This is the third article in our 4-part Edge Computing Market Research Series. In this article, we will discuss the top companies working on edge computing based on their research activities, number of patents, products and services related to Edge computing, and M&As.
Competitive intelligence is pretty essential for any executive to make an informed decision. As an R&D head or a C-suite executive, you would want to know — who is your competition, what these companies are up to, who are the upcoming players in the domain, all their past and ongoing M&A activity, and more.
When it comes to edge computing, while the domain is still in its infancy, a lot of work is being done by both large companies and startups in the domain. There are several players within the global edge computing market working on the technology intensively. Today, we will discuss the top 10 players in this domain, along with insights from their edge patent portfolio.
We have also converted the entire report into a pdf. To get the report in the pdf, please fill the form below:
How did we come up with the list?
We used the combination of patent data and market data. We looked through the patent portfolios of the top organizations in the edge computing domain.
From the patent analytics, State Grid Corp of China is the top company with 456 edge computing patent families. Beijing University is in the second position with 189 patent families while Guangdong Power Grid is in third place with 171 patent families.
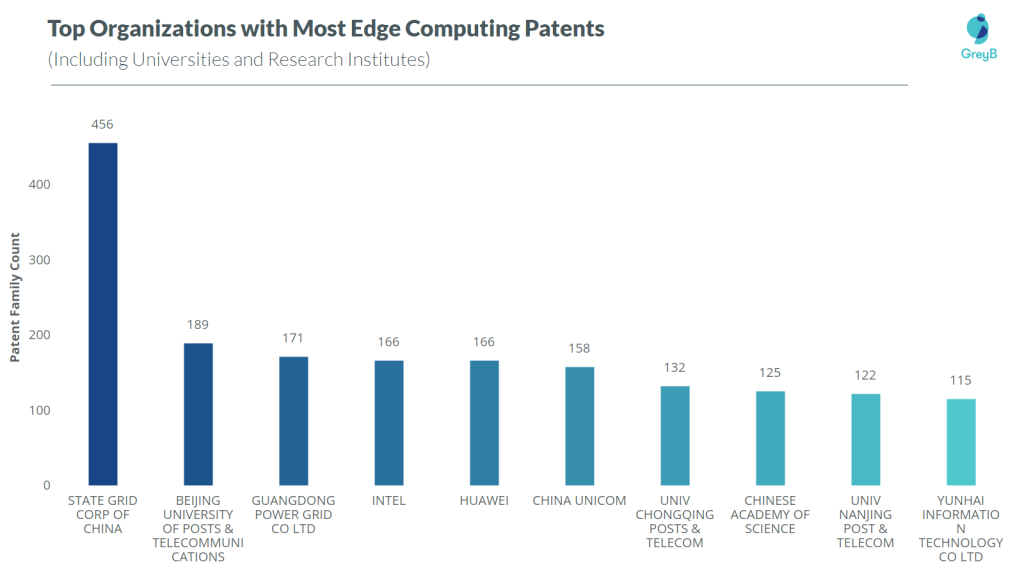
The list contains four research institutes, all belong to China, in the top 10 list. And with 9 Chinese organizations on the list, China seems to be leading in terms of patents.
If we exclude the research institutes in the top 10 list, Samsung and Verizon take places in the list.
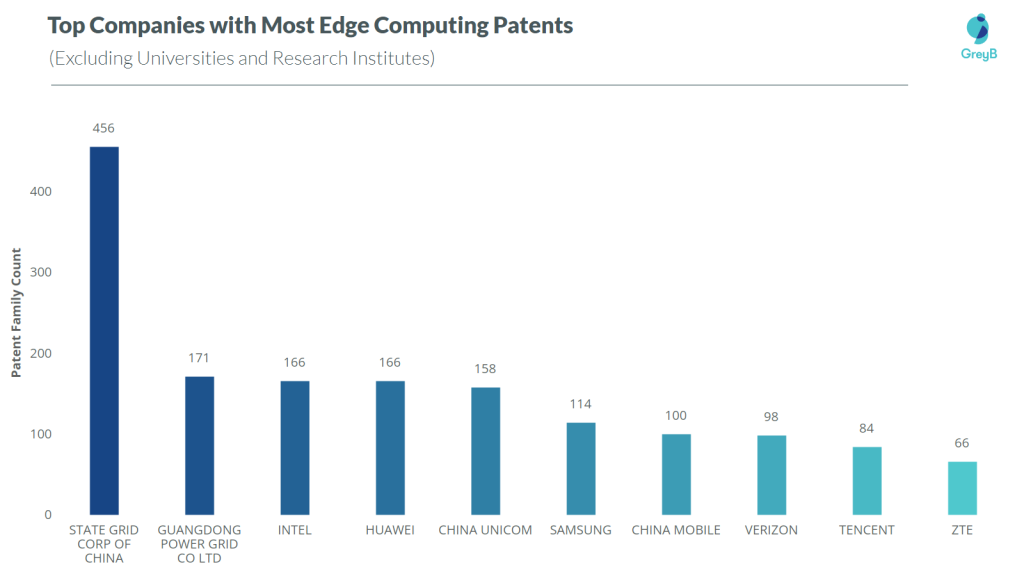
These are the top 10 companies leading in Edge Computing.
Not only companies, but Chinese research institutes are also heavily filing patents in edge computing or its applications. Here are the top 10 research institutes in terms of patent family count to give you an idea.
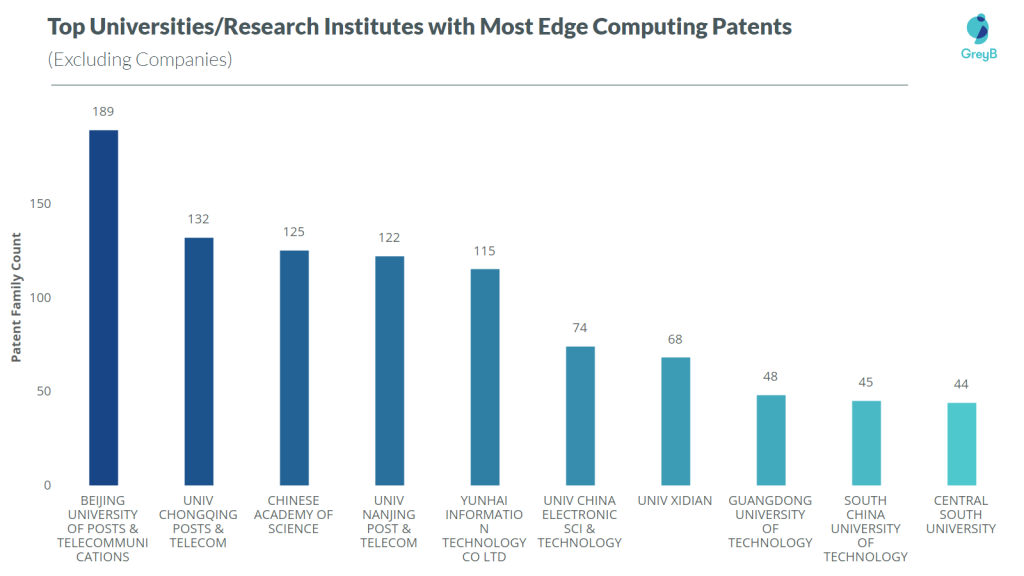
These are the top 10 universities with the most edge computing patents and all of them are Chinese.
So, in terms of patents, China companies and universities are miles ahead in Edge computing technology and its applications.
Methodology to get Patent Data
As a first step we gathered various concepts that are related to Edge computing. For example – edge server, cloudlet, fog computing, etc. are some of the terminologies that resonate with edge computing.
We used these terminologies to formulate search queries and logics, and used commercial databases to extract the patents filed globally related to Edge Computing.
Once we had the patent data, after some filtration and removing irrelevant results. We were able to find answers to questions like:
- Which companies are innovating the most?
- How many of these top entities are Universities and research institutes?
- From which countries the innovations are originating from?
- How has the patent filing evolved over the years, important patents, etc.
But then again, patents don’t show the complete picture but an important portion. That’s where market data comes into play.
With the intense market research along with the patent insight, we were able to identify companies best in providing edge computing solutions.
The top 10 edge computing are given below:
IBM
IBM has been working on Edge Analytics for the past few years that deal with deploying ML models, Neural Nets, and Data Analytics at the edge. It has also developed IBM Watson Studio which is a tool for data scientists to visually design their neural networks and experiment with the training data using the NVIDIA Tesla V100 GPU with a preferred deep learning framework, which can then easily be deployed to the cloud or at the edge.
As per the patent data, IBM has the 7th most Edge computing-related patents. Some of the patents filed by IBM discuss solutions for particular challenges faced in Edge computing.
For example, IBM filed a patent (US20200293914A1) which solves the challenge of determining the set of instructions for edge computing networks in absence of network connection to the cloud server. The invention proposes using a local neural network to predict an action for the edge computing device under a certain confidence threshold. This output is further converted into instructions using natural language processing.
Products or Technologies
Below listed are the products and technologies IBM is working on in the field of edge computing.
IBM Edge Application Manager – It is an automated platform providing real-time research for AI, analytics, and IoT operations that are positioned, and managed in remote areas. It is an advanced, stable, and adaptable platform that manages edge computing by itself. (Source)
IBM Maximo Visual Inspection – It makes artificial intelligence more accessible to business users through deep learning. It analyzes data at the edge, allowing for a quicker response time to advanced analytics. The software can be easily integrated into edge devices and can be operated with high efficiency. (Source)
IBM Maximo Visual Inspection Mobile – It is an edge computing device that helps deliver customized machine learning data insights to the edge. (Source)
IBM Cloud Pak for Network Automation – It is an AI-powered Telco cloud platform allowing network operations to be automated so that service providers can transform their networks, minimize expenses and deliver faster services. (Source)
IBM Cloud Pak for Data – The edge analytics on the Cloud Pak for data keeps the data close to the devices where it is being generated rather than getting stored far away from a centralized location. (Source)
IBM Storage – The Storage systems are designed to bring AI systems to function at the edge and enable market insights for all forms of data, including the influx of live visual information produced at the edge. (Source)
IBM Power Systems & AI Solutions – It is an IT network that uses AI solutions to provide market insights at the edge with diverse workloads. It allows good AI deduction capabilities in the possession of IBM Visual Insights and IBM Visual Inspector experts running on the POWER 9 processor. (Source)
IBM Edge Architecture – The edge computing architecture helps in managing all the connected edge computing devices securely.
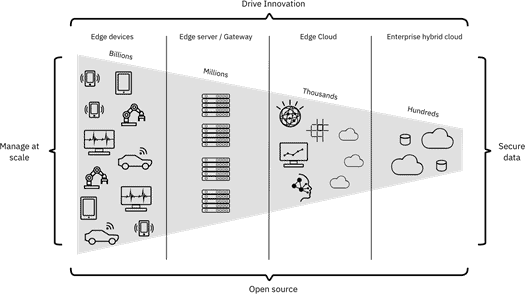
IBM EDGE COMPUTING ARCHITECTURE
The IBM Edge Computing Architecture follows four principles which are as follows:
Securing user data – IBM edge computing devices secure the data generated by the industries while reducing the risk factors by keeping the data at the edge of the network.
Innovative solutions – IBM continuously innovates new products. The Edge Application Manager offers a wide range of services such as Watson AI, IVC, and IoT. It also allows the users to do machine learning and deep learning at the edge of the network.
Portable solution with open-source technology – IBM created an open-source technology to help applications run on the edge of the network, and allow these applications to easily move from one system to another.
Managing a wide range of devices – IBM edge computing products help in managing edge workloads at a wide scale. (Source)
Collaborations
- In 2021, IBM collaborated with the HPE Spaceborne Computer-2, ISS National Lab, NASA, and University of California to provide custom edge computing solutions for DNA sequencing on the International Space Station (ISS). IBM is using edge computing to deliver an analysis of large data in real-time on the International Space Station (ISS). This is done to avoid moving the data to earth for results. (Source)
- In 2021, FogHorn and IBM collaborated to provide AI-based solutions at the edge of the network. With Red Hat OpenShift, the combined approach was used to operate and handle workloads on nearly any edge endpoint, including computers, clusters, servers, gateways, and machines that support Linux operating systems. (Source)
- In 2021, IBM and Siemens entered into a collaboration where Siemens would develop its MindSphere IoT software on IBM’s hybrid cloud platform. Siemens stated that this collaboration is a pathway to help build its edge computing network. (Source)
- In 2021, IBM and Acromove Inc. entered into a collaboration. This partnership allowed IBM’s Cloud Computing AI, 5G, and IoT applications to run smoothly on Acromove’s range of edge computing products “Edge Cloud in-a Box” (ECiB). The product range of Acromove includes ServerPack Edge, BladePack Edge, and NetPack Edge. (Source)
- In 2020, Samsung and IBM collaborated to develop edge computing, 5G, and hybrid cloud solutions. The organizations planned on combining Samsung’s 5G end-to-end solutions and IBM’s hybrid cloud technologies and edge platform network to help companies across different industries modernize operations. (Source)
- In 2020, Mimik Technology, a hybrid edge cloud developing organization collaborated with IBM to create AI-enabled integrated workflow technologies and make edge computing more attainable for the manufacturing, retail, IoT, and healthcare industries. (Source)
- In 2020, IBM and ClearBlade collaborated to offer edge computing and IoT solutions. Using the IBM Edge Application Manager and ClearBlade Edge Platform the companies aimed to create end-to-end edge computing solutions for engineering logistics, healthcare, and other industries and help businesses work on the edge and gain real-time results. (Source)
- In 2020, IBM and Verizon collaborated to develop 5G and edge computing solutions. The combination of Verizon’s 5G technology and IBM’s skills AI, multi-cloud and edge computing tech aimed to help customers identify, track, and react to system failures in near real-time. (Source)
- In 2020, IBM and AT&T entered into a collaboration enabling IBM’s edge computing solutions to work on AT&T’s 5G network. IBM recently launched its “Cloud Satellite” service using edge computing and as a result of the collaboration, the cloud satellite customers get access to AT&T’s 5G network and Multi-Access Edge Computing (MEC) offerings. (Source)
- In 2020, IBM and CISCO collaborated to develop the IBM Edge Application Manager using components from both CISCO and IBM. (Source)
- In 2020, EuroTech and IBM collaborated to use the applications developed with IBM’s Edge Application Manager and install them on EuroTech devices offering data scientists and developers teams more efficient access to IoT data, allowing them to develop, deploy, and manage AI-enabled edge applications. (Source)
- In 2020, IBM collaborated with Hazelcast, an open-source in-memory computing platform. This collaboration helped the customers benefit from a versatile, low-latency edge computing solution that incorporates IBM Edge Application Manager and IBM Cloud Pak for Applications as the control plane and the Hazelcast In-Memory Computing Platform as the data plane. (Source)
- In 2020, IBM and Equinix collaborated to use the IBM Cloud Pak and Equinix metro-edge, creating a hybrid multi-cloud that allows the applications to run at the edge of the network. (Source)
Mergers and Acquisitions
In 2019, IBM acquired Red Hat, one of the leading providers of open-source solutions delivering high-performing Linux, cloud, container, and Kubernetes technologies. The value of this acquisition was approximately $34 billion. After the merger, IBM launched its edge computing solutions platform which was going to be operated on the Red Hat OpenShift platform. (Source)
Intel
Intel has been working under the radar in edge computing tech, and through a series of strategic moves, it has stealthily become a player to watch for in the domain. Apart from releasing several SoCs related to Edge computing, Intel made some strategic acquisitions which helped the company get an edge in edge tech.
In 2019, Intel acquired the smart edge intelligence-edge platform business from Pivot Technology solutions which is a cloud-native, scalable and secure platform for multi-access edge computing (MEC). The expansion of computing at the edge is an important growth opportunity for the chip giant — as it is estimated to become a $65 billion market by 2023.
In terms of patents, as a US company, Intel has the most number of patents in edge computing. Given its chipset business, most of these patents are particularly related to Edge computing hardware solutions. One of those patents, for instance, is EP3734453A1 which suggests methods for identifying, obtaining, and composing required hardware for edge computing platforms. The patent describes how to design and integrate a disaggregated chipset for modular Input-Output in Edge Computing.
Products or Technologies
Below listed are the products and technologies Intel is working on in the domain of edge computing.
Movidius Neural Compute Stick – It is the world’s first USB-based machine learning prediction device and self-contained artificial intelligence (AI) accelerator that offers a wide variety of host edge devices with specialized deep neural network computing capability. (Source)
Intel Xeon Processors – With a strong and flexible foundation of edge computing, it can manage real-time analytics, AI, and other challenging workloads. In 2018, Intel launched its Xeon D -2100 processors designed specifically for edge computing needs. (Source) (Source)
Intel Core and Intel Atom Processors – These processors have a wide range of options that combines efficiency and performance while supporting real-time AI and analytics at the edge. In 2020, Intel launched the 11th Gen Intel Core processors and Intel Atom x6000E series offering artificial intelligence, real-time deductions, and security to edge users. (Source)(Source)
Intel Movidius VPU – It offers incredible deduction capabilities to smart cameras, drones, and other edge devices with machine learning and artificial intelligence. The Intel Movidius Myriad X VPU is a dedicated hardware accelerator for deep neural network inference. (Source)
Intel FPGAs – Intel offers wide-ranging capabilities in security, I/O, and networking offering value in high-throughput and low-latency applications. Some of the processors in this segment are Intel Agilex FPGAs, Intel Stratix Series, Intel Arria Series. (Source)
5G Technology – Intel’s combination of 5G and Edge computing will allow data centers to stay close to the end-user devices improving the quality of experience, reducing latency, and providing fast data transfer. (Source)
Intel Optane Solid State Drive (SSD) – It helps to reduce the inefficiencies in data center storage and facilitates a larger, more accessible collection of data. It increases overall data center efficiency by speeding up processes, lowering processing costs for latency-sensitive workloads, and accelerating applications. (Source)
Intel OpenVINO – It is a free toolkit enabling deep learning inference from edge to cloud and AI workloads such as machine vision, audio, speech, language, and suggestion systems are all accelerated. (Source)
OpenNESS – It is a Multi-Access Edge Computing (MEC) software toolkit that optimizes dynamic edge service management through a range of network platforms and network applications. (Source)
Intel Smart Edge – It is a multi-access edge computing platform offering low latency, better security commercialized for on-premise business sector use cases. (Source)
Intel DevCloud for the Edge – It is a virtual AI prototyping tool allowing users to run and test edge workloads on Intel hardware. (Source)
Intel Deep Insight Network Analytics Software – It is the world’s first monitoring system that offers complete access to every packet in the network and server offering the ability to detect and report problems in real-time with high accuracy. (Source)
Collaborations
- In 2021, Intel and Google cloud collaborated to develop 5G technology across different platforms using edge computing. The collaboration aimed to help different industries such as manufacturing, retail, and healthcare by accelerating the 5G network and edge applications in multi-cloud frameworks. (Source)
- In 2021, Lanner Electronics launched its Edge AI Starter Kit for industrial automation. Lanner Electronics collaborated with Intel and developed the product using Intel Edge Insights software. The LEC-2290 was designed to endure harsh conditions allowing it to compute-intensive AI applications at the industrial edge. (Source)
- In 2021, Hitachi collaborated with Intel and developed an edge computer, “Hitachi Industrial Edge Computer CE series Embedded AI model” allowing productive on-site job allocation, as well as workforce automation and savings. (Source)
- In 2020, Wipro collaborated with Intel to develop 5G solutions using edge computing to help industries by offering applications close to the source of the data, increasing business efficiency. Wipro also offered customer support services for Intel’s OpenNESS Multi-Access Edge Computing (MEC) software toolkit. (Source)
- In 2020, China mobile IoT collaborated with Intel and launched Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) servers with the Intel Visual Cloud Accelerator Card – Analytics (VCAC–A) allowing high processing capabilities and strong deep learning inference capabilities for machine vision at the edge of the network. (Source)
- In 2020, Intel and Red Hat collaborated to pair Red Hat OpenShift, Kubernetes platform, and Intel’s wide range of software and tools such as Intel Xeon processors, Intel Ethernet Network Adapters, FlexRAN software, and OpenNESS (Open Network Edge Services Software) edge computing software toolkit to accelerate the innovations of 5G service from hybrid cloud networking to edge computing. (Source)
- In 2020, Altran and Intel collaborated to develop the ENSCONCE edge computing platform integrated with the Open Network Edge Services Software (OpenNESS), an open-source toolkit developed by Intel. This platform was developed to increase computing and I/O performance and reduce network latency. (Source)
- In 2020, Intel collaborated with Baidu to bring innovation in the area of 5G and edge computing. The companies had developed an edge computing solution using the OpenNESS toolkit developed by Intel and Baidu IME (Intelligent Mobile Edge) which offers AI capabilities for low latency applications. (Source)
- In 2019, Intel collaborated with Ericsson, AT&T, and Warner Bros. to offer innovative 5G technology solutions combined with edge computing making advancements in augmented virtual reality. (Source)
- In 2019, Edge computing systems based on Intel’s Xeon processors were developed in collaboration between ZTE and Intel. This processor aided ZTE in the creation of their Light cloud solution. It provides powerful processing and network services at the network’s edge. (Source)
- In 2018, Arrow Electronics collaborated with Intel and developed an edge-computing standard called Ambient Science. It was developed to serve multiple applications in smart cities, smart buildings, and Industrial IoT. (Source)
- In 2018, Intel and Alibaba collaborated to launch a joint edge computing platform. It was developed using components of both the companies to transform information at the edge into business insights. (Source)
- In 2018, Intel and Tencent teamed up to create AI applications that run from the cloud to the network’s edge. The firms had developed new solutions for stretching the cloud to the network’s edge and address problems including latency and high data costs. (Source)
- In 2017, Intel collaborated with Ericsson and Toyota to develop edge computing solutions used in connected vehicles. The companies collaborated to use edge computing to collect and analyze data used in automated vehicles. (Source)
- In 2017, Intel and Dahua Technology collaborated to develop an AI-enabled surveillance camera with the capabilities of analyzing, and retaining information similar to a human brain. The Dahua 2 MP High-Definition box camera was equipped with Intel’s Movidius Myriad 2 (VPU), a processing unit made from edge computing giving the camera capabilities such as crowd density monitoring, stereoscopic vision, facial recognition, people counting, etc. (Source)
Mergers and Acquisitions
- In 2019, Intel acquired the edge computing platform, the Smart Edge Technology from Pivot Technology. Intel acquired the software business for approximately $27 million. The company aimed to combine Smart Edge with its technologies and help communications service providers offer cloud-like services closer to the users. (Source)
- In 2016, Intel acquired Movidius, a chip designing company that made vision processors used in drones and VR devices. The acquisition was estimated to be approximately $400 million. In 2017, Intel launched its Movidius processors using edge computing technology. (Source)
Huawei
Huawei is a leading 5G company that holds the most Core 5G SEPs, as per GreyB Essentiality Check Report.
This gives the company an edge over other companies, no pun intended. The company holds the most patents for edge companies and its edge portfolio, which is further strengthened by its in-house technical expertise and collaborations with other players.
In 2017, Huawei launched the Edge-Computing-IoT (EC-IoT) Solution which allows edge nodes to provide intelligent services nearby and implements network management in the cloud. Until now, the EC-IoT Solution has been applied to the elevator network, power IoT, city and lighting IoT, smart energy, smart manufacturing, engineering machinery, and the Internet of Vehicle (IOV).
Its 400 patents discuss many solutions for different challenges. Some of them are related to the efficient deployment of application programs between all levels of edge computing platforms. For this, Huawei filed a patent application US20200218590A1 which suggests creating a global application platform containing the data of applications at all edge levels. This further helps in sending data from the second edge computing platform to first and then back again, thereby deploying application programs between all levels of edge computing platforms.
Products or Technologies
Huawei Edge Computing – IoT (EC– IoT) – The solution allowed edge nodes to send intelligent applications nearby and integrated network management in the cloud with the company’s SDN -based Agile Controller and edge computing IoT gateways (AR500 series). The solution also helped add edge computing and cloud-managed platforms on IoT-based devices. (Source)
Huawei Atlas 500 Pro AI Edge Server – It is a device used for edge applications. This server offers cloud-edge collaboration, superior computing performance, and excellent adaptable capabilities. It can be implemented at the edge of the network to meet the requirements in diverse situations such as retail stores, shopping areas, transportation, etc. (Source)
Huawei AR502H Series – This device is an Edge Computing – Internet of Things (EC–IoT) gateway. It offers superior edge computing experiences, Computer Development Kits, as well as free software and hardware tools for more flexible computing, storage, and networking environment. (Source)
Huawei 5G MEC – The company launched its next-generation multi-access edge computing solution, Clover. It brings application resources and content closer to customers and enables network integration, ensuring that users have a consistent and excellent experience. (Source)
Huawei iMaster MAE -CN – In situations involving Multi-access edge computing, it combines management and monitoring, cloud-edge teamwork, and organizational autonomy with big data processing, intelligent decision-making, and automated closed-loop control to provide an automatic driving solution. (Source)
Collaborations
- In 2017, Huawei and China Mobile Beijing collaborated to develop a smart stadium at the Beijing South railway station. With the help of the Huawei edge computing solution, China Mobile was able to incorporate video sources into the edge gateway of the smart stadium. This allowed the users to benefits like low-latency, low freeze rate, and ultra-HD video quality only available in the stadium. (Source)
- In 2017, Huawei collaborated with Infosys and Wapwag to develop and released innovative technologies such as smart robots, machine tools, and smart water affairs solutions using the open edge computing IoT and applied those technologies to different industrial applications. (Source)
Amazon
As one of the top providers of cloud computing, it isn’t surprising that Amazon is also a leading company of Edge computing despite having fewer patents related to the technology. However, Amazon has enough technical expertise and sources to develop an Edge portfolio for providing “A to Z” edge computing solutions. Let’s have a look at some of them.
Products or Technologies
AWS wavelength – It is an AWS framework that allows creators to develop applications with very low latency for cellular devices. The edge computing platform uses regular AWS computing and storage facilities at the edge of 5G networks for telecommunication carriers. (Source)
AWS Snowcone – It is a portable edge computing data transfer device. The Snowcone is used to enable applications at the edge, collect and process the data, and move that data to AWS without staying online. (Source)
AWS Outposts – AWS Outposts is a fully managed solution that offers a seamless hybrid experience, to nearly every data center, co-location space, or on-site facility. AWS Outposts are suitable for workloads that include connections to on-site systems, local data processing, or local data storage with low latency. (Source)
AWS Local Zones – It is an edge computing service where developers can run applications with ultra-low latency close to the end-users. AWS Local Zones are suitable for use cases like production of media & entertainment content, real-time gaming, live video streaming, and inference from machine learning. (Source)
AWS Storage Gateway – It is hybrid storage offering unlimited cloud storage. Consumers use Storage Gateway to ease storage management and lower costs. This involves transferring backups to the cloud, using cloud storage-backed on-site file shares, and offering low latency access to AWS data for on-site applications. (Source)
Amazon CloudFront – It is a worldwide content delivery network (CDN) platform that provides customers with low latency and fast transmission rates seamlessly via files, images, games, and APIs. (Source)
AWS Snowball – It is an edge computing, data transfer, and edge storage device. This device can be used to collect, process, and store data for different industries or in remote locations. (Source)
AWS RoboMaker – An application for robotics developers to create, prototype, and model robotics applications before launching them to the edge. (Source)
Amazon SageMaker Neo – Developers can prepare machine learning models and run them anywhere in the cloud or at the edge with Amazon SageMaker Neo. It enhances the prototypes to run at high speed with no loss in accuracy. (Source)
Amazon SageMaker Edge Manager – It is a software agent that runs on edge devices. It helps the users to optimize, secure, monitor, and maintain ML models on edge devices. (Source)
Amazon Monitron – It is an integrated device that uses machine learning (ML) to detect irregular activity in industrial machinery, allowing the user to perform proactive analytics and eliminate unscheduled downtime. (Source)
AWS Panorama – It is a machine learning system and Software Development Kit (SDK) that enables businesses to introduce computer vision (CV) to on-premises cameras and make predictions with high accuracy and low latency.
AWS IoT Greengrass – It is an open-source edge platform and cloud service for the Internet of Things (IoT) that aids in the development, deployment, and management of system apps. (Source)
FreeRTOS – It is web-based real-time software for microcontrollers that makes it simple to program, deploy, stable, link, and control lightweight, low-power edge devices. (Source)
AWS IoT Core – It lets users connect IoT devices to the AWS cloud without the need to manage servers. The AWS IoT Core lets the users keep track of all the devices even when it is disconnected.
AWS IoT SiteWise – It is a regulated platform that collects, stores, organizes, and monitors the data from industrial equipment in large volumes and helps make better data-driven decisions.
Collaborations
- In 2021, Telstra and Amazon Web Services (AWS) collaborated to integrate the edge computing solutions of AWS into Telstra’s 5G network enabling network applications on 5G devices to access cloud services operating at the edge of the network. (Source)
- In 2020, Amazon Web Services (AWS) and SK Telecom collaborated to launch a 5G cloud service that assists edge computing workloads allowing companies to develop applications requiring low latency. (Source)
- In 2020, NXP semiconductors collaborated with Amazon Web Services (AWS) to integrate the edge and cloud computing services with NXP’s new S32G vehicle network processor for automatic vehicles. (Source)
- In 2020, Amazon Web Services (AWS) collaborated with Mimik Inc. to offer a hybrid edge cloud platform to developers across different industries to develop applications using edge devices and AWS facilities. (Source)
- In 2020, Amazon Web Services (AWS) collaborated with Megh Computing, Carnegie Mellon University’s Living Edge Lab, and Federated Wireless to offer visual analytics solutions on 4G/5G networks for business and educational campuses using edge computing. (Source)
- In 2019, Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Vodafone collaborated to use the AWS Wavelength, the edge computing platform developed by AWS on its 5G network. Vodafone and AWS introduced a new incubation program Vodafone Business Edge Innovation Program (EIP), a 3-month program allowing start-ups, developers, and businesses to get access to the edge computing training and develop 5G applications on the AWS wavelength and Vodafone 5G platform. (Source)
- In 2019, Molex collaborated with Amazon Web Services and Accenture to incorporate edge computing on the Molex Automotive Ethernet Network Platform. This platform offers an automatic vehicle communication facility for automotive manufacturers. (Source)
- In 2019, Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Verizon collaborated to use the AWS Wavelength and introduce edge computing on its 5G network where developers can experiment with the developed applications on ultra-low latency. (Source)
- In 2019, Amazon Web Services (AWS) and KDDI collaborated to develop edge computing services on KDDI’s 5G network. KDDI is one of the many telecom operators incorporating AWS wavelength on its network. (Source)
- In 2017, Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Nokia collaborated to introduce new 5G and edge computing solutions for their customers. (Source)
Just like Amazon, Google also took a venture from the cloud to the edge and is now considered one of the leading players in technology. Google, like Amazon, isn’t on the top patent count list, however, its edge portfolio could provide a complete solution as the company actively participates in 5G and IoT technologies through several collaborations with various companies.
Let’s have a look at some of the products and collaboration efforts by Google in edge computing.
Products or Technologies
Google Edge TPU – It is a new hardware chip that allows artificial intelligence (AI) to run on the edge accurately. This product uses edge computing to fulfill growing needs such as consumer privacy, ultra-low latency, and rise in connected devices. The Edge TPU is applicable in a wide range of uses such as predictive maintenance, anomaly detection, machine vision, robotics, voice recognition for different industries. (Source)
Google Cloud IoT Edge – It is software that uses edge computing to expand the machine learning and data processing capabilities of Google cloud and enable its uses on gateways, cameras, and end devices making the applications faster, secure, and more reliable. (Source)
Google Anthos – It is a hybrid multi-cloud platform for developing applications on the network. Anthos at the edge helps in bringing the applications closer to the users offering high performance with low latency ensuring the businesses are compatible in different locations and can be accessed globally. (Source)
Google Coral – It is a machine learning platform for edge applications. It helps the users develop their own devices using the local AI. This platform also helps in providing hardware acceleration on edge devices. (Source)
Collaborations
- In 2021, Google and Intel collaborated to develop edge computing services using Intel’s compute optimization strategies and designs. By accelerating the 5G network and edge technologies in multi-cloud frameworks, the partnership is planned to assist numerous sectors such as engineering, hospitality, and healthcare. (Source)
- In 2021, Google and TELUS collaborated to develop 5G and Multi-Access Edge Computing services using the Google Anthos platform. These services are expected to expand TELUS’s reach in wired and wireless services across different businesses such as security, agriculture, and healthcare. (Source)
- In 2020, Google Cloud collaborated with AT&T to enable different businesses to use Google’s edge computing solutions on AT&T’s 5G network. The aim was to help businesses move the data and applications from centralized data centers to the edge of the network and operate those applications closer to the end-users with ultra-low latency, better security, and a better end-user experience. (Source)
- In 2020, Google and Orange collaborated to develop edge computing services. The partnership was projected to support businesses across Europe such as retail, gaming, etc., and meet the requirements of low latency and fast services. (Source)
- In 2020, Google Cloud and Telefónica collaborated to make developments in 5G edge computing. The two companies are developing a collection of 5G solutions using Google Cloud’s Mobile Edge Computing platform. (Source)
- In 2020, Litmus and Google collaborated to develop edge computing solutions for different industries using 5G and Google Cloud. Using the edge computing solutions creators can use the 5G devices to operate advanced AI-based visual observations. (Source)
- In 2020, ClearBlade and Google collaborated to incorporate edge data on the Google Cloud Pub/Sub services. This platform will help businesses connect different types of devices and process the data with edge computing. (Source)
- In 2020, Google Cloud and Amdocs collaborated to focus on developing new 5G edge computing solutions to support telecom operators to incorporate 5G networks on the edge. (Source)
- In 2020, Google Cloud and Theta Labs collaborated to use edge computing on its video streaming platform and reach viewers in remote areas where video streaming was inaccessible. (Source)
- In 2020, Google entered into a partnership with Telecom Italia to widen its public, private, and hybrid cloud service offerings, as well as provide edge computing services for all the different industries based in Italy. (Source)
Microsoft
Microsoft is a leading cloud computing company, but unlike Amazon and Google, Microsoft owns a fair number of edge computing patents in its portfolio, most of which discuss solutions to the challenges faced in the industry.
One of Microsoft’s patents, for instance, WO2020214409A1 provides a solution to dishonest or fake users subverting the foreign language lesson application by avoiding or bypassing the call to the trusted metering application. This is due to loopholes in security as well as a monitoring system. The invention proposes a method for metering execution of an application module and securing transmission of workload packages in an edge computing device. This is done by creating a unique provisioning service authentication token for every particular application package.
Along with its patents, Microsoft also has a range of products dedicated to edge computing. Azure IoT Edge, for instance, is a fully managed service built by Microsoft for the users to deploy cloud workloads, artificial intelligence models, business logic, and the Internet of Things (IoT) on edge devices via standard containers. Tools like Azure Defender are exclusively designed and upgraded from time to time to ensure end-to-end threat protection on the edge servers.
Products or Technologies
Below listed are a few more products and technologies developed by Microsoft in the domain of edge computing.
Azure SQL Edge – It is an edge-optimized SQL database engine with a pre-installed AI. This product lets the user choose a platform, manage real-time data analysis at the edge, and make real-time data deduction at the edge using the Open Neural Network Exchange (ONNX) framework.
Vision AI DevKit – It was configured to run containerized Azure resources locally and transfer tasks to the network edge. The device was developed using a Qualcomm Visual Intelligence Platform for accelerating the hardware of AI along with eInfochips, a leading provider of design services in vision-based AI and the Edge to Cloud services. (Source)
Microsoft HoloLens 2 – It is an edge computing device that is very flexible as it can be operated offline as well as connected to any cloud. When it is connected to Microsoft Azure, it can be accessed from any device or platform. (Source)
Microsoft Azure Stack edge – It is a cloud-managed, AI-enabled edge computing device with the capabilities of storing and transferring the data into Microsoft Azure. It helps the businesses to run workloads close to the source of the data, enhancing the processing times, reducing latency, and conserving bandwidth. (Source)
Microsoft Azure Edge Zones – It is an Azure extension with a limited range located in populated areas. The Azure edge zones help the developers to run applications close to the end-users offering low latency and high throughput. These edge zones are useful for streaming games, content delivery, and real-time analytics. (Source)
Azure IoT Edge – Azure IoT Edge is an Internet of Things (IoT) service that expands the IoT Hub and allows users to perform edge computing. It offers low latency decision-making, offline operating facilities, and real-time results. (Source)
Azure Sphere – It is a microcontroller used at the edge computing nodes. It was built with the ability to process data in real-time with the capability to run a high-level operating system. It also helps in securing the user data with multiple layers of protection. (Source)
Collaborations
- In 2021, Microsoft, Hewlett Packard Enterprise, and NASA collaborated to develop an edge computing device, Spaceborne Computer -2 for the astronauts in the International Space Station (ISS) to help make faster assumptions based on the data generated and speed up the workloads. (Source)
- In 2021, Microsoft and Singtel collaborated to offer solutions incorporating the 5G edge computing platform developed by Singtel on Microsoft’s Azure cloud platform. This collaboration is projected to help businesses run applications such as automatic guided vehicles (AGV), drones, robots, and virtual/augmented reality near the users at high speed and in low latency. (Source)
- In 2021, Microsoft collaborated with Dell to develop an edge computing platform using the Azure IoT Edge and Dell’s edge gateways. The goal of the collaboration was to minimize the latency issues while transferring data to the cloud from the edge. (Source)
- In 2020, Microsoft announced a collaboration with Qualcomm to help enhance the AI and Machine learning experience of the developers. Microsoft also recently launched their edge computing product Vision AI DevKit which uses the Qualcomm visual Intelligence Platform. (Source)
- In 2020, Microsoft and Verizon collaborated to combine Azure edge services and Verizon’s 5G edge network to provide edge computing solutions that will help organizations deliver high-speed 5G applications and analyze data in ultra-low latency. (Source)
- In 2020, Microsoft and Fujitsu announced a collaboration to incorporate the edge computing solutions of Microsoft on Fujitsu’s private 5G networks. This collaboration was projected to help the users process and analyze data in real-time using edge computing. (Source)
- In 2020, Microsoft collaborated with Arm Ltd. to deliver Azure edge products for the developers using Arm-based processors and AI solutions on their edge computing devices. (Source)
- In 2020, Samsung and Microsoft entered into a collaboration to combine the Multi-access edge computing technologies of Samsung into the Azure devices and bring innovations using edge computing and lowering the entry barriers for retail stores, smart factories, and entertainment venues in using 5G networks in their systems. (Source)
- In 2020, Microsoft and Telkomsel collaborated to incorporate AI-based edge computing solutions for different industries. This collaboration was done to help customers in remote areas get access to internet connectivity and AI solutions using Azure Stack Edge. (Source)
- In 2020, Microsoft and Etisalat collaborated to develop an edge computing solution by combining edge computing with the 5G network enabling the development of different types of applications related to smart cities, automatic systems, gaming, AR/VR, IoT, and vision computing solutions. (Source)
- In 2020, SK Telecom and Microsoft collaborated to incorporate the Azure public cloud platform with the 5G network and mobile edge computing services of SK Telecom to develop 5G-based mobile edge computing solutions that offer low latency for the connected mobile devices. (Source)
- In 2020, Microsoft and CISCO entered into a collaboration to develop technologies and solutions related to IoT and edge computing. The solutions were projected to help manage a large amount of data at the edge of the network. (Source)
- In 2019, Microsoft and NVIDIA collaborated to develop technologies related to edge computing to help organize the rise in data from retail stores, warehouses, manufacturing facilities, connected buildings, urban infrastructure, and other environments. (Source)
- In 2019, D-Link and Microsoft entered into a collaboration to offer smart city solutions using the edge computing services developed by Microsoft such as the Azure IoT Edge and Vision AI developer kit. (Source)
Mergers and Acquisitions
- In 2020, Microsoft acquired Affirmed Networks for ~$1.35 billion. Affirmed Network offers a software platform known as network function virtualization which allows mobile users to depend upon off-the-shelf servers to look after different network-related functions. Microsoft had planned to use this platform to introduce its edge computing services for cellular device users. (Source)
- In 2019, Microsoft acquired Express Logic, a company specializing in real-time operating systems (RTOS) for IoT and edge computing devices. The acquisition helped Microsoft use Express Logic’s ThreadX backed devices for developing edge computing solutions. (Source)
Ericsson
Ericsson is a leading 5G company that directly competes with players like Huawei and ZTE. The company which is a leading player in 5G and other telecommunication technologies, has accrued a solid patent portfolio to make it to the list of top players in edge computing.
Let’s have a look at what it has been up to in the edge computing domain.
Products or Technologies
Ericsson Edge NFVI (Network Functions Virtualization Infrastructure) – The platform was designed to transfer traffic across a distributed network at the edge of the network providing low latency, low cost, and high throughput 5G use cases. It has a compact design that allows it to run cloud applications and virtual network functions on this platform. This also makes the platform very flexible. (Source)
Edge Gravity – The Edge Gravity Unified Delivery Network was an edge cloud platform that was developed in collaboration with broadband service partners to offer the next generation of edge-scale applications across specific industry lines of business. It was launched in 2018 but in 2020 Ericsson closed this unit as it did not meet the key targets set by the company. (Source)
Collaborations
- In 2021, Ericsson and T-Systems collaborated to develop an integrated campus network solution using Ericsson’s campus network infrastructure and T-Systems’ edge computing technologies. This collaboration was aimed to solve the connectivity requirements of various organizations with high throughput, low latency, and increased security. (Source)
- In 2021, Ford collaborated with Ericsson to improve its production. In this collaboration, Ericsson offered its edge computing, advanced robotics, and artificial intelligence technologies to improve the efficiency of the Ford warehouses by optimizing distribution and logistics channels. (Source)
- In 2020, Ericsson collaborated with Qualcomm Technologies and NVIDIA offering VR solutions using edge computing. The VR solution comprised of 3 components: the Qualcomm Snapdragon XR2 5G head-mounted device (HMD), NVIDIA’s RTX graphics processing unit (GPU), CloudXR and GPU virtualization software, and Ericsson’s high performance 5G network connecting the device on the edge and providing high speed, low latency, ultra-reliable wireless connectivity. (Source)
- In 2020, Ericsson and Telstra collaborated to develop an enterprise edge cloud solution for the Telstra network. This collaboration was projected to bring innovations across different industries such as agriculture, industrial IoT, enterprise branch services, and smart cities. (Source)
- In 2020, British Telecommunication PLC. (BT) collaborated with Ericsson and used the Ericsson 5G core to develop services on its networks such as advanced mobile broadband, network slicing, and mobile edge computing for various industries. (Source)
- In 2020, Ericsson and AT&T collaborated to organize a live three-dimensional augmented reality music performance using 5G, Machine Learning and Edge Computing. The companies stated that it was a step forward towards holographic communications using these technologies. (Source)
- In 2019, Ericsson, AT&T, Intel, and Warner Bros. collaborated to make progress in the areas of augmented and virtual reality using technologies such as 5G and edge computing to offer new solutions. (Source)
- In 2019, Ericsson, Telstra, and Commonwealth Bank of Australia collaborated to incorporate 5G edge computing solutions in the financial sector. The collaboration was projected to utilize the bandwidth conservation benefits of edge computing and accelerate the data transfer and offer better security for transactions. (Source)
- In 2018, Limelight Networks and Ericsson collaborated to use the Content Delivery technology of Limelight on Ericsson’s edge cloud platform and expand its global delivery network. This collaboration was done to help the growing data needs and low latency applications for the users. (Source)
- In 2018, Ericsson collaborated with Sprint and combined both technologies of the companies to develop a platform for tackling the most challenging applications such as edge computing, AI, robotics, etc. with very low latency and high security at the chip level. (Source)
Mergers and Acquisitions
In September 2020, Ericsson acquired Cradlepoint, the market leader in the US in Wireless WAN Edge 4G and 5G solutions. Ericsson paid approximately $1.1 billion to acquire Cradlepoint. Ericsson aimed to combine its 5G network with the acquired company’s technologies and concentrate on developing private networks, edge computing, and IoT solutions. (Source)
Cisco
Cisco is a prominent wireless hardware company with expertise in 5G technology. Using its technical expertise and experience, Cisco managed to build an “edge” portfolio to provide edge computing solutions. Let’s look at some of its offerings.
Products or Technologies
CISCO IOx – This platform was developed to help developers develop business software at the edge of the network. It helps in edge application management that allows management, tracking, and troubleshooting of edge applications on the CISCO IOx platform such as FND, GMM, and DNA-C from remote places. (Source)
HyperFlex Edge – It provides users with versatile options for incorporating computing and storage to the edge environments in a hyper-converged infrastructure solution that is easy to manage and functions efficiently. (Source)
Catalyst 8000V Edge Software – It is a virtual edge platform that offers the users flexibility, protection, and visibility required in the modern multi-cloud environment, allowing the ability to customize applications for the best possible user experience. (Source)
Catalyst 8200 Series Edge – This is a 5G cloud edge platform designed for secure access service edge (SASE) providing secure, versatile, and scalable connectivity to the users’ multi-cloud architecture. (Source)
Catalyst 8200 Series Edge uCPE – It is a versatile networking platform that offers multi-cloud technologies, industry-leading network functions virtualization (NFV), and stable edge connections. (Source)
Catalyst 8300 Series – It is an edge computing platform that helps users benefit from accelerated services, multi-layer encryption, cloud-native agility, and edge intelligence accelerating their path to the cloud. (Source)
Catalyst 8500 Series – It is a high-performance cloud edge platform with edge information, multi-layer stability, and cloud-native flexibility. (Source)
CISCO Edge Intelligence – It is an application that helps extract, convert and send data from IoT edge devices to different applications. It also allows users to link devices with different forms of networks, making it simple to manage and safely handle data extraction. (Source)
Catalyst IE3x00 Rugged Switches – This platform offers integrated real-time data at high speeds on a modular, streamlined architecture. Cisco rugged switches provide edge computing simplicity, reliability, and protection. (Source)
IR1101 Integrated Services Router – It has a highly portable, lightweight, modular architecture that is ideal for critical applications. With SD-WAN technology, edge computing, and IOS XE, it provides improved advanced router security and management. (Source)
Collaborations
- In 2020, CISCO collaborated with IBM and developed the IBM Edge Application Manager using a combination of IBM and CISCO technologies. CISCO had used the IBM Application Manager on a wide range of its products such as its servers, industrial gateways, routers, switches, SD-WAN, and wireless connectivity services for edge computing. (Source)
- In 2020, CISCO and Intel collaborated to develop a robotic arm using edge computing that can communicate with its operators at ultra-low latency Wi-Fi 6 technology with close to zero lag. (Source)
- In 2020, CISCO and Verizon collaborated to integrate the 5G mobile edge computing of Verizon with CISCO’s products. The goal was to provide next-generation networking and infrastructure services in sports and entertainment facilities after they reopen after the pandemic. (Source)
- In 2020, CISCO and Schneider Electric collaborated to develop a new edge computing solution from a combined integration of HyperFlex Edge and 6U Wall Mount EcoStruxure. The collaboration helped in developing computing capabilities that are resilient, stable, and localized and that are closer to where data is generated, processed, and stored. (Source)
- In 2020, Microsoft and Cisco announced a partnership to develop IoT and edge computing technologies and solutions. The technologies were expected to aid in the management of vast amounts of data at the network’s edge. (Source)
- In 2018, CISCO collaborated with Reliance Jio and used multi-access edge computing to develop a mobile content delivery network (CDN) for improving the video experiences on the network. (Source)
Mergers and Acquisitions
In 2020, CISCO acquired Banzai Cloud, a software company developing end-to-end cloud applications. Both CISCO and Banzai cloud joined forces to develop technologies related to edge computing for present-day distributed applications. (Source)
Tencent
Tencent’s entry into the edge computing domain came as a surprise, and it is even more surprising that they hold a significant number of patents in the technology. In October 2020, Tencent opened its first Edge computing center for the public in Binhai New Area to show off Tencent Cloud’s cutting-edge products, its one-stop product matrix in the fields of hardware, network, platform, and multiple levels of applications.
You might be wondering about all the work Tencent did in the domain of Edge computing. We had the same questions and here’s everything we found.
Products or Technologies
Tencent Smart Edge Connector (TSEC) – It helps in developing 5G carrier networks. It would act as the bridge between the cellular device users and the service providers with a high-quality and distinguished edge computing internet protocol service, collaborating the applications in the cloud, edge, and end-user devices. The major responsibilities of the Tencent Smart Edge Connector (TSEC) are off-loading mobile traffic, mobile network acceleration, edge traffic forwarding, mobile network tunneling, and IoT access control. (Source)
Tencent Edge Computing Machine (ECM) – Edge Computing Machine (ECM) transfers computing power from the central node to edge nodes near to customers, resulting in low-latency, high-availability, and low-cost edge computing services. According to business needs, the customer can adapt the service area and size of edge modules, react quickly and flexibly to market adjustments, and have a quicker response at a lower cost. (Source)
IoT Edge Computing Platform IECP – It is an edge computing platform that offers low-latency, portable, stable, and versatile edge computing services for the users of IoT enterprise, lowering the operating and maintenance costs, as well as growth and network bandwidth costs. (Source)
Edge Availability Zone TEZ – It is a Tencent Cloud local extension that can help with processing, storage, and system compatibility problems. It helps the developers run latency-sensitive applications close to the users. (Source)
Collaborations
- In 2019, ZTE and Tencent collaborated to develop advancements in the technologies such as 5G, edge computing, quality-of-service (QoS) acceleration, network slicing, and open network capabilities. They jointly opened an R&D facility to commercialize a 5G edge computing framework for industrial usage. (Source)
- In 2018, Intel and Tencent collaborated to develop AI solutions from the cloud to the edge of the network. The companies were innovating on technologies by extending the cloud to the edge of the network to solve the issues such as latency and expensive data. (Source)
- In 2018, Tencent collaborated with Nokia and established a joint research facility where both the companies applied the artificial intelligence and automation management features of the 5G network on applications using the edge computing technology to provide solutions in various industries such as transportation, finance, energy, intelligent manufacturing, and entertainment. (Source)
ZTE
ZTE, just like its local competitor Huawei, is a leading 5G company that also holds a significant number of 5G patents. ZTE patents for Edge computing, its in-house technical expertise, and the collaboration with other players make it one of the leading players of edge computing.
In 2020, ZTE Corporation collaborated with China Mobile to launch China’s first 5G medical edge cloud platform. Apart from this, for the past 3 years, ZTE has been working on 5G-oriented edge computing which would enable a wide range of services, including AR/VR, IoT, industrial automation, and autonomous driving on edge.
ZTE’s patents discuss the solution to integration or migration of other technologies in an edge application when it comes to patents. For example, one of ZTE patents (CN110535896A) discusses migrating an edge computation application for processing a high definition video, virtual reality (VR), or augmented reality (AR) image by applying a user device over a vehicle network i.e. third-generation partnership project (3GPP) cellular network.
Products or Technologies
ZTE Common Edge MEC (Multi-Access Edge Computing) – The Multi-Access Edge Computing (MEC) helps compute and storage resources close to the end-users. This allows high-bandwidth, low-latency access to services. The ZTE edge computing solution offers video recognition solutions, low latency video streaming, and supports services from third parties. (Source)
E5430 G4 – It is an edge computing server that caters to the needs of edge equipment rooms. It satisfies the needs of 5G, IoT, AI, and other device scenarios for collecting, analyzing, and processing edge data. (Source)
ZTE MEC Integrated Cabinet – The ZTE Common Edge embedded cabinet is a plug-and-play edge cloud system for industrial sectors that satisfies the complex market conditions of 5G scenarios and allows operators and vertical industries to transition digitally. (Source)
Lightweight Dual Engine Edge Cloud – Rich cloud-native infrastructure platforms are introduced by mixing container and virtual machine deployments to support ICT edge applications for quicker distribution, implementation, resiliency, and cross-cloud migration. (Source)
Collaborations
- In 2020, ZTE and China Mobile launched the first 5G medical edge cloud platform in China. The 5G medical edge cloud platform can flexibly analyze, store and calculate large sets of data of health care services on the edge of the cloud. (Source)
- In 2020, Zong and ZTE corporation collaborated to launch the first Multi-Access Edge Computing trails in Pakistan. It allows Zong to offer features of MEC such as low latency and improved user experience on the existing 4G network and lay a strong base for the 5G rollout. (Source)
- In 2019, ZTE and Tencent worked together to create 5G, edge computing, QoS optimization, network slicing, and open network capabilities, among other developments. They collaborated to open a research and development center to commercialize a 5G edge computing system for industrial use. (Source)
- In 2019, ZTE and Intel collaborated to develop edge computing solutions using the Xeon processors of Intel that support edge computing. This processor helped ZTE develop a Light cloud solution. This solution delivers strong computing capability and services at the edge of the network. (Source)
- In 2019, ZTE, Telefonica, and Bank of Santander collaborated to develop 5G banking services in Spain. The collaboration allowed virtual visiting of co-working spaces using technologies such as virtual reality technologies, 360 videos, and edge computing. (Source)
M&A Landscape of Edge Computing
Having looked at the activities of all the top companies in the edge computing domain, let’s now have a quick look at the merger and acquisition scene here, starting with the list of the 3 biggest M&As in the domain.
3 Biggest M&As in the Edge Computing Industry
In 2020, Microsoft acquired Affirmed Networks, a company that provided the Affirmed Cloud Edge (ACE) solution for Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) offering Communication Service Providers (CSPs) the ability to host applications and store information close to the customers to reduce latency and increase performance. Microsoft valued Affirmed Technologies at approximately $1.35 billion. Microsoft used the software to assist mobile carriers to deploy NFV-based applications that can manage conventional network services and provide edge computing services for business and government organizations. (Source)
In 2019, IBM announced the acquisition of Red Hat for approximately $34 billion. IBM and Red Hat combined to include a next-generation hybrid multi-cloud interface, which aimed to accelerate innovation. The IBM acquisition allowed the tech giant to use Red Hat’s tools to build innovative edge computing technology, allowing it to gain a stronger foothold in the industry. With hybrid multi-cloud offerings that combine Red Hat OpenShift and IBM’s industry experience to meet corporate requirements, IBM is assisting its clients in taking full advantage of edge computing and 5G. (Source)
In 2019, Intel acquired the edge computing software business, Smart Edge from Pivot Technology. The acquisition was approximately priced at $27 million. The application, that runs on Intel processors, speeds up processing machines by separating data and bringing it closer to the users. Intel intends to use it in devices for the new 5G wireless network, which has already begun to phase out. (Source)
Which Companies made the Maximum Acquisitions in Edge Computing?
Amongst the top companies developing edge computing solutions, the companies with maximum acquisitions related to edge computing are as follows:
| Sr.No. | Company Name | Acquisitions |
| 1. | NVIDIA | In 2020, NVIDIA acquired Arm for $40 billion to accelerate its growth in Edge Computing. (Source)
In 2020, NVIDIA acquired Mellanox for $7 billion as next-gen data centers are rising in popularity with the rapid increase in edge computing requirements. (Source) In 2020, NVIDIA acquired Cumulus Networks, a company that developed solutions at the edge of the network through its collaboration with Mellanox. (Source) |
| 2. | Intel | In 2019, Intel acquired the Smart Edge platform from Pivot Technologies for approximately $27 million. (Source)
In 2016, Intel acquired Movidius, a chip designing company for approximately $400 million to develop edge computing products. (Source) |
| 3. | Apple | In 2020, Apple had announced the purchase of Seattle-based edge-AI company Xnor.ai for $200 million. (Source)
In 2018, Apple acquired Silk Labs pushing AI/ machine intelligence to the edge. (Source) |
| 4. | Microsoft | In 2020, Microsoft acquired Affirmed Networks to accelerate its push towards developing edge computing solutions. (Source) |
| 5. | IBM | IBM acquired Red Hat for approximately $34 billion to build innovative edge computing technologies. (Source) |
Future Outlook
The companies which we have discussed above are good contenders for the top player’s list. Tech giants like Google, Amazon, IBM, and Microsoft already have cloud and AI expertise. On the other hand, Huawei, ZTE, Cisco, and Ericsson have 5G expertise that has the potential to transform Edge computing. Moreover, Intel has chipset capabilities.
Thus each company has something in its arsenal that will help them stay ahead in the edge computing race. If you’re trying to make your place in the edge computing domain, and your name was not on the above list, I got to tell you this – The competition is tough.
However, a series of strategic moves can help you here. While patent filing to protect your in-house R&D, and collaboration with universities are two such routes, both of them take time.
One good option to opt for in this case would be startup acquisition. Yes, acquiring startups would be the best way to get an edge over the competitors (pun intended). With multiple startups working on Edge Computing, companies can make a series of good moves and get a lead in the race.
However, with the hundreds of startups working in the domain, it can get difficult to choose one. Don’t worry, we have a solution. To help you make an easy information-backed decision, we created a list of the top 10 startups of Edge computing. These startups have been chosen based on their technical expertise, investment funding, top investors, involvement of big companies, and patent activities.
Want to know all about them? Click here to find the top edge computing startups.










