobile’s Shanghai unit to launch the 5G Digital Indoor System at Hongqiao Railway Station. The digital indoor system, expected to be deployed by the end of the year, will offer fast 5G network services to all passengers.
- Maxis and Huawei signed a memorandum of understanding (MoU) at Mobile World Congress 2019 in Barcelona to accelerate the deployment of 5G networks in Malaysia. The MoU establishes the beginnings of cooperation between Maxis and Huawei to start full-fledged 5G trials with end-to-end systems and services.
- On Feb 28, 2019, Huawei announced two 5G agreements with VIVA Bahrain and Nova Iceland – at the Mobile World Congress (MWC 2019) in Barcelona. The telecom network maker has revealed that VIVA Bahrain will upgrade its infrastructure based on non-standalone 5G core and 4/5G dual-mode radio and backhauling technologies to offer 5G services across Bahrain by June 2019. Huawei signed an agreement with Nova to conduct 5G testing in Iceland.
- Huawei and Vodafone carried out a connected vehicle demonstration during the 2019 Mobile World Congress event in Barcelona, Spain. German carmaker Audi supported the demonstration, which used cellular vehicle-to-x technology.
- On March 4, 2019, Huawei and Deutsche Telekom announced that they were demonstrating cloud-based “5G” end-to-end network slicing, which included radio access, transport, and core network elements. The demo occurred at DT’s 5G lab in Bonn, Germany.
- In 2022, Huawei signed an MoU for TurkTech 2.0 with Türk Telekom, which includes provisions for working together on 5G. The firms collaborated to work on 5G-ready networks and quality network applications to build industrial 5G applications and strengthen the ecosystem strategically.
- In 2022, Huawei signed an MoU with XL Axiata to build a ‘5G City’. The goal is to develop a smart city with 5G networks while envisioning the future of technology, running networks smartly, and enhancing the user experience. Both 4G and 5G networks will be utilized in the development of the smart city. The two companies are working on green 5G with simplified site solutions, multi-antenna-enabled radio modules, and rural network solutions to enhance coverage in remote locations.
- In 2022, Huawei and Dronetech collaborated on 5G smart farming in Austria. The companies will work to bring new 5G technologies into the agriculture field that can help with sustainability. In addition to 5G services, Huawei will provide cloud computing solutions that will serve as the foundation for AI analysis performed in real time.
Patent Analytics
Both Iplytics and GreyB’s 5G Report show that Huawei is leading with the most declared 5G patents.
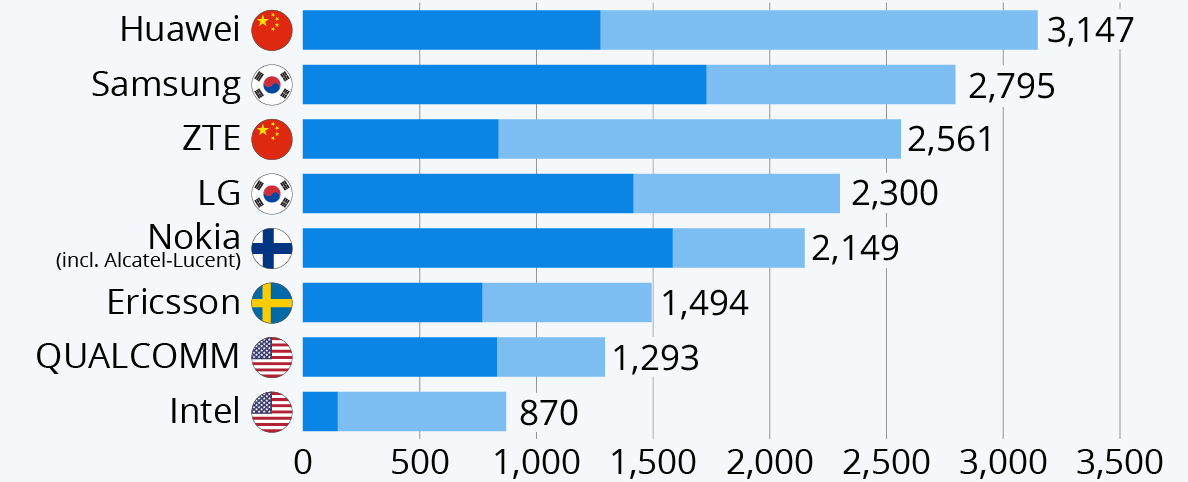
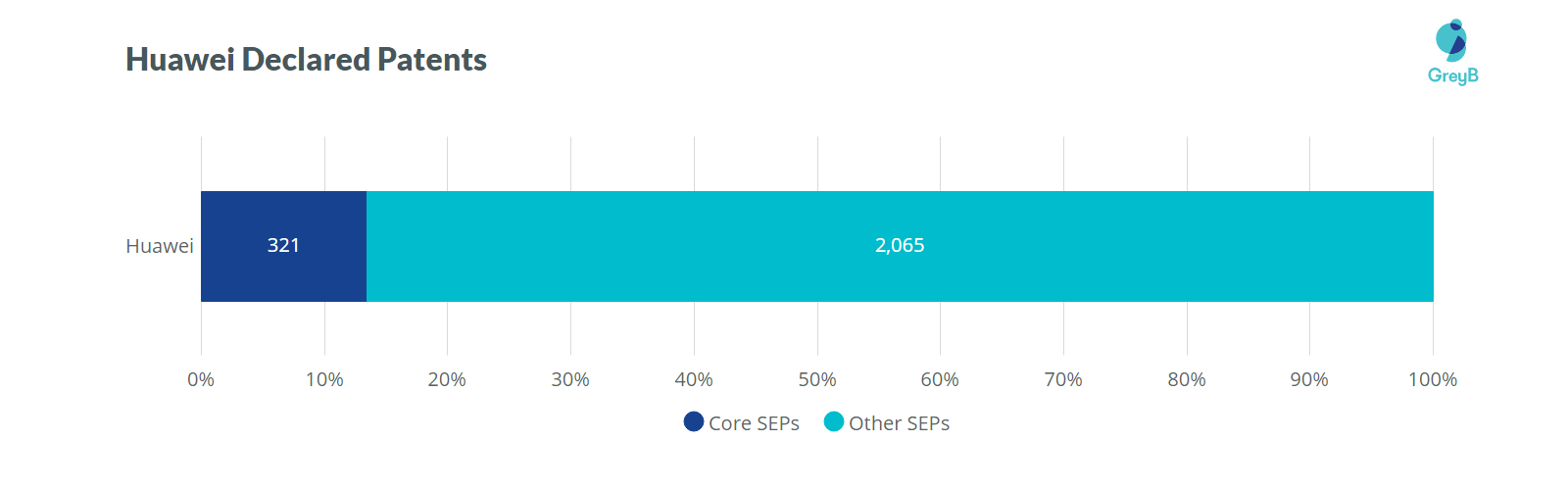
Further, when discussing Core 5G SEPs, Huawei is leading the count with 321 patent families out of 2386 declared patent families as of Mar 31, 2019. Moreover, Huawei‘s 88% of declared patent families belong to 5G.
3. LG (South Korea)
LG has been among the top 5G players in research activities, products, and even patent analytics. In 2019, Bloomberg cited the 5G era as the era of LG as the company managed to ship more than 100K 5G smartphones in the Korean market.
The Korean company has been researching 5G for quite some time and has built a reputation by getting published in many 5G-related reports. LG has a few companies, like Samsung and Huawei, that do not just deploy 5G networks but also build products too which utilize the 5G networks.
Here are some noteworthy research activities and partnerships of LG related to 5G technology.
2018
- On Oct 30, 2018, LG U+ announced that it would use Huawei equipment for its 5G services despite Huawei facing backlash from the US over security concerns. LG U+ used Huawei LTE equipment in the past, so it would be better to choose Huawei for 5G. Otherwise, it needs to replace all the LTE equipment as well.
2019
- On Jan 28, 2019, LG Electronics announced that with KAIST, they opened a 6G research center to lead in next-generation mobile telecommunications. The LG-Electronics-KAIST 6G Research Centre is housed at Daejeon, home to the university’s KAIST Institute research complex.
- On Feb 25, 2019, LG unveiled its first 5G smartphone LG V50 ThinQ at MWC 2019, held in Barcelona, Spain. The company partnered with 10 major telecom operators in the US, South Korea, Australia, and a few European countries, where 5G services were expected to be launched that year.
- On Mar 15, 2019, LG Uplus announced to offer of a wide range of media services to a wider customer base that they gained by acquiring the nation’s No.1 cable operator, CJ Hello, in Feb 2019. The company would speed up the deployment of the 5G network and develop various services to create new business opportunities, CEO Ha Hyun-hoi said.
- On Apr 18, 2019, Operation support systems (OSS) vendor Comarch touted its products in the launch of the LG U+ 5G network in South Korea. Comarch’s Telecom division offers pre-integrated solutions for service monitoring and managing network resources. Its portfolio of products covers things like resource inventory, service inventory, and service fulfillment; integrated assurance and analytics; performance monitoring; and an OSS/BSS data analytics platform.
- On May 6, 2019, LG U+ announced that it would use 5G equipment from Samsung for base stations that will be installed in Seoul. LG U+ has been using Huawei 5G equipment for Seoul and Gangwon Province. Samsung is its main supplier for the remaining areas in the country, while Ericsson and Nokia act as secondary suppliers.
- On Aug 6, 2019, LG U+ announced that it’s working with Syniverse, the world’s most connected company, to offer a 5G roaming service to mobile operators worldwide. As part of this, mobile customers of LG U+ from Korea can access Elisa’s 5G services while traveling in Finland. LG U+ also completed the world’s first commercial testing of 5G roaming in Finland. Elisa Finland’s 5G network is now available for LG U+ customers, and 5G roaming service has been available on this network by LG U+ since July.
- On Sep 30, 2019, It was found that LG U+ adopted a successful 5G strategy through its augmented and virtual reality service portfolio. LG U+ had a 29% 5G market share then, facilitated by a strong focus on AR and VR content.
- On Oct 15, 2019, LG Innotek announced the successful development of a communication module for automotive based on a 5G Qualcomm chip. It is the first company to develop a 5G communication module for automobiles using Qualcomm chips that can be applied to vehicles. The module helps to share real-time traffic information, precise location measurement, V2X communication, and transmission of larger amounts of data. In other words, this module secures the key functions needed for entirely autonomous driving that requires no driver involvement.
- On Oct 18, 2019, LG U+ announced that it selected Ericsson as a 5G radio access network supplier for its 3.5 GHz Non-Standalone (NSA) 5G network. With this contract, Ericsson has commercial 5G RAN contracts with all three major Korean telecom companies. This first 5G RAN contract with LG U+ sees Ericsson deploying 3GPP standards-based 5G New Radio (NR) hardware and software from Ericsson Radio System (part of Ericsson’s 5G platform).RAN deployment got underway in October 2019. Ericsson solutions are going commercially live as they are deployed in the LG U+ network.
2020
- On Nov 7, 2020, during a 5G speed test in Seoul, Incheon, and Busan, the average 5G Download Speed was in excess of 300 Mbps on all three mobile operators – SK Telecom, KT, and LG U+. In Seoul, with 363.7 Mbps, LG U+ had the highest average 5G Download Speed. SK Telecom’s 5G customers also had the highest average 5G Download Speed with 363.7 Mbps. KT users achieved 5G speeds of 329.3 Mbps.
- On Nov 12, 2020, It was found that LG was piloting a next-generation C-V2X platform. Verizon revealed LG Electronics was among a trio of companies testing connected car services on its 5G mobile edge compute (MEC) platform as it expanded the capability to two new cities.
- On Dec 8, 2020, LG U+ deployed South Korea’s first 5G mmWave network using a commercial 5G smartphone with Qualcomm and LG Electronics at the Kumoh National Institute of Technology (KIT). The 5G mmWave network will enable new services for KIT employees, professors, and students, showcasing the technology’s ability to power a “smart campus” model. The smart campus services will be accessible through the LG Uplus 28 GHz 5G mmWave network on a commercial smartphone by LG Electronics, which is powered by the Qualcomm Snapdragon 865 Mobile Platform with the Snapdragon X55 5G Modem-RF System.
- On Dec 18, 2020, LG Uplus and Hanyang University’s automotive electronic control lab and ControlWorks, a self-driving solution company, demonstrated the world’s first 5G-based self-parking in an online news conference on Dec. 17. 5G self-parking is a kind of autonomous valet parking in which a car goes to a nearby parking lot and parks in an empty space on its own. It marked the first time in the world that 5G-based autonomous driving and parking have been demonstrated on roads and in a public parking lot in an uncontrolled environment.
2022
- In 2022, LG Electronics successfully completed testing the wireless transmission and reception of terahertz (THz) data as part of their study toward the development of future 6G networks. The 6G test was conducted at a distance of 320 outdoors at a frequency that ranged from 155 to 175 GHz. The test, conducted at the Fraunhofer Heinrich Hertz Institute (HHI) in Berlin, Germany, is a big step toward making 6G THz commercially available in urban areas.
- The 5G telematics system offered by LG Electronics features an Over The Air (OTA) service that allows for the online updating of vehicle software, a high-precision positioning technology that lowers vehicle location error, and Dual SIM Dual Active (DSDA) technology for premium connected-car and autonomous driving experiences. In the 5G telematics communication module industry, LG got approvals for 10% of the world’s 5G patents. In 2022, LG got orders from European automakers to supply them with 5G telematics parts.
- LG is working on its ‘5G Connected Car Platform’ with Qualcomm Technologies. 5G automotive platforms connect cars to the cloud via Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and C-V2X technologies. 5G platforms link automobiles to base stations for real-time transmission, gaming, navigation, and emergency calls. 5G systems can help develop self-driving cars with minimal latency and ultra-fast connectivity.
Partnerships and Collaborations
- On Jul 30, 2018, LG signed a global patent license agreement with Ericsson to utilize Ericsson’s SEPs across 2G, 3G, and 4G.
- On Mar 22, 2019, LG Uplus Corp. announced an exclusive deal with Nvidia to launch Nvidia’s GeForce NOW cloud gaming platform for Internet Protocol (IP) television services and upcoming 5G smartphones thus, provide access to a rich array of games to its mobile and Internet subscribers.
- On Jun 26, 2019, LG partnered with SK Telecom to commercialize the cloud-based autonomous robots, which will be connected to SK Telecom’s 5G network. Feature updates for the robots will be downloaded across this network. They’ll be used for detecting abnormalities and patrolling for security 24/7 in facilities and warehouses. Quantum cryptography technology will secure the robot service.
- On Aug 20, 2019, LG and Qualcomm agreed to a patent licensing that enables LG to access Qualcomm’s 3G, 4G, and 5F cellular modem technologies for its smartphone business. The agreement is proof of Qualcomm’s consistent global licensing terms and the value held by its world-class patent portfolio.
- On Sep 17, 2019, LG U+ partnered with China Unicom to offer roaming service for its 5G customers traveling in China. The operators began roaming trials in China in June and completed network integration tests in mid-August. And on Nov 20, 2019, LG Uplus teamed up with Viettel to launch a roaming service for its 5G customers traveling in Vietnam.
- On Oct 30, 2019, LG Electronics partnered with chipmaker Qualcomm to develop an in-vehicle infotainment platform for connected cars. Under this strategic partnership, LG Electronics and Qualcomm would develop the automotive platform, which would combine entertainment and information delivery for both drivers and passengers.
- On September 21, 2020, LG U+ partnered with Google to develop 5G mobile edge computing (MEC) technology together. Under the partnership, LG Uplus will work with Google Cloud, which will provide its artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies, to develop new services that utilize MEC on the telecom operator’s 5G network.
- In 2021, LG U+ and KDDI inked an MoU on 5G and 6G. The firms wanted to collaborate on 6G and 5G business applications. As per the terms, the two companies were supposed to share their 5G network technology and solutions and look for other ways to use the latest generation of mobile network technology. In addition, the MOU states that the companies will work together to develop 6G technology.
- In 2021, LG U+, Celcom Axiata Bhd, and Media Prima Bhd collaborated to investigate how local consumers could use 5G content and services combining VR and AR. The purpose of the partnership was to utilize AR/VR and 5G technology to offer digital entertainment material from South Korea as well as local content.
- In 2022, LG U+ and Nokia teamed up to work on 5G and 6G research projects. These research projects will focus on non-terrestrial networks, energy harvesting, open LAN, reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RIS), and more. In addition, the ongoing research on non-terrestrial networks may result in a 6G service being introduced soon.
- In 2022, to expand its 5G service options, LG U+ successfully acquired an extra 20 megahertz of spectrum from the Korean government. LG U+ agreed to purchase the extra spectrum for a price of KRW 152.1 billion.
Patent Analytics
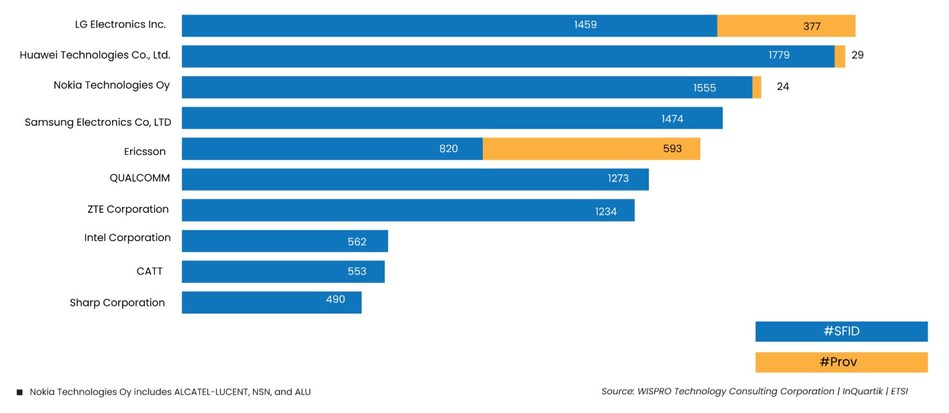
As per Patent law firm Wispro, LG had filed the highest number of 5g applications in the US.
Moreover, LG is also one of the leading companies with 5G standard essential patents, as per GreyB’s 5G Patent Report.
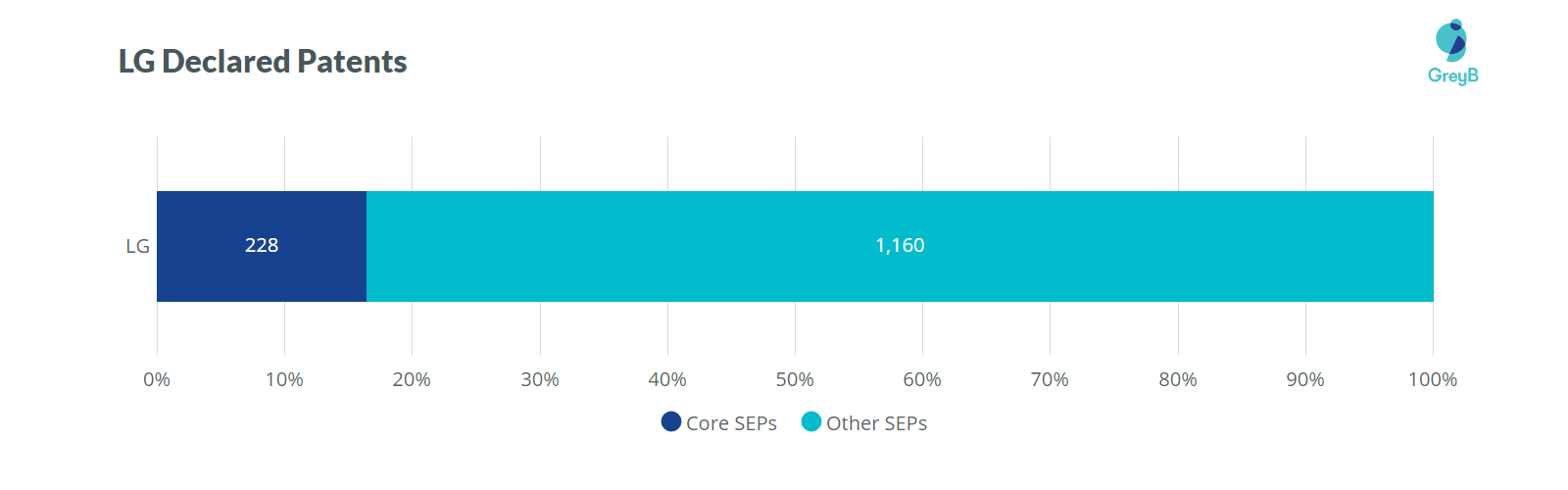
As of Mar 31, 2019, LG has declared 1388 patent families to ETSI. And by further research, it’s been found that out of 1388 patent families, 62% of patent families were declared for 5G. Only 228 patent families believe to be Core SEPs, says GreyB’s 5G SEP Report.
4. Nokia Networks (Finland)
Nokia has also joined the race of 5G by developing, researching, and partnering with other entities to render 5G communication as fast as possible.
The company is using an 8000-hectare site to carry out key 5G tests in collaboration with Deutsche Telekom and Hamburg Port Authority for their project 5G MoNArch. The project aims to gain knowledge and experience from 5G networks in the real-world environment. Its industrial uses could be traffic light management, data processing from mobile sensors, and VR applications.
Additionally, Nokia implemented Future X network architecture for 5G to deliver robust network coverage and reduce costs.
Let’s look at the timeline of Nokia’s journey in 5G.
2018
- Nokia unveiled its ReefShark chipsets to outline the scope of its Future X architecture for 5G. It’s the basis for its new reference silicon design and the foundation of its 5G technology and services portfolio.
- Nokia announced a bunch of services designed to help operators with the major undertaking of moving to 5G at 5G World 2018. The main offering was Nokia 5G Digital Design, which uses AI to simulate 5G use cases to help with real-world design and stress test their business cases.
- Nokia also completed the 5G New Radio data call based on 4G/5G connectivity during a demonstration in China.
- In August 2018, Nokia outlined its licensing rate expectations for 5G mobile phones. The company is a long-term innovator in developing fundamental wireless communications technologies and has contributed significantly to developing related standards for over two decades. This research and development investment has resulted in a significant portfolio of standard-essential patents (SEPs). Nokia has committed to license these SEPs on fair, reasonable, and non-discriminatory (FRAND) terms, in line with the applicable intellectual property rights policies of relevant standard-setting organizations (SSOs).
- On October 25, 2018, Nokia’s state-of-the-art manufacturing unit in Chennai in South India started manufacturing 5G New Radio equipment based on the 3GPP 5G New Radio Release 15 standard. The Chennai plant is one of the country’s largest telecom equipment manufacturing plants, having crossed the 4 million annual production milestones of 2G, 3G, and 4G units. It serves domestic and global customers, shipping to over 100 countries.
2019
- At Mobile World Congress 2019, the company introduced a new FastMile 5G Gateway that allows operators to upgrade their LTE network to capture new Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) revenue and accelerate 5G rollouts. Nokia’s FastMile 5G Gateway uses the same sub-6GHz 5G that operators will use to upgrade their LTE grid, providing broader coverage of FWA and enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB) services.
- On Oct 30, 2019, the company hired 350 employees for research and development in Finland to fix a 5G chip problem that could be problematic for its mobile business. Nokia also said it had been recruiting mainly for system-on-a-chip development but declined to provide staff numbers for its overall R&D function.
2020
- On Jan 9, 2020, Nokia disclosed the count of its commercial 5G contracts. The company said it reached 63 commercial 5G contracts worldwide with customers such as AT&T, Verizon, Sprint, T-Mobile, KDDI, NTT Docomo, Korea Telecom, and LG Uplus. The 63 signed commercial contracts exclude any other type of 5G agreements, such as paid network trials, pilots, or demonstrations. It further elaborated that if such agreements were to be included, the total number of 5G agreements would reach over 100. It also said its 5G products are running in 18 live networks.
- On Feb 11, 2020, Nokia announced that it became the first company in the world to successfully demonstrate how non-standalone 5G technology can be used to operate connected cars commercially. SoftBank Corp. even used state-of-the-art equipment from Nokia’s end-to-end 5G portfolio to install NSA 5G networks, suited to connected vehicle testing at a Honda Research and Development site in Kamikawa-gun, Hokkaido, Japan.
- On Feb 20, 2020, the company disclosed that it completed a 5G core standalone (SA) network trial with KDDI Corporation, a leading telecoms company in Japan. The trial helped move the operator closer to providing 5G-enabled services. The standalone trial, using its 5G AirGile cloud-native core solution, was conducted entirely independently of previous generations’ mobile network architecture.
- On Feb 25, 2020, Nokia said it became the first vendor to launch new end-to-end slicing network functionality for 4G and 5G New Radio (NR). The solution will support connectivity from 4G and 5G devices over the sliced network to applications running in private and public clouds. Its new solution enables operators to build their network-slicing business with LTE and 5G NR. The slicing capability can be deployed via a software upgrade into existing LTE and 5G non-standalone (NSA) networks and, subsequently, 5G standalone (SA) networks.
- On Feb 27, 2020, it deployed a 5G industrial-grade private wireless network with Lufthansa Technik, the leading provider of technical aircraft services. The aim was to accelerate a project that enables remote engine parts inspection for its civil aviation customers. Through Lufthansa Technik’s ‘Virtual Table Inspection’, the hyperfast 5G private wireless network will remove the need for customers to physically attend servicing by providing seamless video access to the engine overhaul shop floor.
- On Mar 9, 2020, Nokia drew a €500 million ($561 million) loan to accelerate the development of 5G technology. The company said that its R&D loan facility with the European Investment Bank (EIB), which has an average maturity of about five years after disbursement, was agreed upon in August 2018 and was available until February 2020
- On Mar 19, 2020, the company extended its Worldwide IoT Network Grid (WING) services with 5G capabilities. Nokia would be offering the services on a subscription basis for enterprise customers. Due to the capabilities of 5G, its IoT use cases can be expanded across multiple sectors, such as AR, VR, healthcare, connected vehicles, and smart manufacturing.
- On Mar 23, 2020, it announced it is working with LG Uplus to automate its IP transport for 5G services and core networks. This will allow the operator to launch 5G services faster while providing subscribers with higher speed and unprecedented quality, reliability, and security. This software-defined networking (SDN) automation deployment is designed for 5G cloud architectures.
- On Mar 24, 2020, it announced the declaration of 3000 5G patents to the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI). The move launched into an emerging battle for 5G patent bragging rights among the world’s big-three vendors and also pumped approximately €4.4 billion into broader technology R&D in 2019 alone.
- On Apr 28, 2020, Nokia declared it secured a $1 billion (nearly ₹7,636 crores) deal with Bharti Airtel to supply its Single Radio Access Network (SRAN) solution across nine geographic regions. It will deploy 300,000 radio units across several of the carrier’s spectrum bands by 2022. In addition, the company will provide its RAN equipment, including its AirScale Radio Access, AirScale BaseBand, and NetAct OSS solution.
- On May 10, 2020, Nokia announced its FastMile 5G Gateway is now available on Vodacom in South Africa. Vodacom started offering Nokia’s wireless 5G WiFi router with its new 5G plan. The Nokia FastMile 5G Gateway provides solid 5G connectivity with less lag and high-speed internet. The router connects with your end devices using either the 2.4GHz or 5GHz bands.
- On May 19, 2020, Nokia announced a new 5G deal with Taiwan Star Telecom, where it will supply its end-to-end AirScale Radio Access Network (RAN) portfolio. The RAN portfolio will help TST deploy non-standalone (NSA) 5G networks, laying the foundations for the future deployment of standalone 5G networks.
- On May 20, 2020, the company also announced that its team achieved the world’s fastest 5G speeds using the Over-the-Air (OTA) network in Dallas, Texas. They managed to achieve a speed of 4.7 Gbps by using commercially available 5G hardware and software. At that speed, it would take only 22 seconds to download the Android One currently running on Nokia 7.2.
- On May 21, 2020, Nokia revealed its WaveFabric Elements portfolio of photonic chips, devices, and subsystems, including Photonic Service Engine V (PSE-V). The surging demand for video and mobile bandwidth over the past 10 years has been met through the continual advancement of optical and silicon technology. But as the technology approaches its limit, network operators must find new ways to scale their networks to meet the surging demands of 5G and cloud networking while containing cost. The key to this transition is 400 Gigabit Ethernet (400G) technology.
2022
- In 2022, Nokia implemented its 5G Edge Slicing solution on real commercial networks with Cellcom and Telia. It enables operators to offer 5G Virtual Private Network services on 4G and 5G public networks, as well as new enterprise services. Its Edge Slicing system comprises a virtualized RAN-Transport-Core-Enterprise network with a distributed cloud core installed at or in the vicinity of a customer’s premises. Nokia’s 5G Edge Slicing solution builds on the previously revealed 4G/5G slicing capability.
- In 2022, Nokia released its ruggedized 5G field router, allowing companies to access operational data via secure, dependable private wireless networking of vehicles and industrial equipment. The field router will enable the country’s asset-intensive firms to connect vehicles and equipment and leverage operational data to achieve new levels of agility and productivity. This allows the companies in Japan to leverage dedicated coverage and capacity using the recently released 5G n79 band or other accessible 4.9G/LTE spectrum bands for local networks.
- In 2022, Nokia launched its 5G Open Lab as part of its existing Advanced Technology Center in Seoul, Korea. It will assist Korean organizations, communications service providers (CSPs), and partners acquire new capabilities and operating efficiencies by exploiting 5G private wireless networks. The lab is outfitted with Nokia’s 5G private wireless network solution, which includes its radio, core, and service platform. It is powered by the company’s latest AirScale, Modular Private Wireless, and FastMile 5G Gateways. Its lab will contribute to developing a thriving 5G private wireless network ecosystem, allowing end users to benefit from various industrial-grade private wireless use cases such as Industry 4.0, Virtual Reality, Augmented Reality, and factory automation.
- In 2022, Nokia announced that it would lead Hexa-X-II, the second phase of the European 6G flagship project, after its lead in Hexa-X. While Hexa-X concentrates on developing a unified 6G vision for Europe as well as potential use cases and technological enablers, Hexa-X-II is going to work on developing a pre-standardized platform and an overall system perspective. Hexa-X-II received financing from the European Commission’s Smart Network and Services Joint Undertaking (SNS-JU). Hexa-X and Hexa-X-II aim to make Europe a 6G leader.
- In 2022, Nokia stated that it would lead the German-funded 6G-ANNA project. 6G-ANNA, a part of ‘6G Platform German’, carries a total budget of €38.4 million and will last for three years. The German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) will fund 6G-ANNA to enhance and advance German and European 6G agendas and drive pre-standardization operations worldwide.
Partnerships and Collaborations
- Nokia is supplying its technology to enable China Unicom to improve the quality of its voice services and prepare its network for evolution to 5G technology.
- Nokia also seems to have strengthened its position in Saudi Arabia as the nation’s telecom providers requested Nokia to help them upgrade their networks. As a result, Nokia has won several network improvement contracts with Saudi telecom companies in recent months.
- The company also conducted joint research in November 2017 with the University of Bristol for 5G mobile networks in Bristol. The test network ran over Bristol City Council’s dedicated fiber infrastructure around Bristol Millennium Square.
- Nokia has also shown their interest in India to expand 5G mobile networks as the company inaugurated a new R&D facility in Bangalore in December 2017 and announced that by the end of 2018, they would be adding manpower into the facility. For the record, the R & D laboratory in India is Nokia’s fourth, with the other three in Europe (2) and China (1).
- Nokia also partnered with Telia in November 2017 to initiate a network called 5G Finland which is said to revolutionize 5G in Finland. Telia has kept 5G Finland open for all Finnish companies and organizations.
- SK Telecom also signed a Memorandum of Understanding with Nokia to develop 5G mobile network technology. Their joint goal was to demonstrate 5G in 2018 and to commercialize the service in 2020. A particular focus would be on developing cmWave/mmWave 5G technology which uses wideband spectrum resources from 6 GHz or higher.
- Nokia has also collaborated with telecom companies like T-Mobile & Intel on the 5G network to introduce a 28 GHz outdoor 5G commercial radio system on air in Bellevue, WA.
- In May 2018, Nokia and SFR successfully completed a 5G call using the 5G new radio system on the 3.5 GHz frequency band.
- In May 2018, Nokia completed the first technical trial in Calgary in collaboration with Canadian carrier Shaw Communications, with 28 GHz and 3.5 GHz wave spectrums.
- In June 2018, Nokia and T-Mobile celebrated successfully completing the USA’s first bi-directional 5G transmission based on a 3GPP-compliant 5G New Radio system.
- On July 6, 2018, Nokia and China Mobile signed an MoU to investigate the potential of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning to optimize future networks and enable the delivery of new Edge Cloud and 5G services. The companies planned to establish a laboratory in Hangzhou, China, to develop the demo system to verify technology use cases using Nokia 5G Future X architecture. At the same time, China Mobile leads the research in scenario selection, requirements confirmation, open API standardization, and solution definition.
- On July 30, 2018, T-Mobile and Nokia announced a landmark $3.5 billion agreement to accelerate the deployment of a nationwide 5G network. According to the deal, Nokia would provide T-Mobile with a complete end-to-end 5G technology, software, and services portfolio, assisting the Un-carrier in its efforts to bring its 5G network to market for customers in the critical first years of the 5G cycle.
- On Aug 17, 2018, Verizon and Nokia continued to advance the development and deployment of 5G technology by achieving another major 5G milestone. The first successful transmission of a 3GPP New Radio (NR) 5G signal to a receiver situated in a moving vehicle, seamlessly handing off the signal from one radio sector to another. The test took place at Nokia’s campus in Murray Hill, NJ. It follows the company’s successful completion of a series of outdoor data sessions over the 5G NR standard and the successful multi-carrier aggregation to boost those signals into the Gbps range that took place in June – also both industry firsts.
- In Sep 2018, Nokia and France Télévisions – the French National Public TV broadcaster – planned to showcase the results of a proof-of-concept demonstration of the world’s first 8K Ultra High Definition (UHD) TV streaming in real conditions over 5G at IBC 2018. Nokia and France Télévisions’ ‘Innovation and Prospective department’ conducted the tests by transmitting a program recorded in 8K over a 5G wireless network at the Nokia Paris-Saclay Campus in France in July.
- In Oct 2018, Nokia partnered with the University of Technology Sydney (UTS) to launch a new training facility – the Nokia 5G Skills Accelerator – to increase Australian industry knowledge and skills in next-generation telecommunications technologies such as 5G and foster their integration into Australian academic programs.
- On Nov 27, 2018, Nokia and StarHub completed the first outdoor pilot of 5G New Radio on the 3.5 GHz frequency band in Singapore. The companies demonstrated industrial and consumer applications to staff, industry partners, and enterprise customers over ‘live’ Nokia 5G cells and core network technology at StarHub’s headquarters in Singapore.
- In Dec 2018, Sandvik and Nokia collaborated to deliver Industrial IoT to the mining industry over LTE and 5G Networks.
- On Dec 7, 2018, Nokia and China Mobile Research Institute signed an agreement to jointly optimize 5G networks using a more open architecture. Nokia will work closely with China Mobile Research Institute to simplify interoperability between multi-vendor radio access network (RAN) technologies and enable new service performance levels for customers.
- On Dec 19, 2018, Nokia and Telefónica Deutschland completed building their joint “Early 5G Innovation Cluster” in Berlin. The “Early 5G Innovation Cluster” incorporates five sites in Telefónica’s cellular network in Berlin-Friedrichshain. These sites, equipped with Nokia 5G Airscale radio and Wavence Microwave technology, will be used in the next months primarily to test and measure the performance and coverage of the first 5G services in a dense urban area.
- AT MWC 19, Nokia announced the results of the Nokia 5G Maturity Index, produced in partnership with Analysys Mason, which provides operators with best practices for planning and deploying 5G services. The industry’s first benchmark of 5G operator maturity revealed that two-thirds of operators expect 5G to create new revenue streams. In contrast, more than 70% of operators are focused on 5G to help improve existing consumer services.
- At the same event, Nokia announced that Bharti Airtel would trial its homogenous fronthaul solution, which can support 4G, 5G, and enterprise services through a common platform. This trial is part of Bharti Airtel’s strategy to make its network future-ready to meet the growing demand for high-speed data driven by the digital revolution in India.
- Nokia and leading Australian network operator Optus announced several breakthroughs to establish Australia’s the first 5G commercial services. Optus became the first operator globally to deploy Nokia’s FastMile 5G indoor gateway in a live network and successfully launch a 5G Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) service using the 5G New Radio standard. Highlighting a clear path to commercial 5G, the successful deployment enables Optus to use the 3.5 GHz 60 MHz band to deliver the greater capacity needed to support multiple devices and ultra-high-definition video streaming services in the home.
- At Mobile World Congress 2019, Nokia and Vodafone demonstrated two massive Multiple Input Multiple Output (mMIMO) innovations to improve 5G capacity and performance. The companies will jointly showcase how 5G services can be delivered using low power, compact form factor, and more easily deployed RFIC-based mMIMO antennas, which reduce the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) compared to conventional mMIMO antennas.
- AT MWC 19, Nokia and Korea Telecom (KT) signed a Memorandum of Understanding to collaborate and trial various 5G technologies, including NFV and network slicing, to develop new applications and business models for the operator’s enterprise customers.
- On Dec 19, 2019, Nokia said that it extended its partnership with SETAR, the leading communications provider in Aruba. Under the agreement, Nokia will provide a full end-to-end 5G network transformation to SETAR. In a phased approach, the deal will see Nokia upgrading RAN access and modernizing core and data management system elements. This is the first end-to-end 5G deal for Nokia in Latin America.
- On Feb 10, 2020, Nokia announced a “long-term end-to-end network collaboration” with Orange Slovensko to utilize its 5G New Radio (5G NR)-based AirScale hardware and software for new 5G frequency bands. The agreement, which will support Orange Slovensko’s evolution of its recently updated AirScale-based 4G network, is expected to boost Orange’s network capacity and offer improved experiences and innovative 5G services to consumers and enterprise users.
- On Feb 14, 2020, Nokia announced it would extend its long-standing partnership with Iliad Group to roll out 5G networks across France and Italy. The 5G deal will focus on network modernization and 5G introduction in France and 5G introduction in Italy, making 5G available to 17 million Iliad subscribers across both countries.
- On Mar 2, 2020, Nokia announced that it is collaborating with Singtel for the 5G development and trial of 5G network slicing capabilities to support different 5G use cases such as cloud gaming, manufacturing, and maritime operations.
- On Mar 4, 2020, Nokia said it sought the help of Marvell to resolve 5G product problems that have wiped billions off their market value and threatened its progress in the 5G market. Marvell has been hired to work on Nokia’s new range of system-on-a-chip and infrastructure processors under the ReefShark brand. It will specifically contribute customized chips based on processor designs by ARM, a UK-based company whose licensees compete against Intel in semiconductor markets.
- On May 21, 2020, Nokia announced a partnership with KDDI in a joint initiative to deliver a fully cloudified RAN solution. The planned lab-based Proof of Concept, which will use Nokia’s AirScale All-in-Cloud BTS solution, will enable KDDI to explore how virtualized technology could deliver flexibility in its 5G network.
- In 2021, Nokia and Microsoft collaborated on 4G/5G private wireless use cases for businesses. The cooperation coupled Nokia’s Cloud RAN (vRAN) with Microsoft Azure cloud services and developer ecosystem to give new functionality to end users. The project backs up Nokia’s plan to work with public cloud providers to help end users get the business results they need to make 4G/5G deployments profitable.
- In 2022, Nokia and Vodafone NZ signed a Memorandum of Understanding to work together on developing novel applications and services using Nokia’s breakthrough mobile network expertise. The partnership will strengthen Vodafone’s 4G/5G network and, in the future, will look into what 5G-Advanced and 6G networks can do.
- In 2022, Nokia and Flex Brazil agreed to work together to put 5G SA private wireless networks in Nokia’s manufacturing units in Brazil. The first use cases will look for expanding wireless applications and finding out what 5G can do for reliable connections, large operational data transfers, and more flexible layouts on the shop floor.
Patent Analytics
Nokia said in its blog that The PA Consulting 5G report concluded Nokia to be No.1 for ownership of granted patents that the researchers found essential to the 5G Standard.
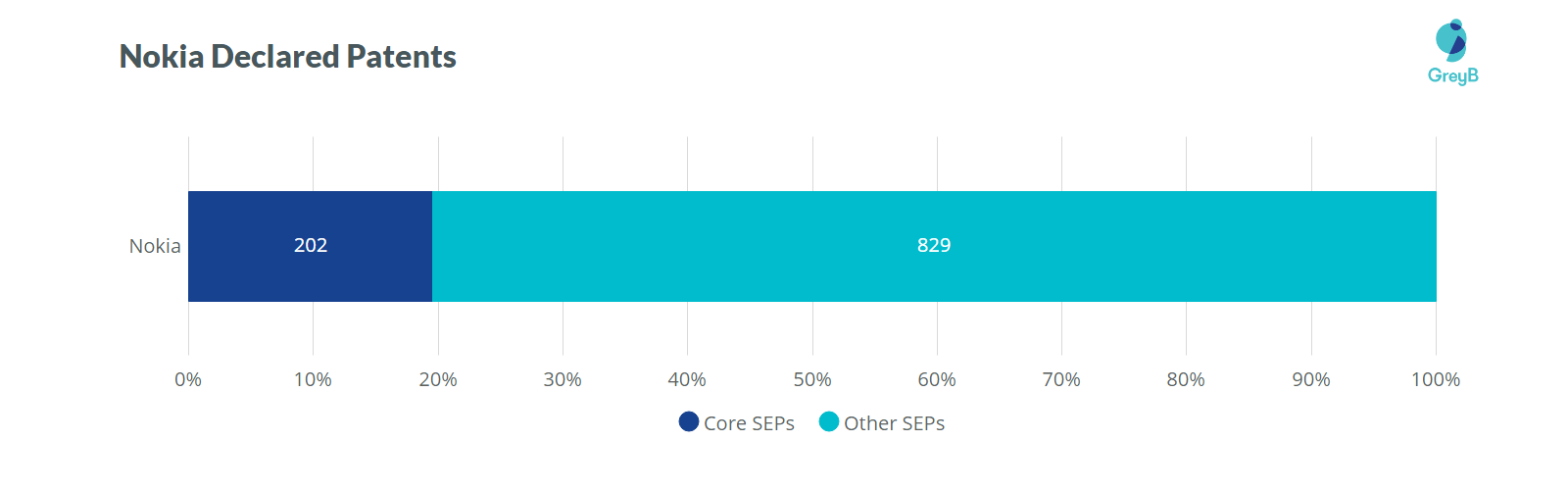
As per GreyB’s report, as of Mar 31, 2019, Nokia had declared 1031 patent families to ETSI, of which 202 patent families were believed to be Core SEPs. Nokia has declared 53% of patent families for 5G out of 1031 patent families.
This company can be found in many 5G patent reports, as the company’s portfolio holds many standard patents. In March 2020, Nokia announced that over 3000 patent families had been declared to ETSI. As of now, the number has grown to 3500 patent families.

5. Ericsson (Sweden)
Ericsson’s 5G radio prototypes are the first products designed to enable operators to conduct live field trials in their own networks. This helps them better understand the potential of 5G in their own networks and environments.
Given their expertise in the 5G domain, many companies across the globe have collaborated with Ericsson.
The company has already performed several trials by collaborating with domestic vendors. Below listed are a few of them, along with their research activities.
2018
- In February 2018, Ericsson and Korea Telecom with Intel conducted a 5G trial connecting a car to a live 5G network right in the center of Seoul. In the dense urban environment, a 4K video was streamed to and from the car, showing how 5G will change the experience for car passengers.
- Multiple companies teamed up to make 5G available in some cities. Tallink, Telia, Ericsson, and Intel created a 5G test and an exploration area at the Port of Tallinn. The trial network delivers internet to commercial passenger cruise ships while in the port.
- Ericsson showcased the first-ever live 5G demonstration in India in November 2017. The demonstration using Ericsson’s 5G testbed and 5G New Radio (NR) delivered an output of 5.7 Gbps at an ultra-low latency of 3 milliseconds.
- Ericsson’s collaboration is also present in the Pacific region, where they aligned with Australian telecom NBN to kick off 5G trials in Melbourne.
- In April 2018, Ericsson was selected by Italian operator Wind Tre to virtualize its core network as part of the evolution of its network to 5G Core. The transformation enables Wind Tre to work more agilely when providing customer services using fixed and mobile access and improving operations.
- In Aug 2018, The company showcased the first live demonstration of 5G technology in the Philippines. It announced a Memorandum of Understanding with PLDT wireless subsidiary Smart Communications to deploy a 5G pilot network in 2019.
- In Oct 2018, Telstra announced Ericsson as its key 5G partner under an agreement to deliver the next generation of mobile technology for Australia. The agreement, signed by Telstra and Ericsson, marks another important milestone in the nation’s 5G technology development and rollout.
- In Nov 2018, Ericsson inked a new deal with Telenor Group, the Norwegian multinational telecommunications company, to transform its core network in Sweden, Denmark, and Norway.
2019
- On Feb 28, 2019, Mobily Saudi Arabia deployed Ericsson’s full-stack telecom cloud solution, focusing on transforming its wireless network and providing a 5G Cloud Core. Mobily will gain a flexible, agile, and programmable network to improve customer experience and support the development of new services.
- On Feb 28, 2019, Ericsson, Huawei, and Nokia agreed to initiate discussions to extend an OSSii(Operation Support System Interoperability Initiative) Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to cover 5G network technology.
- On Feb 25, 2019, Ericsson was selected by Ooredoo Qatar to make its ‘Supernet’ fully 5G-enabled. The 5G deal will see Ericsson Radio System, 5G New Radio solutions, and 10 Gbps microwave solutions digitally transform and modernize Ooredoo’s existing mobile networks and introduce the latest 5G technologies across Qatar.
- On Feb 26, 2019, Ericsson was selected by Etisalat to deploy a 5G radio network in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) to help position the UAE at the forefront of 5G network deployment globally. The deal is part of a strategic partnership that will also see Ericsson and Etisalat working together to explore 5G opportunities.
- On Feb 27, 2019, Ericsson and Telefónica connected 5G at the famed Camp Nou stadium using massive MIMO active antennas in 3.5GHz frequency. Telefónica, Ericsson, and FC Barcelona streamed live images from Camp Nou to MWC 19 Barcelona. Along with exclusive footage of the first team’s training at the Ciutat Esportiva Joan Gamper stadium and a virtual tour of the stadium. The project has been developed in collaboration with GSMA and Mobile World Capital Barcelona within the framework of the 5G Barcelona initiative.
2020
- On Feb 12, 2020, Ericsson said that it achieved 4.3Gbps – the fastest 5G speed to date. The new milestone was achieved at Ericsson’s lab in Kista, Stockholm, with a technical specification comprising 8 component carriers (8CC) aggregating 800MHz of millimeter-wave spectrum. This landmark event was achieved during interoperability testing using commercial solutions.
- On Mar 4, 2020, Ericsson announced that its smart factory in Lewisville, Texas, produced its first 5G base station. The first product manufactured at the factory is the millimeter-wave Street Macro solution. The solution is key to Ericsson’s 5G portfolio for North American customers. All radio access components are housed in one lightweight enclosure, allowing service providers to rapidly grow 5G coverage in complex city environments.
- On Mar 18, 2020, Ericsson announced it was selected by Taiwan’s largest telecom service provider, Chunghwa Telecom Co. Ltd., to provide 5G platform to support its future network. The operator would deploy a non-standalone (NSA) New Radio (NR) network on mid and high-frequency bands. It will use Ericsson Radio System base stations and Ericsson’s 5G Core, including 5G Evolved Packet Core.
- On Mar 24, 2020, Ericsson said that it was chosen by Greece’s largest mobile communications service provider COSMOTE under a major network modernization deal for its sole 5G Radio Access Network (RAN) vendor.
- On Apr 27, 2020, Ericsson announced that it had been selected by True Corporation Plc as a 5G Radio Access Network (RAN) vendor. Products and services from Ericsson Radio System will enable True to operate 5G on 700MHz (low-band), 2.6GHz (mid-band), and 26GHz (high-band) frequencies in the North, Central-West, and Upper South regions of Thailand.
- On Apr 28, 2020, Ericsson announced that VodafoneZiggo, the leading Dutch communications service provider, is launching 5G, with Ericsson’s Spectrum Sharing and 5G Core. These 5G technologies will help for an economical and seamless roll-out of the latest mobile technology, offering enhanced network performance.
- On Apr 30, 2020, Ericsson announced its plans to deploy a dual-mode 5G Core solution onto British Telecommunication PLC (BT) Network Cloud. The solution will form a key component in BT’s move to a single converged IP network. Further, by using Ericsson Expert Analytics and built-in software probes, it will incorporate network orchestration and automation as well as continuous delivery and integration processes into BT’s existing customer experience management platforms.
- Ericsson helped T-Mobile achieve the first SA 5G data session between commercial modems from two suppliers on a production network. In addition to this, the first low-band SA 5G voice call using Evolved Packet System (EPS) fallback to VoLTE was also done through this collaboration. This technology enables high-quality voice services utilizing VoLTE in the SA architecture while the industry fully develops voice-over new radio (VoNR) 5G technology.
- On May 13, 2020, Ericsson announced that Europe’s largest 5G research network went live in Aachen, Germany, powered by its 5G products and solutions. With multiple partners, the 5G Industry Campus Europe aims to develop and implement digital and networked production applications and solutions for 5G production in Europe.
- On May 19, 2020, Ericsson secured 91 commercial 5G agreements with unique communication service providers, of which 36 are live networks. The company believes the standardization of 5G is the cornerstone for the digitization of industries and broadband. Moreover, Ericsson foresees mainstream 4G offerings to give way to 5G technology in the future.
2021
- In 2021, Ericsson developed a 5G network slicing solution for radio access networks. (RAN). This allowed communications service providers to offer tailored 5G services with guaranteed performance. Ericsson 5G RAN Slicing is commercially available and provides multi-dimensional service differentiation handling across slices while allocating radio resources at 1-millisecond scheduling. This improves the capability of end-to-end slicing for dynamic resource management and orchestration.
- In 2021, Ericsson launched Time-Critical Communication for real-time 5G experiences. It is a 5G network end-to-end software toolkit that provides the consistent low latency and high reliability required by time-critical applications and services for consumers, corporations, and the public sector. Time-Critical Communication will improve experiences in cloud gaming, AR/VR, and industrial control and open up new ones in remote control, mobility automation, and industrial control. It also may be readily deployed as a software upgrade on public and private 5G networks across vast and local areas and any 5G frequency range.
- In 2021, Ericsson released Ericsson Private 5G, which provides safe and simple 4G LTE and 5G Standalone (SA) connection primarily aimed at, but not limited to, the manufacturing, mining, and process industries, offshore, and power utilities. It streamlines and simplifies company operations with cloud-based network management, maintains sensitive data on-premises, provides zero downtime upgrades, and ensures excellent performance via Service-Level Agreements (SLAs).
Partnerships and Collaborations
- In May 2017, the company joined Celcom Axiata Berhad for the first-ever 5G testing in Malaysia. It’s also the first 5G trial conducted on the 28 GHz band in South East Asia.
- In the same month, Ericsson, in collaboration with Batelco, conducted Bahrain’s first 5G trial to drive innovation for IoT applications using the next-generation mobile network technology. The trial was conducted at Batelco’s Headquarters during their 5G Forum event. It demonstrated 5G capabilities in a real-world environment and over a live network, including speed, latency, and beam steering tests, reaching a record speed of 25 Gbps.
- In India, Ericsson partnered with Indian telecom Bharti Airtel for 5G.
- In a partnership with SK Telecom and BMW Korea, Ericsson used advanced 5G technology to track a connected car traveling up to 170 km/hour to demonstrate data transmission speeds on a 5G network. Using advanced beamforming and beam tracking, the high-performance network connection supported point-to-point data transmission from a connected car traveling up to 170 kmph with downlink speeds of 3.6 Gbps.
- Ericsson has partnered with the Fraunhofer Institute for Production Technology to develop blade-integrated disks, or blisks, for Germany-based jet engine manufacturer MTU Aero Engines.
- Ericsson recently signed a 3-year deal with Movistar Argentina to transform its Radio Access Network to expand network coverage and improve the mobile broadband experience for its customers.
- In June 2018, Telia, Ericsson, and the KTH Royal Institute of Technology announced their partnership to boost the development of 5G in Sweden. The expansion of 5G will drive the entire digitalization of society through IoT and applications such as smart manufacturing and connected vehicles.
- In June 2018, Ericsson partnered with AT&T, Fox Sports, Fox Innovation Lab, and Intel to enable FOX Sports to broadcast 4K video wirelessly over 5G at the 2018 U.S. Open.
- On Sep 17, 2018, PJSC VimpelCom (marketed under the Beeline brand) and Ericsson signed a two-year strategic partnership agreement to develop 5G and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies.
- On Oct 25, 2018, Ericsson announced that it signed an MoU with Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited(BSNL), one of the leading telecom operators in India, to work together on developing new 5G use cases, knowledge sharing on 5G technology concepts, industry and innovation trends including 3GPP standardization progress.
- In October 2018, Ericsson and Telia, in partnership with Einride, showed how driverless truck transportation is possible through enhanced connectivity based on 5G at the DB Schenker facility in Jönköping, Sweden.
- Ericsson and STC Solutions, a subsidiary of Saudi Telecom Company, signed a sales channel partnership agreement to allow STCS to resell Ericsson hardware, software, post-warranty, and training across networks, digital services, managed services, emerging business & technology business units to end-users – including STC subsidiaries such as VIVA Kuwait and VIVA Bahrain. The announcement was made during the MWC 2019.
- At Mobile World Congress 2019, Ericsson and Transdev announced their collaboration for the Rouen Normandy Autonomous Lab* (RNAL) project as the first on-demand shared and autonomous transport service on open roads in Europe. The RNAL project enables the autonomous operation of four ZOEs Renault and, soon, an i-Cristal Transdev – Lohr shuttle.
- On Feb 25, 2019, Saudi Telecom Company (STC) and Ericsson signed a deal to launch a mid-band 5G network in Saudi Arabia. The deal was announced at a signing ceremony at Mobile World Congress 2019 in Barcelona.
- On Feb 28, 2019, U.S. Cellular and Ericsson announced a multi-year contract for Ericsson to support U.S. Cellular’s 5G network deployment. Under the contract, Ericsson will provide U.S. Cellular with 3GPP standards-based 5G New Radio (NR) hardware and software.
- On Mar 19, 2020, Ericsson said that it agreed to a five-year contract for the deployment of 5G in Hong Kong with SmarTone, one of the leading communication service providers in Hong Kong. Ericsson has partnered with SmarTone for 28 years as the sole supplier of SmarTone’s 4G network and will continue as their sole 5G vendor.
- On May 1, 2020, Ericsson announced that it joined forces with MIT Technology Review Insights to release a report into the challenges and opportunities for mobile network operators implementing 5G networks in today’s climate. The report, entitled “The 5G Operator”, examines how telecom operators are preparing to scale up their fledgling 5G offerings within the next several years.
- On May 18, 2020, Ericsson announced the partnership with China Telecom and China Unicom to deploy its Radio System products and solutions, including Ericsson Spectrum Sharing. Ericsson said it would provide outdoor and indoor solutions to build capacity and coverage in the 3.5GHz and 2.1GHz bands. Network services, including provisioning, installation, and testing, will be provided to meet the CSPs’ technical needs and enable them to build and share 5G networks.
- In 2021, Ericsson and Leonardo joined hands to make new 5G solutions and business models for industrial, public safety, and critical infrastructure. Both companies shared their research and development skills in 5G networks, cyber security, and service evolution. The collaboration agreement is meant to propel solutions that help industries transform their operations, make them safer and more secure, and develop new services and products.
- In 2022, Ericsson and the Aerial Experimentation and Research Platform for Advanced Wireless (AERPAW0 established a partnership to advance 5G drone operations for smart agriculture. Remote monitoring and assessment of fields, farms, and livestock will be possible with the developments. An Ericsson 5G radio and core network broadcasted drone video with uplink speeds of over 100 Megabits per second and downlink rates of over 450 Megabits per second.
- In 2022, Ericsson and the University of Texas (UT) at Austin expanded their collaboration for 6G-powered extended reality (XR) research. The goal of the research was to come up with solutions that can be used to make XR use cases bigger in the 6G era. The project was led by three professors from different departments at UT Austin, along with Ericsson’s researchers in the field.
Patent Analytics
The company has secured most of its research and inventions through IP. For example, to secure the R&D done on 5G, Ericsson filed a landmark patent application for 5G with WIPO and USPTO.
The patent application, which combines the work of 130 Ericsson inventors, is the largest in cellular communications in terms of the number of inventors anywhere in the world. It shows the industry how Ericsson has approached 5G standardization with a comprehensive view that connects individual inventions in a complete 5G telecommunications network rather than focusing on smaller individual inventions. Moreover, as per Bird & Bird analysis, Ericsson is leading with the most standard patents, with a share of 15.8% of all 5G standard patents.

As per the GreyB report, Ericsson had declared 1350 5G patent families to ETSI by Mar 31, 2019. Out of which, 63% of families declared for 5G, and only 152 patent families were found to be Core SEPs by the analysts.
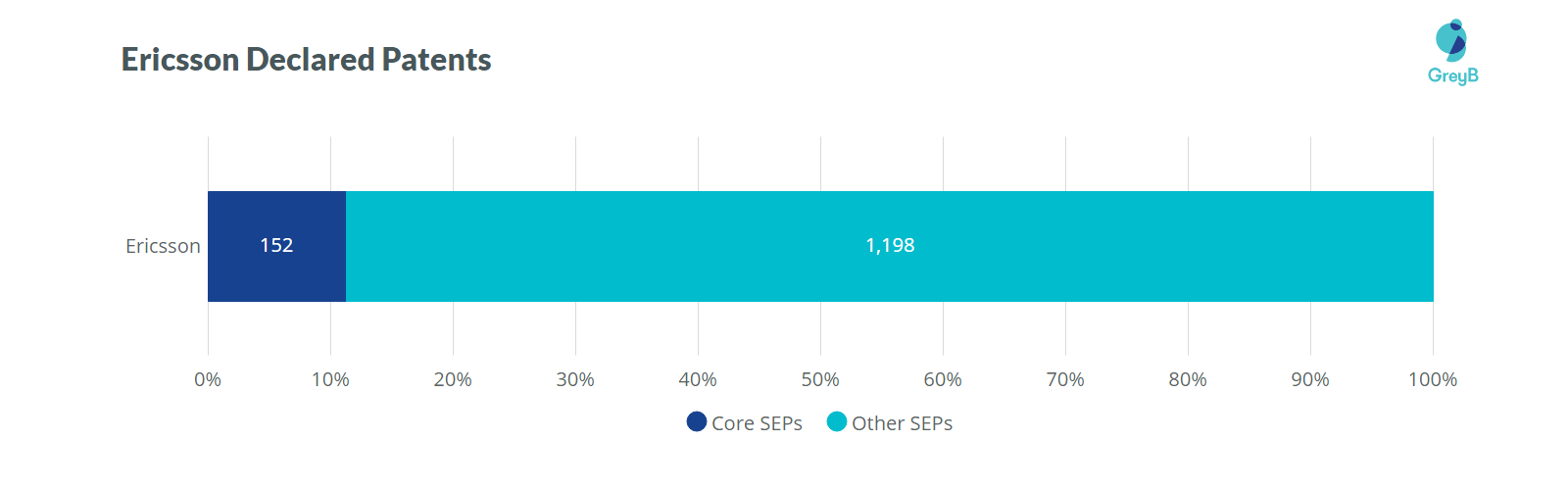
6. Qualcomm (US)
When other companies were just talking about 5G, Qualcomm actually started building the technologies, which eventually turned it into a leader in 5G. To date, it has been able to build technology with a wide range of products and solutions that enable the development and deployment of 5G networks.
Let’s take a look at Qualcomm’s timeline and how it reached where it is today.
2018
- After 3GPP set 5G standards in 2016, Qualcomm started working on the next wave of 5G NR technologies to pave the way to the subsequent 5G NR standard releases. At MWC 2018, Qualcomm demonstrated three of these 5G NR expansion areas.
- Qualcomm Research started designing the new 5G wireless air interface well before 3GPP standard efforts kicked off. In a live demonstration to Industry Analysts, Qualcomm Research demonstrated a key 5G technology enabler to these extreme mobile broadband experiences— millimeter wave (mmWave).
- Qualcomm is also working to design and standardize the new 5G NR unified air interface.
- In February 2018, Samsung and Qualcomm announced their intention to expand their decade-long foundry relationship into EUV (extreme ultraviolet) lithography process technology, including the manufacturing of future Qualcomm® Snapdragon™ 5G mobile chipsets using Samsung’s 7-nanometer (nm) LPP (Low Power Plus) EUV process technology.
Using 7 LPP EUV process technology, Snapdragon 5G mobile chipsets will offer a smaller chip footprint, giving OEMs more usable space inside upcoming products to support larger batteries or slimmer designs. Process improvements, combined with more advanced chip design, are expected to significantly improve battery life.
- In the same month, Qualcomm and Microsoft announced that leading retailers worldwide would offer a range of new Microsoft Always Connected Windows 10 PCs powered by the Qualcomm® Snapdragon™ Mobile PC Platform.
- Qualcomm, along with Verizon and Nokia, completed a series of data sessions over the 3GPP New Radio 5G standards outdoor and a successful multi-carrier aggregation to boost those signals into the Gbps range.
- Qualcomm also got permission from FCC to conduct R&D tests in New Jersey and California.
- The company claims to offer the 5G NR platform for a small cell which has also been used by 3G and 4G networks in urban areas. Its FSM100xx platform works with sub-6 GHz frequencies and higher millimeter Wave (mmWave) spectrum.
2019
- In Feb 2019, Qualcomm Technologies and a group of the world’s leading mobile network operators, made a declaration in February 2019 of their progress in realizing the vision for 5G. As the companies planned to begin the first trials of standards-compliant mobile 5G NR networks, at the heart of the mobile test devices, they used the Qualcomm Snapdragon X50 5G modem to ascertain the performance of these emerging networks.
- On Feb 19, 2019, Qualcomm announced an expansion of its 5G test networks to include new end-to-end over-the-air (OTA) configurations for both millimeter-wave (mmWave) and sub-6 GHz bands.
- On Feb 25, 2019, to facilitate next-generation connected vehicles that can perform as envisioned, Qualcomm announced 2nd generation Qualcomm Connected Car Reference Design. It features a highly advanced suite of connectivity technologies, precise positioning technology, and integrated processing.
- On Feb 25, 2019, Qualcomm announced its first 5G customer premise equipment (CPE) reference design for sub-6 GHz and millimeter wave (mmWave) 5G fixed wireless broadband (FWB) products at MWC 19 Barcelona. The reference design features the newly announced second-generation Qualcomm® Snapdragon™ X55 5G modem and next-generation Qualcomm® RF front-end (RFFE) components and modules for sub-6 GHz and mmWave deployments.
- On Feb 25, 2019, Qualcomm announced the PC industry’s first commercial 5G PC Platform, the Qualcomm® Snapdragon™ 8cx 5G compute platform. Featuring the groundbreaking second-generation Qualcomm® Snapdragon™ X55 5G modem, the Snapdragon 8cx 5G platform will help PC manufacturers take advantage of the global rollout of 5G networks.
- At Mobile World Congress, Qualcomm announced the Qualcomm® Snapdragon™ Mobile Platform with 5G integrated into a System-on-Chip (SoC). The Company builds on its 5G leadership with the Snapdragon X50 and X55 5G modems and RF front-end (RFFE) solutions by offering a newly integrated Snapdragon 5G mobile platform, which reinforces the Company’s role in providing the global mobile ecosystem with the flexibility and scalability needed for broad and fast 5G adoption.
- At MWC 19 Barcelona, Qualcomm delivered Wi-Fi 6 to the world in two groundbreaking ways: First, it announced Qualcomm Snapdragon 855 Mobile Platform-based devices with their WCN3998 chipset integrated to support key Wi-Fi 6 features, and second, it provided a distinctive view of what a full-featured Wi-Fi 6 mobile SoC looks like, ready for standard certification later this year.
- On Oct 22, 2019, Qualcomm announced that its Snapdragon X55 Modem-RF has been selected by Cradlepoint to power its “5G for Business” solution roadmap. Cradlepoint is working with major carriers to develop its solution offering.
- On Oct 24, 2019, Qualcomm Inc said it created a $200 million venture capital fund to invest in startup companies looking to use 5G technology in devices other than smartphones. Qualcomm has already been supplying chips for 5G to smartphone companies, but to cover more markets, it is seeking more devices to implement 5G technology.
- On Nov 20, 2019, Tata Consultancy Services and Qualcomm announced the launch in Hyderabad of an innovation hub that will be used to build domain-specific solutions that utilize the combined power of AI, IoT, and 5G technologies. On Dec 5, 2019, Qualcomm announced that it is working with Reliance Jio, Flipkart, and Amazon India to build new use cases for 5G. The chipmaker also wanted to put conditions for the fast development of 5G services in markets like India. Senior vice-president and general manager of the mobile business unit at Qualcomm Technologies, Alex Katouzian, said India could be instrumental in building new use cases for 5G. “We work with Reliance Jio for their services and are involved with them on a fairly active basis for building 5G use cases,” Katouzian said.
- On Dec 9, 2019, Qualcomm revealed the world’s first 5G-supported extended reality (XR) platform along with two new 5G Snapdragon mobile platforms, i.e., the flagship Snapdragon 865 and the mid-tier Snapdragon 765/765G. The Snapdragon 865 Mobile Platform included the Snapdragon X55 Modem-RF System and was designed to deliver unmatched connectivity and performance for next-gen devices.
2020-21
- On Jan 7, 2020, Coolpad announced that it will utilize Qualcomm® Snapdragon™ 765 5G Mobile Platform to build out its 5G device offerings. Coolpad is building a research and design team with 5G testing equipment to power next-generation products.
- On Feb 18, 2020, Qualcomm showed the world its expertise by unveiling its Snapdragon X60 5G modem for the upcoming 5G smartphones to boost wireless signal speed. The modem is made of 5 nanometers which results in lower power consumption and a smaller footprint for even sleeker devices. X60 will run from 2G to 5G networks and will access a more reliable sub-6 GHz network.
- On Feb 25, 2020, Qualcomm announced a complete end-to-end solution with ZeroLight that will utilize the XR2 and 5G. The prime reason for “Boundless XR” is to replace the wires in mixed reality headsets with high wireless connections, thus, providing lightweight, low-power headsets.
- In 2021, Qualcomm Technologies, Inc. introduced the Snapdragon X65 5G Modem-RF System, their fourth generation 5G modem-to-antenna solution. It is the world’s first 10 Gigabit 5G modem-RF system and the first 3GPP release 16 modem-RF system. It is intended to offer the fastest 5G speeds currently available while providing fiber-like wireless performance and using the available spectrum for maximum network flexibility, capacity, and coverage.
- In 2021, Qualcomm Technologies, Inc. launched its second-generation Qualcomm 5G RAN Platform for Small Cells (FSM200xx), which will significantly improve Radio Frequency. The platform is one of the industry’s first 3GPP Release 16 5G Open RAN platforms. It’s compatible worldwide with all commercial mmWave and Sub-6 GHz bands, including the new n259 (41 GHz), n258 (26 GHz), and FDD bands.
Qualcomm also disclosed their royalties price for every 5G phone, which could be up to $16.25, threefold than Ericsson’s price. This is not the final price, as the licensing agreement often includes cross-licensing deals, which could affect the price drastically.
Partnerships and Collaborations
- On Mar 3, 2019, France Brevets, IMT, and EURECOM announced a joint agreement with Qualcomm Incorporated to foster research into new technologies for future 5G standards. Under the terms of the agreement, Qualcomm will contribute funding and standards expertise to support wireless communications research by EURECOM and its partner organization Institut Mines-Télécom (IMT), while France Brevets will provide support in the area of intellectual property strategy.
- On March 5, 2019, as per an announcement, a Qualcomm subsidiary and Robert Bosch will research collaboratively with a focus on 5G New Radio (NR) technology applications for the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT).
- On Oct 21, 2019, Radisys® Corporation announced an agreement with Qualcomm to be a key independent software vendor for optimizing L2-L3 5G NR software on the Qualcomm FSM100xx 5G Platform. Both companies are helping service providers to accelerate their 5G development by providing them with a complete, pre-integrated, pre-tested, and pre-validated 5G platform for both mmWave and sub-6 GHz bands.
- On Nov 28, 2019, Qualcomm announced that together with Siemens, they implemented the first private 5G SA network using the 3.7-3.8GHz band in a real industrial environment. Siemens is providing the actual industrial test conditions and end devices, and Qualcomm is supplying the 5G test network and the relevant test equipment. The 5G network was installed in Siemens’ Automotive Showroom and Test Center in Nuremberg.
- On Feb 20, 2020, Qualcomm said that it’s working with Corning Inc. to develop 5G mmWave infrastructure systems for enterprises. Qualcomm will provide its 5G and mmWave technology with Corning’s industry-proven small-cell expertise to deliver affordable and easy-to-install 5G-ready networks indoors.
- On May 8, 2020, Qualcomm Technologies announced that together with Fujitsu, they successfully completed a 5G NR data call using 5G sub-6 GHz carrier aggregation. The connection was established using non-standalone architecture, aggregating a non-contiguous spectrum on 3.5 GHz (n78) and 4.9 GHz (n79) bands. For this experiment, they used a Fujitsu 5G NR base station and a 5G smartphone powered by a Qualcomm Snapdragon X55 5G Modem-RF System.
- In 2022, Qualcomm and Microsoft collaborated to develop a unique, first-in-the-industry, chip-to-cloud, private network solution for enterprises. This solution is meant to make it easier for businesses to adopt new technologies to set up private 5G networks worldwide. This partnership brings together Qualcomm’s 5G technology and hardware ecosystem with Azure’s private MEC and Private 5G Core.
- In 2022, Qualcomm and Vodafone collaborated to design, test, and incorporate 5G Distributed Units (DUs) and Radio Units (RU) with Massive MIMO capabilities for the Open RAN commercial launch in Europe. The Qualcomm® QRU100 5G RAN Platform and Qualcomm® X100 5G RAN Accelerator Card will fuel the 5G Open RAN.
- In 2022, Fastweb and Qualcomm collaborated to market 5G SA mmWave on Qualcomm® 5G Fixed Wireless Access Platform Gen 2 with Snapdragon® X65 and X62 5G Modem-RF Systems for Fixed Wireless Access (FWA). The goal of the collaboration was to help Fastweb quickly expand its FWA deployments so that by the end of 2025, about 12 million homes and businesses in Italy can use 5G to the fullest capacity.
Acquisitions
In 2022, Qualcomm acquired Cellwize to drive 5G RAN innovation and application. With Cellwize’s 5G network deployment, management software system, and automation, its 5G infrastructure solutions drive industrial digital transformation, power the connected, intelligent edge, and help the cloud economy grow.
Patent Analytics
From the US, Qualcomm is the only leading company with 5G standard patents. Qualcomm’s patent portfolio is, well-recognized by the industry players as top companies like LG also sort of taking a patent license from them for cellular technologies.
As per GreyB’s report, Qualcomm had declared 1042 patent families to ETSI as of Mar 31, 2019, of which 61% of patent families declared for 5G. Furthermore, of 1042 patent families, only 191 patent families are believed to be Core SEPs.
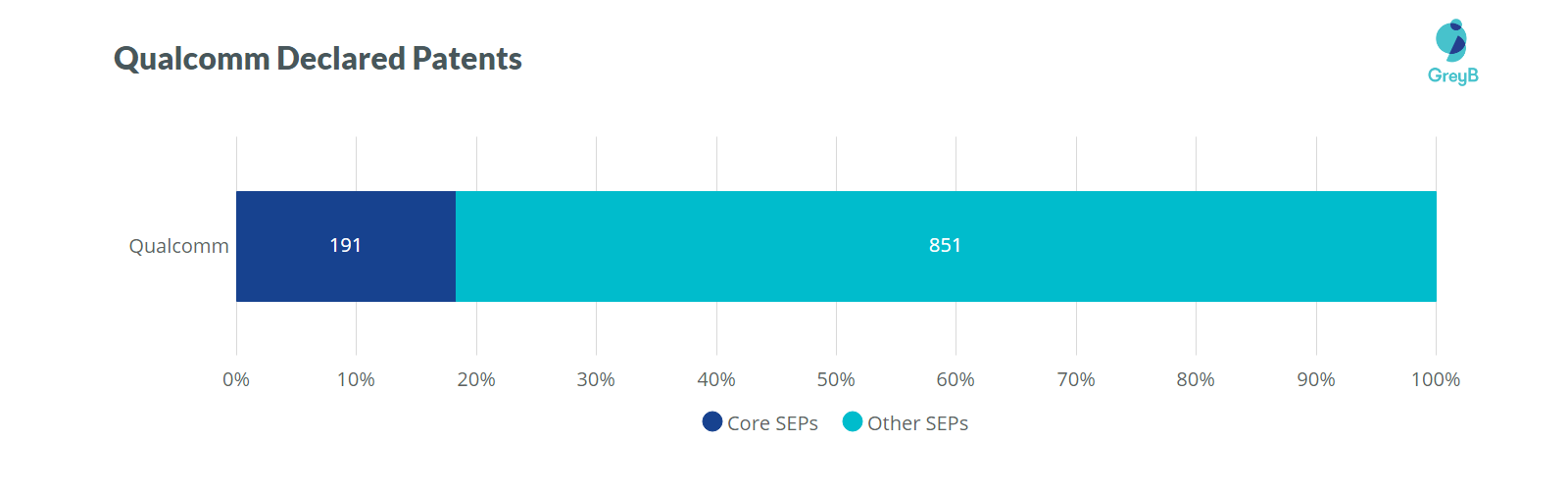

7. ZTE Corporation (China)
Regarded as one of the leaders in 4G LTE, the Chinese telecom equipment company – ZTE Corporation also maintains its position in the 5G research and tests. The 4G network faced various bottlenecks in the Internet of Things because of its performance and capabilities. At that time, ZTE was the first company to propose its Pre5G concept and series solution.
After that ZTE opened many research centers in various countries and did many collaborations and investments in 5G technology which you can find below:
2015-16
- On November 4, 2015, ZTE corporation opened a new Research and Development Center in Tokyo focusing on the development of 5G and other next-generation network technologies. This new R&D center will support ZTE’s partnerships with operators and academic institutions in Japan on the deployment of ZTE’s proprietary Pre5G technology and ongoing research on 4G and 5G mobile communications.
- On June 28, 2016, At Mobile World Congress (MWC) in Shanghai, ZTE officially released the Pre5G: Building the Bridge to 5G whitepaper. As the first vendor to propose Pre5G technology concepts and series solutions, they exponentially enhanced the performance and capabilities of 4G networks by providing 5G-like performance and service experience on existing 4G networks, thus implementing a comprehensive evolution to 5G.
2017
- On February 28, 2017, ZTE announced that the company’s 5G solutions are scheduled for commercial pre-deployment starting from the third quarter of 2018, as ZTE enables operators to minimize the time to build 5G-ready networks.
- On April 19, 2017, ZTE Corporation announced that Mr. Sergio Parolari and Mr. Yang Li from ZTE became editors for 5G new radio (5G NR) air interface protocols at the 3GPP radio access network (RAN) WGs in Spokane. It demonstrated the strength and contribution of ZTE in 5G standards.
- On May 16, 2017, ZTE corporation announced its participation in the second phase of China’s 5G test as well as breakthroughs in several technical solution verifications. China’s 5G testing is the world’s first 5G test that is guided and planned by the government. It is led by the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) and implemented by China’s IMT-2020 (5G) promotion group. The project’s research and development (R&D) can be divided into three phases: key technology verification, technical solution verification, and system verification.
- On May 25, 2017, the Director of Wireless Standardization and Industrial Relationships at ZTE Corporation said that telecommunications operators should work towards incubating a globally harmonized ecosystem for 5G mobile communication in the interests of the healthy development of the telecommunications industry.
- On May 25, 2017, ZTE shared next-generation 5G core network architecture at IMS World Forum. They presented on the subject of DevOps-based Cloud-Native IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) at the 2017 IMS World Forum, which took place 23-24 May in Madrid, Spain.
- On June 5, 2017, ZTE Corporation announced that they will showcase their remote control service for 5G VR underwater vehicles at the 5G World Summit 2017, London. With the help of real-time VR video transmission, the demonstration will simulate underwater scenarios such as offshore submarine scientific expeditions and maintenance.
- On June 8, 2017, ZTE became the first vendor who complete the mMTC field test in the second phase of China’s 5G test. The test result showed that the number of connected terminals increased by nearly 600 percent, reaching an equivalent density of 10 million connections. This indicates a major step forward toward the future Internet of Everything (IoE).
- On June 13, 2017, ZTE corporation took the lead in completing the 26 GHz high-frequency field test of its 5G new radio (NR) pre-commercial base station, which delivered an excellent performance in interconnecting with the instruments and chips from several manufacturers in the industry. In addition, ZTE also applied to do official tests for frequency bands greater than 40 GHz in its Shanghai R&D center, indicating a rapid increase in China’s key technological capabilities for high-frequency bands.
- On June 30, 2017, ZTE Corporation doubled its investment in the research of the fifth-generation mobile network (5G). ZTE invested 1 billion yuan( $148 million) in the previous year, and now they are all set to invest 2 billion yuan ( $295 million ).
- On November 16, 2017, ZTE corporation, Qualcomm, and China Mobile announced that they have successfully achieved the world’s first end-to-end 5G NR Interoperability Data Testing (IoDT) system demonstrating a data connection based on 3GPP R15 standard. Following the guidelines of China Mobile, the IoDT connection demonstration took place at China Mobile’s 5G Joint Innovation Center and utilized ZTE’s 5G NR pre-commercial base station and Qualcomm Technologies’ 5G NR sub-6 GHz UE prototype.
2018
- On October 16, 2018, ZTE Corporation developed its 5G core system chips of 7nm and 10nm with independent intellectual property rights. In the first half of 2018, ZTE corporation was sanctioned by the US Department of Commerce. Because its core technology was enslaved to US companies, it was banned from using US companies’ chips and operating systems. But, thereafter, ZTE increased the investment in chip RR&D and later on developed 5G core system chips with 7nm and 10nm processes for 5G terminals.
2019
- On May 30, 2019, ZTE Corporation announced the launch of the ZTE Axon 10 Pro 5G in Finland in cooperation with Elisa, the leading Finnish communications service company in Northern Europe. ZTE Axon 10 pro 5G has been available since 28 May 2019 in Northern Europe and will be on sale via Elisa online and offline stores.
- On June 24, 2019, ZTE Corporation declared 1,424 families of 5G Standard-Essential Patents(SEP) and patent applications to the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI), by June 15, 2019, thereby being included in the global top 3.
- On July 5, 2019, ZTE Corporation officially sold the first 5G smartphone ZTE Axon 10 Pro 5G in Finland. The phone was handed over to the consumer by Veli-Matti Mattila, CEO of Elisa Corporation, on July 3, 2019, in the Elisa Kulma flagship store in Helsinki. It verifies Finland has officially entered the era of 5G and ZTE Axon 10 Pro 5G as the first commercial 5G smartphone in Nordic countries, enabling consumers to gain the ultimate and ultra-fast 5G experiences and services.
- On July 16, 2019, ZTE Corporation won the Best 5G Solution Award at Selular Awards 2019, held in Jakarta, Indonesia. This award recognizes ZTE’s efforts to introduce 5G in the early stages and commitment to establishing cooperation in developing 5G technologies with leading operators in Indonesia.
- On August 5, 2019, ZTE Corporation announced that its shares had been included among the FTSE4Good Index Series for the second consecutive year since 2018. This recognizes ZTE’s commitment to environmental, social, and corporate governance practices.
- On August 9, 2019, ZTE Corporation announced that they would broadcast the 2nd National Youth Games of China with integrated 5G Live TV solutions in collaboration with the Shanxi Branch of China Mobile. With ZTE’s 5G technologies being widely adopted in video collection, editing, broadcasting, and transmission for the 2nd National Youth Games live streaming, it was China’s first 5G sporting event.
- On August 14, 2019, ZTE corporation announced that they had launched 5G applications in Carinthia, Austria, bringing 5G technology to life in collaboration with Drei and the Federal State of Carinthia. Showcasing the new opportunities for digitalization, tourism, and the environment, real 5G applications in the 5G network and 5G smartphones will provide transfer speeds of up to one Gigabit per second.
- On Nov 21, 2019, ZTE Corporation provisioned the MEC-related B2B2C end-to-end network slicing services with the Guangdong branch of China Mobile. The provisioning of the new services will promote new 5G business models and industry innovations. Together with other industry partners, ZTE and the Guangdong Branch of China Mobile have deployed end-to-end slicing operation systems by adopting the MEC solution to provide industrial customers with end-to-end digital transformation support.
2020-22
- On Jan 16, 2020, ZTE announced that the company plans to raise RMB11.46 billion (US$1.66 billion) from a new share issue for its 5G R&D efforts. The company would issue 381 million new shares to ten professional and institutional investors.
- On Feb 25, 2020, ZTE reported that it had already secured a total of 46 5G commercial contracts around the world. The company revealed that these 5G contracts cover China, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and the Middle East. ZTE also highlighted that it has already carried out 5G cooperation with more than 70 operators globally, including China Mobile, China Telecom, China Unicom, Orange, Telefonica, Wind Tre, Hutchison Drei Austria, and MTN.
- On Feb 28, 2020, ZTE announced that it landed a 5G contract with the French operator’s Spanish subsidiary, Orange, which is also using Ericsson and Huawei as network partners. Arnaud Vamparys, Orange’s senior vice president of radio networks and “5G champion,” lauded the technology developed by the Chinese vendor.
- On Mar 2, 2020, ZTE unveiled that it is accelerating its 5G tech evolution by releasing a series of upgraded 5G solutions. ZTE said it is building an extremely simple, high-performance, and cost-effective pan-5G network as it developed 7nm self-developed chips, advanced algorithms, SBA architecture (service-based architecture), and a digital R&D platform – DevOps.
- On Mar 27, 2020, ZTE announced that it would launch nearly 10 5G smartphones worldwide and a total of over 15 5G terminal devices in 2020. ZTE also unveiled a new 5G smartphone this week in Japan in collaboration with KDDI. The new 5G smartphone, ZTE a1, will be compatible with both SA and NSA modes, featuring a 6.5-inch display, an AI quad shooting system, and a 32MP selfie camera.
- On Apr 21, 2020, ZTE provided Xinfengming Group with a comprehensive digital solution for its filament production operation by cooperating with China Mobile Jiaxing Branch. The company took advantage of the large bandwidth, low latency, and mass connection features of 5G to develop the solution. The solution includes applications such as unmanned IGV trolley, 8K high-definition smart monitoring, 5G+AI machine vision for defects detection, and 5G wireless data information collection.
- On May 21, 2020, ZTE Corporation announced the completion of the new three-dimensional coverage solution, 5G Massive MIMO 1+X SSB (Synchronization Signal and PBCH block) solution, with the Guangzhou branch of China Mobile. The solution has greatly optimized the coverage performance of high-rise buildings and improved the vertical coverage rate by more than 30%. In addition, fewer beam transmission has significantly saved resources and reduced power consumption.
- In 2022, ZTE Corporation released its latest 5G fixed wireless access (FWA) and mobile broadband (MBB) product series. The series includes the indoor 5G CPE MC888 series, the outdoor 5G CPE MC889 series, and the portable 5G MiFi MU5120. The indoor MC 888 series consists of two models: MC888 and MC888 Ultra, which are outfitted with Qualcomm Snapdragon X62 and Snapdragon X65 5G modems, respectively.
Partnerships and Collaborations
- On March 25, 2015, at a conference carried by the Next Generation Mobile Networks (NGMN) Alliance in Frankfurt, ZTE announced that they would join Deutsche Telekom’s research in the innovation and key technology fields of 5G. As they are already involved with NGMN for 5G work, they will now cooperate with other operators to promote the standardization of 5G.
- On July 10, 2015, ZTE announced they signed a memorandum of understanding with SoftBank Corp. Under this MOU, both companies have collaborated for research and development on Pre5G mobile communications network technology. This agreement builds on the existing cooperation between SoftBank and ZTE on technologies, including Massive MIMO, UDN (ultra-dense networks), and MUSA (multi-user shared access).
- On July 17, 2015, ZTE signed a strategic partnership with KT Corporation on the research and commercialization of 5G technology. Under this agreement, ZTE launched 5G Test Bed construction in Seoul and jointly developed, presented, and designed the future 5G network architecture based on the Test Bed.
- On August 4, 2015, ZTE and U Mobile announced a new partnership on 5G Mobile Network Research in Malaysia. Where they signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) with U Mobile on the development of pre5G mobile broadband technologies, deepening the two companies’ partnership on next-generation network innovation. This partnership also involved research and development of 5G technologies in addition to Pre5G.
- On February 23, 2016, ZTE corporation announced that they had signed a Pre5G memorandum of understanding (MOU) with Hutchison Drei Austria (hereinafter referred to as “Drei”) to build the first Pre5G trial site in Europe.
- On June 23, 2016, ZTE Corporation signed a MoU to develop 5G technologies with Telefonica, one of the world’s largest operators. This partnership will strengthen ZTE’s position as a strategic technological partner for Telefonica.
- On June 2, 2017, ZTE signed a strategic partnership agreement on 5G and IoT with Telenet, deepening the two companies’ collaboration on next-generation technologies.
- On June 16, 2017, ZTE Corporation and Softbank Corporation announced that they had signed an agreement for a 5G trial over a sub6GHz spectrum at 4.5GHz across metropolitan areas in Tokyo. For this trial, ZTE will provide state-of-the-art 5G end-to-end network solutions and will work with SoftBank to verify the performance of 5G technologies under real-world conditions.
- On March 21, 2019, ZTE Corporation signed an MOU) with U Mobile Sdn Bhd (“U Mobile”), the data-centric and multiple award-winning telcos, to accelerate 5G in Malaysia. In this partnership, both companies will collaborate on various 5G-related developments, including ‘Live testing.’
- On April 24, 2019, ZTE Corporation partnered on 5G for Smart Manufacturing. This partnership is being done for the promotion of 5G integration and industry and to accelerate the digital transformation of intelligent manufacturing.
- On May 15, 2019, ZTE Corporation signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with Ooredoo Myanmar to collaborate on 5G network development. The collaboration is one of many components of Ooredoo Group’s network modernization program and will ensure that Myanmar is ready for the “Evolution to 5G”.
- On June 21, 2019, ZTE Corporation partnered with the operator Hutchison Drei Austria to develop and deploy Austria’s first operational 5G network, available to selected business clients in Linz. In this partnership, Hutchison Drei Austria has received state-of-the-art ZTE E2E 5G solutions to exclusively test-drive the ultra-fast internet of the future. For the showcase in Linz, ZTE and Hutchison Drei Austria have activated a total of 20 5G sites, creating the first-ever continuous 5G coverage throughout an Austrian city.
- On June 24, 2019, ZTE Corporation signed a memorandum of understanding in 5G cooperation with PT Telkom Indonesia, Indonesia’s largest digital telecommunication operator. This document showcases ZTE and Telkom Indonesia’s commitment to building the 5G network and exploring new 5G fields in Indonesia.
- On June 27, 2019, ZTE Corporation announced an inked partnership with leading network operator China Unicom to promote the application of 5G in terminal devices. This partnership came just three weeks after China’s Ministry issued official 5G licenses for commercial use to the country’s three network operating heavyweights: Under their agreement, ZTE and China Unicom will set up a joint operation team for the development and application of 5G Live TV innovations and 5G network technologies.
- On June 28, 2019, ZTE Corporation announced that ZTE and China Telecom will demonstrate 5G 8K+VR ultra-wide bandwidth experience at a 5G experience zone jointly built by China Telecom and ZTE at MWC Shanghai 2019. The company showcased the excellent performance and business-enabled capabilities of China Telecom’s commercial network, and also reflected their excellent 5G end-to-end commercial capabilities, providing a good model for 5G business cases.
- On July 12, 2019, ZTE Corporation and Slovakian Mobile Operator SWAN Mobile jointly conducted the country’s first 5G video call in a major breakthrough for 5G commercialization where they showcased a variety of industrial applications based on 5G in front of reporters and invited guests. The demos were run on a 5G network based on 3GPP R15, using ZTE’s 5G end-to-end solution, which consists of wireless access, core network technologies, and 5G mobile phones.
- On August 1, 2019, ZTE Corporation signed a five-year 5G cooperation agreement with Universidad Distrital Francisco José de Caldas of Colombia (UDFJC University) to establish a 5G Joint Innovation Research Center in Colombia. Universidad Distrital Francisco José de Caldas is a public, coeducational research university based in Bogotá, Colombia. It is also the first university in Colombia to set up an electronic engineering career, which lays a profound foundation for Colombia’s 5G exploration.
- On Oct 14, 2019, ZTE announced the partnership with du, from Emirates Integrated Telecommunications Company (EITC), to represent the Middle East & North Africa’s (MENA) first 5G live 3D hologram. Unlike the flat-screen projection, a 3D hologram that can be viewed from 360 degrees and its demo requires ultra-broadband and extremely low latency for signal transmission.
- On Jan 30, 2020, ZTE said that together with MTN Uganda, it jointly launched the first 5G Standalone (SA) network in East Africa. On demonstration at the Experience the Future Together event in Kampala, the two showcased 5G use cases on the 5G SA network. Using the 60Mhz spectrum, the network achieved speeds of 1.494Gbps allowing it to support such applications as gigabit without fiber connectivity, cloud XR, ultra-HD live broadcast, autonomous driving, and remote surgery. The trial also featured real-time communication of an on-site fixed-wireless access network bionic robot, Cloud VR, and other vertical industries.
- On Apr 17, 2020, ZTE Corporation announced that it had extended its collaboration with Red Hat to accelerate the deployment of 5G networks. The collaboration includes a new reference architecture to enable telecom companies to effectively deploy virtual network functions (VNFs) on the Red Hat OpenStack Platform, Red Hat’s highly-scalable and agile Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) solution on ZTE’s hardware.
- On May 20, 2020, ZTE said in a release that the company and compatriot carrier China Unicom had reached an agreement for the development of “6G” technologies. Based on China Unicom’s network, both companies will jointly explore the prospect and technical trends of 6G, which is expected to be commercialized in 2030.
- In 2022, ZTE Corporation and True Group inked a deal to work together on 5G innovations. The partnership will focus on developing 5G networks, smart islands, digital services, research innovation, intelligent manufacturing, and talent training and build up a 5G innovation lab at Bangkok’s True Digital Park.
- In 2022, ZTE Corporation partnered with Advanced Info Service Plc. (AIS); where ZTE will be AIS’ complete strategic partner to upgrade 5G technologies to improve network quality and create exceptional user experiences while putting Thailand at the leading edge of the digital economy. AIS and ZTE will build Thailand’s first ‘A-Z Center’ (5G Innovation Center) to enhance growth in 5G application areas in industrial verticals.
8. NEC Corporation (Japan)
Japan’s NEC Corporation also rolled its sleeves for 5G and introduced a new business concept, “5G. A Future Beyond Imagination,” to drastically change the industry. According to SVP Toshimitsu Shimuzu, NEC plans to “collaboratively create new business models and services that connect information from different industries and companies by utilizing advanced information and communications technologies (ICT) that combine 5G with NEC’s proprietary AI, IoT, and other digital technologies.”
In 2017, along with other telecom companies, NEC Corporation made a statement that the completion of the first 5G NR standard has set the stage for the global mobile industry to start full-scale development of 5G NR, and announced its commitment towards driving the progress of standardization for a global mobile system and creating secure and intelligent technologies to realize 5G services.
From then on, the organization has made many developments in 5G, which are listed below:
2018
- In Feb 2018, the company also announced the successful remote control of construction machinery for the first time in Japan using a 5G next-generation communications system and 4K 3D monitoring in collaboration with KDDI Corporation and Obayashi Corporation.
- In 2018, NEC claimed a successful transmission of digital beamforming with a massive-element active antenna base station system that supports a 28 GHz band for 5G communications. This is the first time simultaneous beamforming transmission (four multi-user MIMO) from a single massive-element active antenna system (AAS) to four terminals has succeeded (1). In this test, NEC achieved a 3.1 Gbps cell throughput by applying a frequency bandwidth of 300 MHz.
- In June 2018, NEC announced that they had achieved with NTT DoCoMo the world’s first 5G transmission of a 4.5GHz signal using beamforming and inter-base station.
- In Aug 2018, NEC Corporation announced the launch of an enhanced Traffic Management Solution (TMS) for 5G that improves the throughput of high-speed networks that support data transfer rates of more than 5Gbps. TMS increases the quality of experience for end-users and enables Communication Service Providers (CSPs) to operate networks efficiently by providing them with sophisticated control over communications traffic.
2019
- On Jan 11, 2019, NEC Corporation announced that it contributed to a video transmission test utilizing 5G conducted in November 2018 by NTT DOCOMO, INC. and TOBU RAILWAY CO., LTD. through the provision of 5G base stations that support 4.5GHz and 28 GHz bands.
- NEC Corporation announced the provision of a facial recognition demo system utilizing Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC), a network architecture concept for next-generation communications, to DOCOMO 5G Open Lab™ OKINAWA, a 5G technology verification center established in Okinawa prefecture on January 9 and run by NTT DOCOMO, INC.
- On Jan 28, 2019, NEC Corporation, KDDI Corporation, and Obayashi Corporation announced that they had successfully carried out an operation in which the next-generation mobile communication system 5G was used to control two construction machines in a cooperative manner remotely. This field experiment was conducted in a part of the construction area of Aigawa Dam, which is under construction, in Ibaraki, Osaka, from December 3 to 14, 2018.
- On Feb 20, 2019, NEC Corporation announced the global provision of the “NEC 5G Vertical Business Platform” for Communication Service Providers (CSPs) to provide networks, clouds, and applications for the arrival of the 5G era. The “NEC 5G Vertical Business Platform” has been designed to provide full-stack capabilities and deliver innovative vertical business services.
- On Feb 22, 2019, NEC Corporation announced the development of Radio Units (RU) for 5G base stations that comply with O-RAN fronthaul specifications established by the O-RAN Alliance. In the future, 5G will require many small-coverage base station devices. NEC’s RU is ideal for 5G conditions as they are compact, lightweight, and consume a low level of power, which reduces installation and operation costs.
- On Dec 14, 2019, NEC said it is aiming to increase the revenue from India to $1 billion in five years. The increase in revenue would be led by offshore support centers, smart city projects, and 5G. “Right now, we are at $400 million and look forward to increasing that to $1 billion in five years. India is one of the focus areas and a key strategic market,” Takashi Niino, President and CEO of NEC Corporation, told ET in an exclusive interaction.
- On Dec 14, 2019, NEC revealed it had already supplied radio units (RU) for 5G base station equipment to the Japanese operator. The company said that it started shipping three types of small-cell RU that support the 3.7GHz, 4.5GHz, and 28GHz bands and comply with O-RAN fronthaul interface specifications. NEC said the RUs are compact, lightweight, and have low power consumption.
2020
- On Mar 4, 2020, NEC announced the demonstration of bidirectional 10Gbps outdoor transmission. To meet the demand for 5G networks, the Japanese IT company used all-outdoor packet microwave radios with Radio Frequency (RF) IC compatible with the D-band (130-174.8GHz).
- On Mar 24, 2020, NEC said that with Rakuten Mobile, they shipped the first 5G radio unit. The partnership enabled the operator to start the construction of its next-generation mobile network. With production underway and the first radio unit shipped, Rakuten Mobile said it would start deploying 5G base stations in the Tokyo area.
- On Apr 28, 2020, NEC announced that it built the world’s first 5G mobile network radios based on the open and fully virtualized architecture in partnership with various vRAN platforms for Rakuten Mobile. The architecture will cut the costs to build and operate 5G networks and allow operators to lower tariffs and deliver a raft of new services to help the economy recover.
- On May 14, 2020, NEC announced it is developing a learning-based communications analysis technology for private radio communications networks, including 5G networks. This technology ensures the quality of communications, even without the assistance of a network specialist. That will help avoid the quality degradation caused by congestion and competition.
2021 – 22
- In 2021, NEC Corporation deployed its 5G xHaul transformation services, following the construction of 5G transport network Centers of Excellence (CoE) in Europe, the Middle East, Africa (EMEA), and Latin America (LATAM). NEC’s newly created CoEs will play critical roles in providing these xHaul transformation services by centralizing domain expertise derived from decades of experience and participation in global and regional transportation networks.
- In 2022, NEC Corporation launched two new 5G devices of all-in-one integrated compact base stations from the UNIVERGE RV1000 series. Base station radio units (RUs) and base-band units (CU: Central Unit/DU: Distributed Unit) are combined in a single enclosure for small-scale networks. These new products will lower early investment costs and support the rapid deployment of small-scale private 5G networks, thereby promoting private 5G adoption and resolving client difficulties.
Partnerships and Collaborations
- At Mobile World Congress 2018, NEC announced collaborating with NTT DOCOMO to promote 5G by testing coordination technology between cells. In these experiments, coordinated control between Distribution Units (DUs) was achieved by using a massive-element Active Antenna System (AAS) base station system belonging to a Centralized-Radio Access Network (C-RAN) configuration, enabling a Central Unit (CU) to control multiple DUs.
- In Oct 2018, NEC Corporation and Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. announced a partnership of joint effort to strengthen their next-generation business portfolio, including 5G. The partnership combines the best-in-class technology and expertise in 5G, merging NEC and Samsung’s leadership in 5G and IT solutions.
- On Feb 12, 2020, NEC Corporation announced a collaboration with Mavenir to deliver a 5G Open virtualized RAN (vRAN) Solution to the Japanese Enterprise Market. The collaboration will open up Local/Private 5G Network opportunities for enterprises, regional authorities, and other organizations. Under this collaboration, both companies will jointly work on 5G Open vRAN and Local 5G business developments to establish a simple and cost-efficient ecosystem. The partnership will bring together NEC’s expertise in IT, network, and system integration and Mavenir’s field-proven cloud-native network technology.
- On Feb 21, 2020, NEC announced a partnership with Accedian Networks to develop network performance monitoring appliances. NEC said that the Accedian partnership was driven by growing network complexity and for greater visibility of underlay and overlay networks, especially to 5G deployments. The arrangement depends on Accedian’s Skylight software suite, which can correlate network data sources to access application performance and diagnose disruptions.
- On Mar 26, 2020, NEC announced that it has to create a joint venture with Sharp by combining NEC’s Display Solutions (NDS). The venture will help both companies to build upon their strength and address the visualization needs of their customers. It will help bring 8K+5G products to markets as well. As per the agreement, NEC transferred 66% of its NDS subsidiary to Sharp.
- In 2021, NEC partnered with Netcracker and DigitalRoute to offer its 5G mobile core network (5GC) and DigitalRoute’s Usage Data Platform. DigitalRoute and Netcracker will join NEC’s 5GC product range, and with this, NEC will be able to offer an end-to-end 5GC to its customers. Thus, communications service providers (CSPs) can install 5GC with BSS features to commercialize complex B2B, B2B2X, and other 5G business models.
- In 2021, NTT Docomo and NEC teamed up and tested 5G SA using open RAN interfaces. Docomo’s commercial 5G non-standalone baseband unit was upgraded to 5G SA through software. Docomo and NEC continued to test how well 5G CU/DU worked and added new SA units to Docomo’s commercial network.
- In 2022, NEC Corporation partnered with Fortinet® to develop 5G networks for communication service providers (CSPs). Fortinet will offer its complete best-in-class security solutions, such as FortiGate, and NEC will offer its vast experience in the telecom industry to provide carrier-grade, long-term networking for 5G.
Acquisitions
- In 2022, NEC acquired Blue Danube Systems to advance its open RAN and 5G plans. This deal gave NEC more customer support resources and capabilities in North America. It also helps NEC better meet the needs and desires of its clients by expanding its Open RAN solutions range.
- In 2022, NEC acquired Aspire Technology, specializing in 5G network solutions and IT consulting. Both companies emphasize Open RAN 5G. According to NEC, this deal will advance NEC’s system integration (SI) solution for Open RAN 5G applications.
9. Verizon (US)
Verizon has positioned itself at the forefront of 5G technology as it is building modern infrastructure all over the country. According to them, the world needs smart policies for 5G deployment, which they are ready to provide.
Here are some of the developments made by Verizon to play its part in the 5G race:
2017-18
- In Dec 2017, Verizon achieved an industry first with the completion of a successful field trial delivering live 400 Gbps Ethernet traffic on a single wavelength between MPLS Core routers over its Packet-Optical network. This trial proved the interoperability of equipment from two different suppliers and the capability to quadruple the typical capacity carried on a wavelength. This trial used the Verizon network in the Dallas area, confirming the viability of carrying 400 Gbps traffic.
- In Feb 2018, Verizon also successfully completed a call on 5G NR networks in collaboration with Nokia and Qualcomm. The trio used Verizon’s wave spectrum – using Nokia 5G network on a 5G NR prototype device by Qualcomm. The test was conducted at Nokia’s facility in Murray Hill, NJ.
- In April 2018, Verizon completed its first-ever pre-commercial video call using Samsung 5G tablets. It was an international call from Minneapolis to Seoul, Korea. The companies also decided to work together in the future for further developments.
- Verizon has many plans for 5G technology. Most importantly, they claim to be the first-ever company to provide 5G service in the US.
- Verizon selected Sacramento, CA, as the first city that would receive their 5G fixed wireless broadband service as the company gears up to challenge cable broadband providers.
- In June 2018, it was announced that Columbia University was experimenting with VR (Virtual Reality) using pre-commercial 5G technology from Verizon to develop telemedicine solutions.
- In Aug 2018, Verizon and Motorola unveiled the world’s first 5G-upgradable smartphone. The new moto z3 is the first 5G-upgradeable smartphone that tapped into Verizon’s 5G network by simply snapping on the 5G Moto mod.
- Verizon will be the first U.S. wireless provider to offer Samsung’s new 5G smartphone – the Galaxy S10 5G – in the first half of 2019 as its 5G Ultra Wideband NR network goes live.
- Verizon highlighted several use cases for XR using its 5G network at Mobile World Congress Americas in September. One demonstration by Envrmnt by Verizon showed how users wearing a VR headset could be immersed in the 360-degree spatial audio experience. The user was able to attend a concert involving an orchestra of about 100 instruments. As he moved around the concert hall, the instruments grew either louder or quieter as he got closer or farther from each section.
- At Mobile World Congress Americas in September 2018, Voxon Photonics showed off the world’s first 3D holographic call made possible by Verizon 5G. Using Verizon’s 5G network on the Los Angeles Convention Center show floor, Voxon Photonics sent medical data from the Verizon booth to the Ericsson booth – a distance of about 200 feet – and conducted the first-ever real-time video conference where the caller’s holographic face appeared using an Intel RealSense depth camera.
- On Oct 1, 2018, the first commercial 5G network in the world went live in portions of Sacramento, as well as Houston, Indianapolis, and Los Angeles. Installations of Verizon 5G Home installation started on the same day for “First on 5G” members in Sacramento. Built on the Verizon-led open 5G TF network standard, Verizon 5G Home is the next generation of home broadband internet service that provides super-fast Wi-Fi.
- On Oct 4, 2018, The Independent Filmmaker Project (“IFP”), the US’s premier member organization of independent filmmakers and storytellers, and Verizon’s RYOT, a premium entertainment studio (“RYOT”), announced the launch of a new initiative focused on new storytelling forms developed exclusively for the 5G mobile network.
2019
- Oct 18, 2019, Verizon announced an independent GPU-based orchestration system and developed enterprise mobility capabilities to revolutionize mobility for virtual, mixed, augmented reality, and cinematic reality. Together, these capabilities could pave the way for a new class of affordable mobile cloud services, provide a platform for developing ultra-low-latency cloud gaming, and enable the development of scalable GPU cloud-based services.
- On Oct 21, 2019, Verizon said that it released its 5G Home Internet in Chicago on Oct 24. Customers of the Windy City can sign up to use the super-fast wireless broadband powered by Verizon Ultra Wideband Network.
- On Nov 21, 2019, Verizon announced that Snap Inc will use Verizon’s 5G Ultra-Wideband technology to support Snap’s augmented reality, visual communications, and content experiences. As official 5G innovation partners, the companies will work together at Verizon’s 5G Labs to create new experiences for consumers, including opportunities to experience live events in new ways through Snapchat. The partnership will also include premium sponsorship placements within the Snap Originals video series.
2020
- On Jan 30, 2020, Verizon provided Capex guidance in the $17 billion to $18 billion range to focus on 5G. The investment will pay out further densification of the LTE network and the continued deployment of fiber optic cabling.
- On Feb 10, 2020, Verizon opened a new 5G Lab and production studio in London, England, to provide support to its international business and customers. The Lab is now open for business at Verizon’s Mid City Place office in central London. It provides a live Verizon 5G-enabled environment where organizations can develop and test 5G applications and experiences.
- On May 18, 2020, Verizon welcomed 390 new employees after officially closing the deal with BlueJeans Network. The addition made by Verizon is an important move in a crucial time to keep businesses operating at the highest level. BlueJeans products favor Verizon’s business solutions and thus will be integrated into its 5G product roadmap.
- On May 20, 2020, Verizon announced some new 5G milestones, such as the creation of a virtual lab to develop new 5G solutions and applications for consumers, businesses, and government agencies. Verizon also rolled out 5G Ultra Wideband availability in San Diego, making it its 35th city to receive 5G mobility service. Further, it also announced the rollout of 5G uploads in all existing 5G Ultra Wideband cities; and four new 5G technology partners to help extend millimeter wave (mmWave) 5G coverage.
- On May 20, 2020, Verizon said that it will use equipment from Movandi Corp. to expand its 5G networks. Movandi makes components to use with the mmWave system of extremely high-frequency radio signals that are used in high-speed wireless broadband communication.
2022
- In 2022, Verizon debuted the 5G Edge Accelerated Access solution as part of the broader Verizon Business Connected Venue concept, which is rooted in Verizon’s 5G deployment in more than 75 significant public venues in the United States. 5G Edge Accelerated Access is an opt-in solution that leverages video analytics, facial verification, and optional ticket scanning supported by a mobile edge computing infrastructure.
- In 2022, Verizon began transitioning commercial traffic to its cloud-native 5G standalone (SA) core network, allowing the provider to offer more flexible services. The Verizon Cloud Platform (VCP) serves as the foundation for the carrier’s 5G SA core. This includes integrating Verizon’s comprehensive mobile edge computing (MEC) ambitions and supporting standalone, non-standalone (NSA), and voice-over new radio (VoNR) services. A 5G SA core, which includes the user plane, control plane, and shared data layer network operations, enables operators to provide a more resilient core network while also supporting highly touted 5G capabilities such as network slicing, automation, orchestration, and mobile edge computing.
Partnerships and Collaborations
- In Jan 2018, Verizon announced that they would partner with Samsung to use their custom fixed 5G home routers and 5G Radio Access Units (RAN) for the carrier’s initial 5G commercial rollout that was scheduled for the second half of 2018.
- On Nov 9, 2018, Verizon and the Mass Tech Leadership Council (MassTLC), in collaboration with Ericsson, announced the launch of the Verizon 5G Robotics Challenge, a first-of-its-kind opportunity for universities, startups, and other developers in the greater Boston area to create 5G-powered robotics technologies that have the potential to transform, modern industry.
- On Nov 13, 2018, Verizon – in partnership with Motorola, Samsung Electronics America, and Qualcomm Technologies, completed the world’s first 5G data transmission on a smartphone on a commercial 3GPP 5G New Radio (NR) network. This successful test was completed with a moto z3 paired with a 5G Moto mod, the world’s first 5G-upgradeable smartphone, in Providence, RI.
- On Dec 3, 2019, Amazon Web Services and Verizon announced a partnership to bring cloud technology closer to mobile and connected devices at the edge of Verizon’s 5G Ultra Wideband network. Verizon is the first technology company in the world to offer 5G network edge computing. In addition, the company will use AWS’s new service, AWS Wavelength, to provide developers the ability to deploy applications that require ultra-low latency to mobile devices using 5G.
- On Jan 6, 2020, Verizon announced a multi-year partnership with HERE Technology to develop new connected services that utilize Verizon’s 5G network infrastructure. Early work includes two proofs of concept, i.e., targeting collision avoidance for pedestrian safety and Visual Positioning Service (VPS) for better location identification and navigation.
- On Feb 24, 2020, Verizon said that it entered into a strategic partnership with Emory Healthcare to develop and test 5G Ultra Wideband-enabled use cases to help transform the healthcare industry. Verizon made Emory Healthcare Innovation Hub (EHIH) the nation’s first 5G healthcare innovation lab with 5G Ultra Wideband service.
- In 2022, Verizon and the University of South Carolina collaborated to develop a 5G-powered facility to do research and development in a wide range of areas that benefit the general public. Researchers are anticipated to use the network to improve production aspects, such as quality sensing and defect detection. In the healthcare context, they will investigate the effects of remote health monitoring on crisis response and how 5G can facilitate the real assessment of patient vitals and hospital-connected asset facilitation.
- In 2022, Verizon and Meta teamed up to combine Verizon’s 5G technology and edge computing capabilities to develop Metaverse apps. The new alliance will explore Verizon’s 5G Ultra-Wideband network and mobile edge computing (MEC) capabilities coupled with Meta’s technology. These apps will be offered over 5G fixed and mobile connections at home, workplace, and on the go.
- In 2022, Verizon and Google teamed up to offer edge computing services over Verizon’s 5G network. Verizon 5G Edge and Google Distributed Cloud Edge will jointly deliver computing and storage capabilities. Verizon and Google envision this as an initial stage of a bigger partnership, including edge computing and 5G that will also include corporate applications in the future.
Acquisitions
In 2021, Verizon acquired TracFone Wireless and its subsidiaries for $6.9 billion. Verizon’s takeover of TracFone’s brands boosted offerings for U.S. consumers who prefer value wireless plans. Verizon continued offering Lifeline service through TracFone and added new 5G connectivity options. It also kept improving TracFone’s solutions, distribution networks, and key brands.
10. Orange (France)
The French mobile network operator is also participating in the build-out of a more connected planet as the company is exploring three complementary areas:
- Improved mobile broadband up to 10 times faster than 4G.
- High-performance fixed Internet access to complete the fiber network where it’s not available.
- New applications to support digital transformation across business sectors.
Orange also claims that it will be a genuine multi-service network designed to adapt to a whole host of devices: mainly smartphones, but also enhanced 360° content, augmented reality, connected objects, refrigerators, and driverless cars.
The company is engaged in a 5G co-construction process across the whole ecosystem of researchers, universities, tech partners, and different business sectors: transportation, manufacturing, and health to entertainment. This open collaboration allows Orange to better understand the issues, new business models, and needs and to test use cases.
Below are some developments in its pursuit of meeting its 5G goals.
- Orange has been chosen by UTAC CERAM, a world leader in testing and certifying vehicles, including autonomous cars, as its 4G/5G connectivity partner.
- It also collaborated with Ericsson to deploy an experimental mobile infrastructure to test the necessary 5G functionalities for autonomous vehicles.
- Orange also announced that they would use Ericsson 5G equipment to launch France’s first-ever 5G test in Lille and Douai between late 2018 or early 2019.
- Orange Poland launched a commercial pilot of LTE-M technology in Warsaw, Gliwice, Mysłowice, and Tarnow. The pilot allows interested companies, including start-ups, to develop their services and devices based on IoT, which also meets all requirements for the 5G network.
- On Sep 10, 2018, Orange Belgium, was the first to present a set of real use cases that rely on the much anticipated 5G technology. In the presence of the CEO of the Orange Group, Stéphane Richard, Orange Belgium teamed up with Nokia to demonstrate the potential and future applications of 5G. Orange Belgium also confirmed its ambition to deploy 5G technology for its residential and business customers as soon as possible.
- On Dec 14, 2018, Orange announced it aims to launch 5G technology in 17 major European cities across Belgium, France, Luxembourg, Poland, Romania, and Spain in 2019. The telco said that these initial launches would pave the way for the company’s full-scale commercial launch of this technology, which is scheduled to take place in 2020.
- At MWC 2019, Orange’s booth was totally devoted to 5G devices. In particular, it presented its first smartphone, which is 5G-ready. The phone serves as a test machine for the operator’s infrastructure.
- In Feb 2019, Orange showed how the 5G behaves in a real situation by showcasing the first 5G video transmission in a commercial network in Spain. For this, Orange España had teamed up with Ericsson to implement what it described as the first real-time 5G transmission over a commercial network in Spain.
- On 28 February 2019, Orange Poland said it conducted more 5G tests this month, using one of the first standards-compliant devices and spectrum in the 26-28 GHz range. The UKE regulator made the frequencies available for testing by the operator, and equipment by Ericsson was used.
- On Nov 5, 2019, Orange announced that it launched its first commercial network and deployed the technology in three major Romanian cities. The operator launched 5G services in the capital of Bucharest, Cluj-Napoca, and Iași. It also said that other Romanian cities would see the deployment in 2020. Ramon Fernandez, the deputy CEO for Finance, Performance, and Europe, explained the country was a natural choice to lead the operator’s 5G charge.
- On Dec 5, 2019, Orange announced its new strategic plan Engage2025 to look forward to 2025. Stéphane Richard, Chairman and CEO of the Orange Group, made the announcement and said: “If I had to summarise Engage2025, Orange’s new strategic plan, I would use two words: growth and sustainability.” Orange’s ambition is to reinvent its operator model by capitalizing on its leading network position.
- On Dec 12, 2019, Orange Belgium announced the first to activate a 5G testing hub for business in Antwerp, Belgium. The hub will help the company to use 5G technology to its full extent with industrial partners in real-life applications. It will help its partners to provide a strong connectivity and quality service required for industrial use cases.
- On Feb 28, 2020, The technical head of Orange’s 5G program confirmed that China’s ZTE landed a 5G contract with the French operator’s Spanish subsidiary. Arnaud Vamparys, Orange’s senior vice president of radio networks, lauded the technology developed by the Chinese vendor.
- On Apr 5, 2020, Orange said that together with Dell Technologies, they created new opportunities for bandwidth-intensive applications. Dell Technologies also announced that it is building on its agreement with Orange to help people experience the impact and power of 5G.
- In 2022, Orange Jordan established the first Orange 5G Lab in Abdali to investigate new applications for this technology and give related training. This Orange 5G Lab is Jordan’s first of its type. So far, 16 Orange 5G Labs have been created, including 13 in Europe, two in Africa, and one recently in Jordan, and Orange will continue to introduce more to realize the extraordinary potential of cutting-edge technology.
- In 2022, Orange launched the first African 5G network in Botswana, Africa. Its 5G coverage will reach 30% of the population of the southern African country, including Gaborone and Francistown, the two main cities. The company is primarily focused on 5G as a means of providing fast internet in Africa, where low population density makes fiber-optic infrastructure uneconomical to build.
Partnerships and Collaborations
- In Romania, Orange partnered with Samsung and Cisco to conduct tests in real conditions during the second half of 2018. The company also partnered with Nokia and Kathrein to design an antenna for managing 4G/5G connectivity.
- Orange and Huawei finalized the construction of a national network in Spain, a long-distance transmission with the largest capacity in the world. The new Orange Spain network will reach a total capacity of 19.2 Tbps in a single pair of fibers.
- On Feb 21, 2019, Orange and Japanese company NTT signed a strategic research and development framework agreement that will last until 2022. The agreement’s main goal is to share research findings in several key areas, including 5G, network transformation, artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things, cybersecurity, cloud services, smart cities, sports, tourism, and culture.
- On Mar 1, 2019, Huawei and Orange signed an agreement to form the Orange-Huawei IT Joint Innovation Center.
- On Oct 1, 2019, Spanish telecom operator Masmovil penned a 5G agreement with Orange Spain, boosting its EBITDA projection for the next three years. In a press release outlining a comprehensive partnership covering mobile, fiber, and broadband, Masmovil said the agreement would speed up its 5G rollout capabilities and also significantly increase its fiber-optic footprint by up to 14.2 million homes by 2020.
- In 2021, Orange and Samsung Electronics partnered to separate the software and hardware parts of traditional RAN. Samsung and Orange aim to deploy O-RAN Alliance-compliant base stations, initially focusing on rural and indoor setups before moving on to additional deployments in the near future.
- In 2022, Orange Group and Másmovil reached a deal to merge their Spanish operations. This will establish a new fixed-mobile telecom company that will compete with Telefónica, which is currently the market leader. The combined business is estimated to be worth €18.6 billion (US$19 billion), generating an annual revenue of over €7.3 billion ($7.45 billion). It will also have a mobile customer base of around 24.8 million and 7.1 million fixed customers.
- In 2022, Orange and Equinix partnered to extend the Orange Telco Cloud footprint and accelerate the rollout of Orange’s New Generation International Network. The new model lets Orange offer strong on-demand Telco Cloud Points of Presence (PoPs) to enterprise and wholesale clients. These PoPs can deliver essential services, including 5G roaming, SD-WAN, CDN, and voice services, with an estimated latency of <~10 milliseconds.
- In 2022, Orange chose Nokia’s flagship Core networking solutions to help itself offer innovative 5G solutions and enhanced network performance in Europe. This new agreement will expand the long-running collaboration between the two firms will expand further. Nokia’s cloud-native 5G Standalone Core network and Subscriber Data Management will be launched by Orange in its top market, France, and other European countries as well.
11. AT&T (US)
AT&T claimed it would be the first company to provide 5G services in the US. To achieve this feat, they deployed gigabit 5G connections in three cities: Waco, TX, Kalamazoo, MI, and South Bend, IN.
They did not just conduct a test but also showed the world how fast 5G could be.
2018
- In 2018, AT&T announced rendering 5G in the other nine cities. AT&T is on the most aggressive network virtualization path in its industry. They plan to virtualize 75% of the network by 2020, as they completed 55% in 2017.
- One of AT&T’s in-house projects built at the lab is the Advanced 5G NR Testbed System (ANTS). ANTS is a first-of-its-kind 5G testbed system and is proprietary to AT&T.
- The company also wants to demonstrate 5G entertainment experiences. They had asked FCC to demonstrate 5G in the 28 GHz mmWave band at the SHAPE event, set for June 2 and 3 at Warner Bros. Studio in Burbank, CA.
- In Mar 2018, AT&T announced that it would deploy 60,000 white box routers to virtualize its 5G network across the US over the next several years.
- In May 2018, AT&T received the FCC’s permission to conduct a 28 GHz demo that gave gamers at the Electronic Entertainment Expo (E3) an up-close look at how a 5G connection can give them a live gaming experience virtually anywhere where there’s network coverage.
2019
- In Dec 2019, AT&T’s 5G network went live in parts of 12 cities, making it the first wireless carrier to launch a mobile network based on the 5G standard.
- On Jan 21, 2019, AT&T announced three pillars of 5G, i.e., Mobile, 5G Fixed, and Wireless Edge Computing, that will bring the business experience into the future. In addition, the company is building the networks to allow fiber-based connectivity and LTE to work efficiently in parallel with 5G solutions, maximizing the impact of a business’s transformation.
- On Feb 8, 2019, AT&T successfully tested a new software update on a live commercial 5G+ network which resulted in speeds over 1.5 Gbps. This test was conducted in the field using a mobile form factor test device.
- On Feb 8, 2019, AT&T made its Stadium America’s first stadium with 5G. The company expects 5G will eventually help deliver the next generation of connected entertainment at the stadium.
- On Feb 12, 2019, the carrier announced the next two cities: Chicago and Minneapolis, which would get AT&T’s real 5G network sometime later in 2019.
- On Feb 20, 2019, AT&T said that the customers who purchase one of the Galaxy S10s from AT&T would be able to experience 5G Evolution network technologies, which is the first step on AT&T’s path to 5G. For a limited time, AT&T customers who buy a Galaxy S10 128GB, S10+ 128GB, or S10e can get one FREE.
- On Feb 22, 2019, AT&T launched the AT&T 5G Innovation Program to continue to create and develop new customer experiences with the power of 5G. In addition, the program seeks to jumpstart work with app developers, content creators, device makers, and network vendors to bring 5G ideas and experiences to life.
- On March 4, 2019, AT&T said that it wants to test 24GHz millimeter wave equipment and further “sub6” equipment testing in Texas. AT&T applied for a two-year “5G” experimental license to cover testing in the 5GHz and 24 GHz bands in Austin, Texas, on February 20.
- On Nov 26, 2019, As part of its strategic alliance with Microsoft announced earlier this year to bring its business onto the public cloud, AT&T opened previews for Network Edge Compute (NEC). This technology integrates Microsoft Azure services into AT&T network edge, software-defined network, and 5G deployments, bringing the power of Microsoft’s public cloud solutions closer to customers. The initial previews were available to select AT&T customers in Dallas, with projected launches in Los Angeles and Atlanta soon.
2020-22
- On Apr 23, 2020, AT&T announced that it launched 5G in Colorado Springs and 89 other markets in 29 states. To use the 5G services, Customers must use Unlimited Extra, Unlimited Elite, AT&T Business Unlimited Performance, or AT&T Business Unlimited Elite plans and be using one of the following devices: LG V60 ThinQ 5G, Samsung Galaxy S20, S20+, and Galaxy Note 10+ 5G.
- On Apr 24, 2020, AT&T announced that it’s increasing its investment in networks to $5 billion in the first quarter of 2020 as compared to $3.8 billion in Q4 2019. The primary focus of AT&T during the first quarter was an increase in its investment in 5G networks and fiber. The company aims to make an investment of $20 billion in 2020 as compared with capital expenditures of $19.6 billion in 2019.
- On Apr 24, 2020, AT&T said that it delivered speed gains across 51 markets in the early part of 2020, with its wide-scale use of 5-component carrier aggregation and 4×4 MIMO giving it an edge over the competition. RootMetrics temporarily suspended its network testing but published carrier-specific reports on 4G LTE and 5G performance in the first half of 2020.
- In 2021, AT&T officially launched the AT&T 5G Innovation Studio in Texas. It combined the strength of AT&T’s commercial, consumer, and network teams to speed the launch of new 5G-centric product offerings and important projects. The AT&T 5G Innovation Studio aims to accelerate the general adoption of this breakthrough technology while remaining cost-effective.
- In 2022, AT&T stated that its drone operations team had accomplished an industry first by broadcasting its 5G network via drone. The test was conducted in April in rural Missouri using AT&T’s “Flying COW,” or Cell on Wings (COW). A COW serves as a cell site on a drone, and AT&T has used this technology for years to provide LTE coverage to consumers during major events and calamities. Customers with a suitable 5G phone might have gone from no service to super-fast wireless connections in seconds. This could benefit first responders in the future during a search and rescue mission.
Partnerships and Collaborations
- In Jan 2018, Tech Mahindra intends to combine AT&T FlexWare with its System Integration and Services Portfolio and offer the solutions to its global clientele undergoing a digital transformation.
- In Feb 2018, AT&T completed its acquisition of FiberTower, which netted the operator an average of 375 MHz of 39 GHz spectrum in the top 100 US markets. The company planned to put the mmWave spectrum to work later in 2018 as part of its mobile 5G rollout.
- In Apr 2018, AT&T and Crown Castle signed a new agreement simplifying and expanding their long-term leasing deal for wireless network infrastructure. Under the new agreement, leasing management and operations are streamlined to improve the efficiency and flexibility under which AT&T can deploy new technologies and increase network capacity. In Jun 2018, AT&T announced an agreement with Nokia to give its business customers worldwide access to develop next-generation IoT services and pave the way to global 5G networks.
- In Jan 2019, AT&T helped telemedicine take a step forward by partnering with Rush University Medical Center to create the first 5G-enabled hospital in the US. The technology is expected to speed up network communications and reduce latency to help improve care at the Chicago hospital.
- On Feb 12, 2019, AT&T and VITAS® Healthcare, the nation’s leading provider of end-of-life care, launched a study that intends to combine 5G with virtual reality and augmented reality (VR and AR) to test if it can help reduce chronic pain and anxiety for certain hospice patients.
- On Feb. 20, 2019, AT&T, Ericsson, and Intel announced that through 5G-powered location-based, mixed-reality, fans would have a chance to be virtually immersed in an experience featuring DC’s most tech-savvy Super Hero Batman and Super-Villain The Scarecrow at MWC 19 Barcelona.
- On Feb 22, 2019, AT&T announced that it is working with VMware SD-WAN by VeloCloud to implement 5G capabilities into their SD-WAN to give businesses new levels of network control. This transformative combination could be an ideal solution for businesses using SD-WAN with a high-speed, low-latency 5G network as their primary or secondary WAN connection type in combination with other transport connections.
- On Feb 25, 2019, AT&T and Vodafone Business announced at Mobile World Congress (MWC) 2019 in Barcelona that they will cooperate on the Internet of Things (IoT) applications across the automotive space, including safety, security, and entertainment.
- On Feb 26, 2019, AT&T and Microsoft collaborated to test an edge deployment model that splits the difference between network compute elements deployed in a central core and those deployed at the far network edge. The model uses the company’s term “network edge compute (NEC) capabilities” that run network traffic from an edge deployment through Microsoft’s Azure public cloud platform.
- On Mar 9, 2020, AT&T announced that Google’s cloud arm is partnering with AT&T Inc. on a suite of business products to be delivered over 5G networks. The latest tie-up between tech giants and wireless carriers hopes to capitalize on the rollout of faster connectivity. Both companies said they were testing products designed to bring software and data services to 5G customers and an initiative targeting sectors including retail, manufacturing, and transportation.
- On Sep 4, 2019, AT&T announced a new long-term agreement with American Tower Corporation to streamline wireless network deployments on American Tower’s U.S. sites to enhance AT&T’s deployment of 5G.
- On Sep 6, 2019, AT&T announced a multi-year agreement with Tech Mahindra for $1 billion that calls for the IT consultancy to assume management of many of the applications that support AT&T’s network. Tech Mahindra has been pushing deeper into the telecom sector and expects momentum to continue as 5G deployments continue worldwide.
- On May 18, 2020, AT&T announced that it is expanding its relationship with Cradlepoint to easily provide end-to-end wireless wide area network (WAN) solutions to enterprises. With the new agreement, customers can order Cradlepoint wireless edge solutions and pay the bill directly from AT&T.
- In 2021, GM and AT&T teamed up to build a high-performing 5G core network. 5G connection will debut in specific 2024 models. GM’s fifth-generation connectivity will give 4G LTE-equipped vehicles, from 2019 and later models, faster connectivity and some performance benefits of 5G-equipped vehicles cars of the future. This rollout is a key component of a bigger plan by GM and AT&T to deploy the largest fleet of 5G-enabled cars.
- In 2021, AT&T and Google Cloud unveiled new 5G and edge computing technologies. AT&T’s on-premises MEC solution and LTE, 5G, and wireline Network Edge capabilities. AT&T MEC with Google Cloud integrates AT&T’s 5G MEC with Google Cloud features. AT&T Network Edge (ANE) combined with Google Cloud will let organizations install apps at Google Edge POPs connected to AT&T’s 5G and fiber networks. Both firms are working to bring breakthrough capabilities to enterprises in retail, manufacturing, healthcare, entertainment, etc.
- In 2022, AT&T collaborated with Quintar to leverage AT&T 5G to bring exciting in-game AR experiences to sports fans in arenas and venues. AT&T is a 5G sponsor for leading sports leagues providing 5G to fans nationwide. Quintar and AT&T will test innovative applications and second-screen capabilities to engage fans in the venue.
12. Cisco Systems (US)
The US networking hardware company launched its 5G now portfolio in MWC 2018 to support 5G automation and infrastructure, which the company will support in three primary ways:
- Services – enable 5G services so service providers (SPs) can make more money;
- Infrastructure – help build the 5G infrastructure;
- Automation – Make mass scale simpler to operate.
The company knows the potential of 5G and plans to connect more than 30 billion devices in the next three years. Network hardening is a key part of 5G, and Cisco can’t afford to miss any chance.
To join the 5G wagon, Cisco also took steps by joining a network of partners to provide 5G for rural communities in the UK.
Additionally, the company introduced a 5G Security Architecture to Enable Secure Network Transformation to combine AI with deep learning to create a network that will orchestrate physical and virtual resources with equal proficiency resulting in optimal network efficiencies. With this unique approach, Cisco has successfully lowered the time to detection from the industry average of 100 to 200 days to as low as four hours.
Now, let us look at some of the developments made by Cisco to play its part in the 5G race:
2018-19
- In Jun 2018, Cisco Systems introduced the Cloud-Native Broadband Router, billing it as a “containerized, full software rewrite” of Converged Cable Access Platform (CCAP) services.
- On Feb 8, 2019, Cisco launched an ambitious rural 5G trial in the British Isles that includes 29 wireless industry partners to test enhanced mobile broadband, optical wireless (LiFi), radio broadcast over 5G, and agri-tech. The trial is part of Cisco’s 5G RuralFirst initiative to contribute to the business case for improving connectivity beyond cities.
- On Feb 24, 2019, Cisco announced that it is planning to commit $5 billion in 5G funding via Cisco financing over the next three years to help its customers’ network transition to 5G.
- On Feb 26, 2019, Japanese online marketplace Rakuten announced that it would launch its own mobile network in just eight months, thanks to hardware and software from tech giants Cisco and Nokia.
- On Aug 12, 2019, Cisco announced investing $5 billion in 5G for the next three years to focus on the enterprise side of things. “Enterprises primarily use 4G LTE as a low-speed backup for activities like point-of-sale (PoS) traffic, but the latency and bandwidth characteristics of 5G means businesses can use it as a load-balanced primary data source for connectivity and more reliable backup.” Scott Harrell, senior vice president and general manager of Cisco’s enterprise networking business.
2020
- On Feb 22, 2020, Cisco announced advancements to its IoT portfolio that enable service provider partners to offer optimized management of cellular IoT environments and new 5G use cases. New wireless technologies – such as 5G and Wi-Fi 6 – will lead to more devices and new advanced Industrial IoT (IIoT) use cases and will give service providers the tools to create competitive cellular IoT offerings for their customers.
- On Feb 25, 2020, Cisco announced the successful proof of concept for a 5G standalone (SA) network with Japan’s KDDI and boasted the benefits of its cloud-native software, which is a part of PoC. Enhanced features like network slicing are one of the advantages of 5G SA. Cisco said its Ultra Packet Core platform works alongside such enhanced features as Network slicing, NFV, and automation through Cisco’s Network Services Orchestrator.
- On Mar 4, 2020, Cisco unveiled a toolkit of solutions for 5G service providers intended to drive revenue and, ultimately, profitability from their 5G infrastructure. The suite of solutions includes new software, hardware, and flexible business models designed to support service providers’ needs for what Cisco calls the “Internet for the Future.” The Cisco Cloud Services Stack will cover mobility, residential, and content delivery, offering speed-to-market with virtualized 4G and 5G service creation.
- On May 22, 2020, Cisco announced that it upgraded its core networking software which can help provide better support for enterprise multi-cloud integration and management. Further, it will also provide tools to help telecom companies or hyper scalers tie together large-scale data-center networks. The new features are part of the 5.0 release of Cisco’s Application Centric Infrastructure (ACI) software, Cisco’s flagship software-defined networking (SDN) data-center package that runs on the company’s core data center Nexus 9000 systems.
2022
- In 2022, Cisco Systems introduced the private 5G-as-a-service system. They have been conducting customer proof-of-concept trials for quite some time. In India, IoT was one of the first use cases for private 5G. It was one of the factors that accelerated 5G public consumption in all IoT-based use cases, whether it was for factories, especially since there is a big push for manufacturing within the country, and this is something we’ve been working on with government officials for quite some time.
- In 2022, Cisco announced its first-ever private 5G service, as well as a portfolio of Wi-Fi 6E (extended) and Cisco Catalyst 9000X series designed with Cisco Silicon One to address remote working, flexibility, and security. The new enhancements will better equip partners and consumers to meet future connection expectations as the hybrid work trend takes hold. The Catalyst 9136 and Meraki MR57 are two new Wi-Fi 6E access points (APs) from Cisco. Both APs use 6E technology, which more than doubles the RF spectrum available for Wi-Fi use because the standard relies on the broader 6 GHz band, which was opened up for unlicensed use in 2020. Cisco also introduced the Catalyst 9000X family of core switches, which provide the speed, bandwidth capacity, and scale required to provide 100G/400G network access from the campus to the branch.
Partnerships and collaborations
- In Feb 2018, Saudi Telecom Company (STC) and Cisco signed a Strategic MoU to bring the benefits of 5G to Saudi Arabia and collaborate on developing 5G communication systems and networks.
- In Feb 2018, Cisco also teamed up with Airtel to improve mobile user experience by taking their SON collaboration to the next level in India.
- In Feb 2018, Cisco continued its long-standing collaboration with Rackspace to deliver advanced security for a multi-cloud environment. Many organizations are leveraging Multi Clouds because of their operational efficiencies, flexibility, scalability, and growth expansion. More than 50 percent of security professionals said they host networks in the cloud because of better data security.
- In Sep 2017, Cisco, Vodafone, Ericsson, and a number of auto technology partners, successfully drove a BMW car around a test track in Düsseldorf by remote control, connecting the operations of a remote driver to the car over a cellular network.
- On Feb 24, 2019, Cisco announced its collaboration with Sprint to deploy new routing technology to support Sprint’s growing backhaul network traffic as it prepares to launch mobile 5G service in nine cities in the first half of 2019.
- On Feb 25, 2019, Verizon and Cisco announced a partnership to build a mobile SD-WAN offering, which leverages Verizon’s future 5G network. This is the first time Cisco has brought a mobile component, on the cellular side, to SD-WAN.
- On Feb 28, 2019, Cisco announced a partnership with Fastweb on a network modernization project that will enhance the capabilities and performances of Fastweb’s fiber-based networks. This project will put the Italy-based operator in the right position to meet the growing demands of video over broadband, enterprise VPN, and future 5G traffic.
- On Mar 4, 2019, Cisco collaborated with SoftBank on the world’s first Segment Routing IPv6 (SRv6) deployment. With the anticipation of the coming 5G era, Cisco has been assisting SoftBank to deploy an SRv6 network nationwide to build a future network architecture that is extremely scalable, with improved reliability, flexibility, and agility, all while helping to reduce Capex and Opex.
- On Mar 6, 2019, Cisco and Telenor Group announced that they would expand their joint innovation across cybersecurity, the cloud, and the digital workplace and will explore Open Virtualized RAN (vRAN) solutions for 5G.
- On Oct 9, 2019, Cisco announced a collaboration with Tech Mahindra, which will help the Indian IT company to launch 5G-enabled solutions to build wireless and secure “factories of the future” to achieve industry 4.0 goals. Key highlights of the factory infrastructure space include a factory wireless network, factory-to-enterprise software-defined network, cybersecurity, and information technology-operation technology (IT-OT) integration areas.
- On Mar 10, 2020, Cisco partnered with Bharti Airtel to launch India’s largest 5G-ready, 100G IP and optical integrated network. The deployment is part of Airtel’s initiative to build a 5 G-ready network that continues to serve the growing demand for high-speed data services in the country. Cisco predicted in its Annual Internet Report that there would be 67.2 million 5G connections in India by 2023.
- In 2021, Cisco and AT&T partnered to deploy a 5G solution to serve IoT applications in the U.S. The two businesses will handle millions of connected devices using the carrier’s sub-6 GHz 5G network. These devices are used in various sectors, including utilities, manufacturing, transportation, retail, the public sector, and healthcare. AT&T’s public-private safety network, FirstNet, also uses some of these devices. AT&T’s 4G LTE IoT networks formerly serviced these devices.
- In 2022, Cisco and Tech Mahindra introduced Cisco-routed optical networking to modernize optical transport networks. The collaborative efforts aim to make Internet transport networks easier to use by combining services over an IP infrastructure using optical and routing technologies to automate them. Tech Mahindra’s knowledge in developing IP-based, software-driven end-to-end 5G connectivity paired with Cisco’s Routed Optical Networking technology would decrease network complexity for service providers.
- In 2022, Cisco and TM collaborated to provide Malaysian businesses with a private 5G network. Cisco and TM will establish a 5G-as-a-service center of excellence to help Malaysian businesses and industries start with 5G and establish proof of concepts. Cisco’s Private 5G Core technology, along with services and support, will power the private 5G network.
Conclusion
The World Economic Forum describes 5G as the Fourth Industrial Revolution. Qualcomm claims that 5G will be bigger than electricity and their prediction says by 2035, it will be worth $13 trillion to the goods and services industry.
5G is going to generate billions of dollars through unrealized revenue streams. All the telecom giants are motivated to get a hold of the upcoming wave. A lot of public/private partnerships, of which we covered the major ones, have already been witnessed, and a lot more are yet to come.
Since a lot of research is yet to be done in almost all of the areas, numerous whitespaces can be discovered. Therefore, it would be not easy, at this stage, to predict who the industry leader is going to be. However, a highly aligned business approach, research, and patent strategy will win the race.
Authored By: Vipin Singh and Neha Tanwer, Market Research.