Top 10 Companies Leading Artificial Intelligence Research
Whether it’s searching for photographs of loved ones or someone you don’t even know about. AI is revolutionizing the world. Breaking down language barriers via Google Translate, composing emails on the move, or getting things done with a Virtual Assistant.
Not just that, AI offers new perspectives on current issues.
From rethinking healthcare to improving scientific discoveries, companies leverage AI to make a better world. Which are these companies? How far have they come along? And where are they planning to expand next? This article entails all the details you need to know.
Artificial Intelligence Research
We also converted our research into a downloadable PDF that includes Artificial Intelligence market insights, competitive analysis, and patent insights. You can download the pdf by filling out the form below:
Here are the top 10 AI companies:
1. Google
It’s no wonder that Google is amongst the top AI companies. Its aim, as we know, is to aggregate the world’s information and make it accessible and helpful to everyone, individuals or enterprises. Google AI is undertaking cutting-edge research in the area, applying AI to products and new fields, and building tools to guarantee that everyone has access to AI.
Google is working through the initiative to support fundamental research and engineering activities, as well as to empower the social sector with tools, resources, and money while connecting with partners from all sectors to have the greatest effect. Furthermore, they are addressing issues in public health, nature and society, climate and energy, accessibility, and crisis response.
They also feel that the capacity to identify such answers is dependent on the knowledge of individuals all around the world. That is why Google has established research centers in Japan, India, Israel, and Accra, as well as collaborating with charities, universities, and public sector groups to develop systemic solutions.
Products & Technologies
Multitask Unified Model (MUM) – In September 2021, Google stated that it would use AI innovations, particularly a new technology called Multitask Unified Model (MUM), to enhance Google Search. At the Search On event, the business showed new capabilities, including those that use MUM, to better link web searchers to the information they’re looking for, while also making web search seem more natural and intuitive. One of the new features is called “Things to know,” and it aims to make it easier for users to comprehend new topics they’re looking for. This feature learns how people investigate different topics and then displays web searchers the aspects of the topic that they are most likely to look at first.

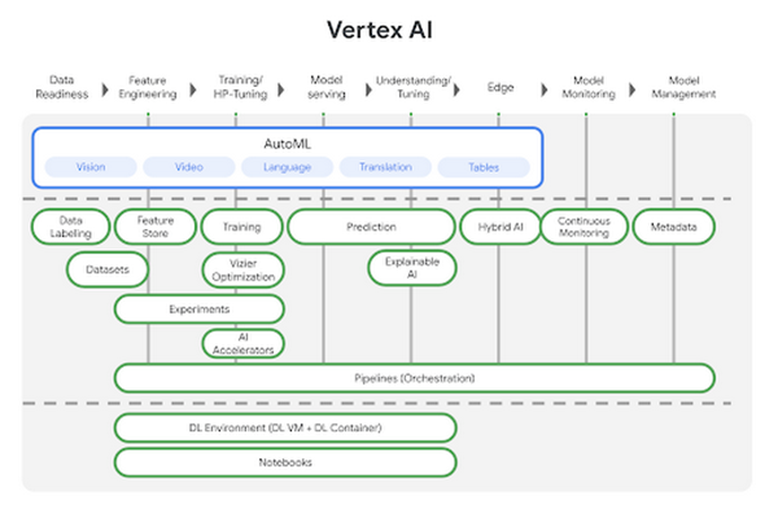
Vertex AI – Google’s Vertex AI was introduced in 2021. Vertex AI combines the Google Cloud resources for creating ML into a single, unified UI and API. Users can now quickly train and compare models in Vertex AI using AutoML or custom code training, and all of their models are saved in a single central model repository. These models may now be deployed to the same Vertex AI endpoints.
Vertex AI is directly connected with BigQuery, Dataproc, and Spark via Vertex AI Workbench. BigQuery ML allows users to develop and run machine learning models in BigQuery using regular SQL queries on current business intelligence tools and spreadsheets, or one can export datasets from BigQuery directly into Vertex AI Workbench and run the models there. Vertex Data Labeling may help to create extremely precise labels for data gathering.
Dialogflow CX – In Sep 2020, Google announced the beta launch of Dialogflow CX, the latest edition of the company’s suite for creating conversational experiences. Dialogflow CX, which is already used by over a million developers, is now generally accessible as part of Google’s Contact Center AI and offers a set of additional features for sophisticated virtual agents.
Dialogflow CX is intended for contact centers that handle conversations and may be deployed across a variety of platforms such as mobile, online, smart devices, chatbots, interactive voice response systems, messaging applications, and others. It includes intent detection and a visual flow builder, allowing developers to create, interpret, and manage dialogues. Furthermore, Dialogflow CX’s design allows 20 separate flows, 40,000 intents per agent, and over 20 languages supported on the voice channel, as well as the flexibility to use the same flow for different languages.
Collaborations
- In Feb 2021, Hologic and Google Cloud announced cooperation to enhance next-generation digital diagnostic capabilities. The collaboration combines Google Cloud’s machine learning technologies with Hologic’s new, cutting-edge Genius Digital Diagnostics System– the first digital cytology platform to combine artificial intelligence (AI) with advanced volumetric imaging technology to aid in the identification of pre-cancerous lesions and cancer cells in women.
- In December 2020, Institut Curie and Google launched a cooperative AI research initiative to develop and deploy deep learning methods for analyzing complicated single-cell transcriptomic and epigenetic data. The collaboration’s goal is to apply deep learning techniques to examine single-cell epigenomics and transcriptomics data in cancer in order to define tumor heterogeneity and, eventually, predict treatment resistance. The goal of this research is to investigate the structure of learning algorithms in order to extract information and understand these components at the biological level.
- In Sep 2020, Google launched a National AI Research Institute for Human-AI Interaction and Collaboration in partnership with the United States National Science Foundation (NSF). Google would provide $5 million to the Institute’s assistance. In addition, they would offer AI expertise, research partnerships, and Cloud assistance to Institute researchers and educators as they expand their understanding and progress in the field of AI. The Google Institute announced in collaboration with the National Science Foundation, would fund multidisciplinary research on a number of forms of contact between humans and AI, including voice, written language, images, and gestures, and how to make these interactions more successful. Furthermore, the Institute’s research, tools, and approaches would be created with human-centered concepts in mind including societal benefit, inclusive design, safety and robustness, privacy, and high scientific excellence, in accordance with the Google AI Principles.
- In September 2019, the Mayo Clinic and Google established a 10-year strategic collaboration to revolutionize how health care is delivered and increase the speed of health care innovation. Mayo Clinic chose Google Cloud as the foundation of its digital transformation. Mayo would transform health care delivery by bringing together worldwide providers and customers to improve health care using sophisticated cloud computing, data analytics, machine learning, and artificial intelligence (AI). The comprehensive partnership would combine Mayo Clinic’s world-class clinical knowledge and experience with Google’s industry-leading digital technology and data security expertise to build solutions for individuals who want medicine to deliver on the promise of scientific and technological breakthroughs.
M&As
- In 2020, Google purchased Actifio, a market leader in backup and disaster recovery (DR). This proposed purchase underscores Google Cloud’s commitment to assisting companies in the protection of workloads both on-premises and in the cloud. Actifio’s business continuity solutions will assist Google Cloud clients in preventing data loss and downtime caused by external attacks, network outages, human mistakes, and other interruptions.
- In 2018, Google paid an undisclosed sum for Onward, a customer service automation firm. Onward’s corporate chatbot platform used natural language processing to extract meaning from client messages. It might customize and contextualize its replies to queries by using signals such as location, login status, and previous actions.
- In 2017, Google acquired Halli Labs, a relatively young business based in Bengaluru, India, that was focused on developing deep learning and machine learning technologies to handle “old problems.” According to the startup, it would join Google’s Next Billion Users team to help bring more technology and information into the hands of more people across the world.
2. Microsoft
Microsoft provides technology, funds, and experience to inspiring individuals and organizations striving to tackle global issues. Microsoft supports researchers, non-profits, and organizations that use technology and artificial intelligence to better the world in a variety of fields, including the environment, accessibility, humanitarian concerns, cultural heritage, and health.
Microsoft AI has the potential to enable anybody to use, develop, and innovate with artificial intelligence in meaningful and relevant ways. AI enables new apps across Microsoft 365 that may help users write and create better, display maps and charts in Excel, and simplify the email. Microsoft Dynamics 365 powers digital transformation with cloud business apps that enhance your business operations by leveraging customer data and insights, LinkedIn integration, and intelligent technologies such as machine learning and predictive analytics.
Products & Technologies
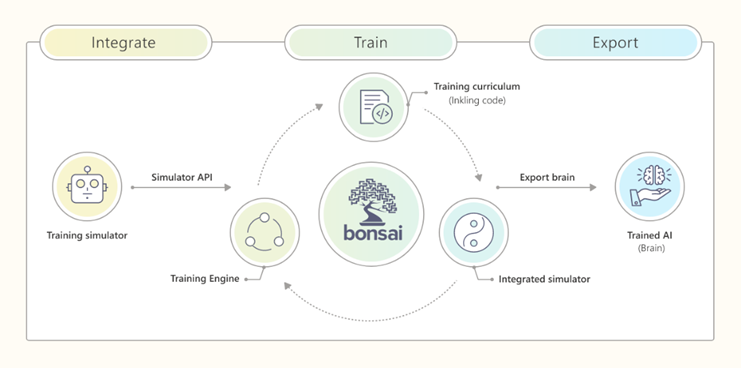
Project Bonsai – During the Build 2020 online conference, Microsoft unveiled the public preview of Project Bonsai, a platform for designing autonomous industrial control systems. The firm also launched Project Moab, an experimental platform meant to acquaint engineers and developers with Bonsai’s features.
Project Bonsai is a machine learning, measurement, and improvement system that offers autonomy to the control systems at the heart of robotic arms, bulldozer blades, forklifts, subsurface drills, rescue vehicles, wind, and solar farms, and other equipment. Control systems are an important component of machinery in sectors such as manufacturing, chemical processing, building, energy, and mining, aiding in the administration of everything from electrical power plants and HVAC setups to fleets of factory line robots.
Spektacom – Spektacom collects data on the quality, speed, twist, and swing of a cricket bat using a tiny sticker sensor on the bat to assist pros in better their game. Using wireless sensor technology and cloud analytics, the sensor sticker collects data and evaluates impact parameters. The data is evaluated using Azure AI models and then sent to the edge for continuous feedback.
Spektacom Technologies unveiled the “Power Bat” in 2018, a one-of-a-kind instrument powered by Microsoft’s Azure Cloud platform, AI, and Internet of Things (IoT) services. The Power Bat may offer real-time statistics on a player’s performance based on characteristics such as ball speed on contact, a twist on impact, and shot quality.
Collaborations
In Apr 2021, UCB and Microsoft established a new multi-year strategic cooperation to integrate Microsoft’s computational services, cloud, and artificial intelligence (AI) capabilities with UCB’s drug research and development skills. Because numerous drug discovery operations need the analysis of high-dimensional data sets or multi-modal unstructured material, Microsoft’s platform may help UCB scientists, particularly data scientists, find novel medicines in a more efficient and inventive manner.
UCB believes that by collaborating with Microsoft, it would be able to find and develop treatments for individuals suffering from severe illnesses in immunology and neurology more quickly. Microsoft would supply AI technology and applied scientists to work with UCB’s scientists and data professionals, with the goal of allowing UCB to identify new correlations and patterns crucial to the discovery of novel and highly personalized treatments.
In Jul 2021, The Arun Jaitley National Institute of Financial Management (AJNIFM) and Microsoft established a strategic collaboration to establish an AI and emerging technology Centre of Excellence at AJNIFM. The partnership aims to investigate the role of cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and new technologies in altering and influencing the future of public financial management in India. The Centre of Excellence would act as a hub for research, AI scenario planning, and tech-led innovation. AJNIFM and Microsoft would collaborate to investigate use cases of new technologies in finance and related fields across central and state ministries as well as public sector companies.
In 2020, Australia’s national research agency, CSIRO, and Microsoft to use artificial intelligence (AI) and other digital technologies to combat global issues such as illicit fishing and plastic waste, as well as to enhance agriculture.
The broad agreement was designed to accelerate critical research that would use AI and machine learning to combat illegal fishing by analyzing data from high-resolution cameras and underwater microphones to assist with fishing management in Australian marine reserves, including the Great Barrier Reef, and detection of explosive fishing in Indonesia. The collaboration would also contribute to CSIRO’s managed data ecosystem and digital academy projects that are reshaping CSIRO’s digital environment with new technologies, data capabilities, and skillsets, and will bring Microsoft’s newest digital technology to CSIRO’s diverse research portfolio.
In October 2019, Novartis announced the establishment of the Novartis AI innovation lab and the selection of Microsoft as its key AI and data-science partner for this endeavor. The new lab intends to substantially strengthen Novartis AI capabilities from research to commercialization and to assist expedite the discovery and development of breakthrough medicines for patients throughout the world. Novartis and Microsoft have committed to a multi-year research and development endeavor as part of their strategic cooperation. This strategic partnership would focus on two main goals including AI Empowerment and AI Exploration.
M&As
- In 2021, Microsoft’s purchasing craze reached a new high with the news of its $19.7 billion acquisition of Nuance, a firm that provides voice recognition and conversational AI services. Nuance is well recognized for its deep learning speech transcription service, which is widely used in the medical field. Prior to the transaction, the two firms had been collaborating closely. Nuance had built several of its products on Microsoft’s Azure cloud platform. And, in the midst of the epidemic, Microsoft had been employing Nuance’s Dragon service in its Cloud for Healthcare offering, which was released in 2020.
- In 2020, Microsoft announced the acquisition of Orions Systems with the goal of improving Dynamics 365 capabilities as well as the Microsoft Power Platform. Orions Systems, located in Washington, creates artificial intelligence-based video analysis systems for governments and Fortune 500 companies that can be trained by people. The solutions make use of design data based on semantics, which Nils Lahr, the company’s creator, refers to as “tagonomy– a system and method of semantic web tagging.” Microsoft intends to employ Orions Systems technologies to improve its Microsoft Dynamics Connected Store solution, which is currently in preview and uses cameras and sensors to monitor things like a store’s stock, customer experience, and refrigerator temperatures. Marks & Spencer, situated in the United Kingdom, has implemented the Microsoft Dynamics Connected Shop solution in a London store.
- In 2020, Microsoft acquired ADRM Software, which produces large-scale industrial data models that businesses utilize as “information blueprints.” The tech titan aims to integrate these models with Azure storage and computation to allow the construction of data lakes, where information from different lines of business is aggregated at scale. The deal’s financial specifics were not disclosed. Combining detailed industry models from ADRM with infinite storage and computing from Azure enables the construction of the intelligent data lake, which allows data from various lines of business to be harmonized more rapidly. These capabilities would be offered at scale in collaboration with Microsoft Azure, allowing its clients to accelerate digital development and minimize risk in a range of key undertakings.
- In 2018, Microsoft acquired Bonsai, a young artificial intelligence start-up. The deal’s terms were not disclosed. Bonsai’s software employs a popular technique known as reinforcement learning, which involves teaching systems to produce better results and make a sequence of decisions through trial and error. After specialists identify key regions in the data and train an AI model, it may be integrated into business applications.
The solution is designed to be installed on Microsoft’s Azure public cloud. Bonsai was created in 2014 and currently employs around 42 people, with offices in Seattle and Berkeley, California. According to Crunchbase, it has raised $13.6 million in venture investment from businesses such as ABB Technology Ventures, New Enterprise Associates, Samsung, Siemens, and Microsoft’s own corporate venturing arm, which is now known as M12.
3. IBM
IBM Research has been exploring methods to assist with all aspects of the epidemic. They recently released multiple articles outlining their research on forecasting the infectiousness of novel COVID-19 variations. Determining how effective masks are, and using AI to simulate viral propagation. The company even established the COVID-19 High-Performance Computing Consortium early in the pandemic, including partners from business, academia, and government. Their objective has been to provide the globe with supercomputing power in order to speed-up viral research.
To reduce the transmission of COVID-19, most experts now advocate wearing some form of facial covering. Sara Capponi and Simone Bianco, AI researchers at IBM’s Almaden lab in Silicon Valley who investigate functional genomics and cellular engineering, utilized computer simulations to demonstrate that masks and social distance work.
Products & Technologies
Telum AI Processor – IBM launched the IBM Telum Processor in August 2021, a new CPU processor that would enable IBM clients to employ deep learning inference at scale. Telum is IBM’s first commercial processor with on-chip AI inference acceleration. This might lead to advancements in fraud detection, credit approval, claims and settlements, and financial trading, with systems capable of inferencing at the pace of a transaction. Telum would be the primary processor chip for IBM Z and LinuxONE systems of the future.
Using Telum financial institutions would be able to shift from detecting fraud to fraud protection. They’ll be able to identify instances of fraud while the transaction is still in progress. Telum’s specialized AI core makes future IBM systems appropriate for applying AI in a variety of financial services businesses, including payment and loan processing, clearing and settling transactions, identifying money laundering, and risk analysis. However, the potential applications transcend beyond banking. The research team believes that these AI cores might be used in natural language processing, computer vision, voice and genomics, and other areas, allowing the deep learning-powered AI revolution.

Snap ML – Snap Machine Learning (Snap ML) is a library that may be used to train and score conventional machine learning models. It was created to address some of the most significant problems that businesses and practitioners encounter when applying machine learning to real-world use cases. The project is a set of multi-threaded CPU solvers, as well as GPU and multi-GPU solvers, that provide substantial acceleration over existing libraries.
Snap ML has become Available in Watson Studio on IBM Cloud and Cloud Pak for Data and has been incorporated into AutoAI.
In 2021, IBM reported that the recent integration of research project Snap ML into AutoAI is already enabling substantial acceleration of new use cases on huge datasets for Watson Studio users. The IBM team creates methods for training models that are better suited to the underlying systems on which they operate, such as a cloud instance with a few vCPUs or a powerful on-premises server with several CPUs and GPUs.
Snap ML can deliver considerably quicker training and inference using these smart algorithms in both cloud and on-premises computing settings, without losing model fidelity. In addition, IBM proved that this integration effort resulted in a 4x quicker runtime by testing this new version of AutoAI over a variety of big tabular datasets.
AutoAI – It is IBM’s flagship automated machine learning product–a software library for rapid training and inference of traditional machine learning (ML) models on contemporary computer platforms. On Watson Studio customers’ datasets, it produces ML pipelines that conduct data cleaning, pre-processing, feature engineering, model selection, hyper-parameter tuning, and other tasks.
On May 31, 2019, IBM revealed the general availability of AutoAI in Watson Studio. IBM has expanded the range of best-in-class data science and machine learning capabilities available in Watson Studio, the flagship enterprise data science framework, with this release. The focus of this version is on the automation of the whole model creation process, from data intake through model deployment. Watson Studio’s objective of increasing the productivity of data science teams large and small is being carried out through automated processes that normally take data scientists days or weeks to complete.
Collaborations
- In Aug 2021, IBM and Black & Veatch collaborated to jointly market Asset Performance Management (APM) solutions, including remote monitoring technologies that combine near real-time data analytics with artificial intelligence to assist customers in keeping equipment and assets running at peak performance and reliability. The businesses are working together to develop solutions that combine Black & Veatch Asset Management Services (AMS) and digital analytics with IBM Maximo Application Suite. These solutions are intended to assist companies in supporting more robust operations for assets in the industrial, energy, and utility sectors.
- In 2019, The Fashion Institute of Technology’s (FIT) FIT/Infor Design and Technology Lab (DTech Lab) and IBM announced cooperation that would revolutionize how the fashion industry functions and would aid in the development of the creative fashion workforce of the future. FIT would use IBM’s artificial intelligence (AI) for fashion capabilities – a package of application programming interfaces (APIs) created and trained for the fashion business that uses deep learning, natural language processing, and computer vision to help fashion brands connect with customers, enhance product styling, advancement, and merchandising actions, and enhances merchandise performance monitoring.
- In 2018, IBM and Nvidia collaborated to Expand Open Source Machine Learning Tools. IBM stated that it intends to integrate the new RAPIDS open-source software into its enterprise-grade data science platform for on-premises, hybrid, and multi-cloud settings. PowerAI would support RAPIDS libraries on IBM POWER9, IBM Cloud, and IBM Watson Studio. RAPIDS would assist in bringing GPU acceleration capabilities to IBM solutions that use open-source machine learning tools such as Apache Arrow, Pandas, and scikit-learn. Key open-source contributors such as Anaconda, BlazingDB, Graphistry, NERSC, PyData, INRIA, and Ursa Labs have provided immediate and widespread ecosystem support for RAPIDS.
M&As
- In Jul 2021, IBM purchased Bluetab Solutions Group in order to expand its offering of data and hybrid cloud consulting services in Europe and Latin America. Bluetab would be a strategic aspect of IBM’s data services consulting business, advancing the company’s hybrid cloud and AI strategy. The company has long-standing connections with top brands in banking, telecommunications, energy, and utilities in Spain, Mexico, Peru, and Colombia. Bluetab helps leading organizations to extract more value from their data by converting existing on-premises data and analytics estates to hybrid multi-cloud data platforms powered by a mix of cloud services and platforms such as Red Hat OpenShift.
- In April 2021, IBM acquired Turbonomic, a Boston-based supplier of Application Resource Management (ARM) and Network Performance Management (NPM) software. The purchase would give organizations complete stack application observability and management to ensure performance and save costs by leveraging AI to optimize resources such as containers, virtual machines, servers, storage, networks, and databases. This would allow them to analyze and manage the performance of any application, anywhere, in real-time. Financial information was not provided.
- In Nov 2020, IBM purchased Instana, an application performance monitoring, and observability firm. The acquisition would assist organizations in managing the complexities of contemporary applications that span the hybrid cloud landscape. The announcement improves IBM’s AI-powered automation capabilities and promotes the company’s Hybrid Cloud and AI strategy. Financial information was not provided. With the purchase of Instana, IBM would assist businesses in overcoming the issue of controlling application performance across various teams and, on average, 2 to 15 clouds. It is also another example of IBM expanding its AI-powered automation capabilities.
4. Intel
Smarter applications benefit consumers’ productivity and profitability, whether they sequence genomes, provide product suggestions, or optimize their supply chain. Intel’s heritage of democratizing technology continues by making it easier, quicker, and less expensive for everyone to incorporate AI into their apps wherever computing occurs.
Intel has developed various intelligent solutions and tools for its general-purpose CPUs with AI acceleration or domain-specific accelerators. They employ the scalable and open oneAPI standard, allowing anybody to unleash infinite knowledge from the edge to the cloud.
Products & Technologies
Intel Movidius Myriad X Vision Processing Units – Intel Movidius Myriad X VPU was released in 2020, and it is programmable with the Intel Distribution of the OpenVINO toolkit for porting neural networks to the edge, as well as through the Myriad Development Kit (MDK), that involves all required development technologies, frameworks, and APIs to incorporate custom vision, imaging, and deep neural network workloads on the chip.
The Intel Movidius Myriad X VPU performs admirably in computer vision and deep neural network inferencing applications. The Intel Movidius Myriad X VPU, a member of the Movidius VPU family renowned for its ultra-low power utilization, is capable of offering viability and effectiveness of over 4 trillion operations per second (TOPS). The Intel Movidius Myriad X VPU, with new performance advancements, is a power-efficient solution that provides sophisticated vision and artificial intelligence solutions to products such as drones, smart cameras, smart homes, security, VR/AR headsets, and 360 cameras.
oneAPI – At Supercomputing 2019, Intel announced the oneAPI industry project, which aims to provide a uniform and simpler programming model for application development across heterogeneous processing architectures such as CPUs, GPUs, FPGAs, and other accelerators. The release of oneAPI represents millions of Intel engineering hours in software development, and it symbolizes a game-changing shift away from today’s restrictive, proprietary programming techniques and toward an open standards-based paradigm for cross-architecture developer interaction and innovation.

Collaborations
- In Aug 2021, Silo AI, the leading Nordic AI solution provider, revealed its offering for industrial AI with Intel. The company’’s Silo Operating Software (Silo OS) includes a variety of industrial quality control use cases, including a modular and configurable AI-powered Visual Quality Control solution for implementing AI workflows on Intel hardware. Silo OS Visual Quality Control has been customized for a number of customers in the forestry, infrastructure, and industrial industries. Silo AI would best use Intel technology, such as accelerators, through Intel’s AI Builders initiative, making it simple to scale installations for a wide range of industrial use cases.
- In Aug 2021, Predera announced a collaboration with Intel, integrating the power of a unified Machine Learning (ML) Operations Platform with the most disruptive advances in AI infrastructure, hardware, and computing. By leveraging the power of Intel’s Machine Learning technologies, Predera and Intel would generate value for both clients and accelerate the industry’s adoption of AI and ML. By using Intel’s hardware, software, and technical enablement capabilities, Predera and Intel would collaborate to enhance key performance benchmarks of AIQ in machine learning and deep learning training workloads. The collaboration would also create new solution frameworks and reference architectures to expedite industry-specific AI solutions that would instantly benefit Predera’s Retail and eCommerce clients.
- In Mar 2021, Sensormatic Solutions announced a continuation of the collaboration with Intel Corporation to offer new solutions to retailers. Intel, a key partner in powering Sensormatic IQ, the new intelligent retail operating platform, would be assisting Sensormatic Solutions in providing enhanced shopper experiences and retail outcomes for its clients. Sensormatic Solutions and Intel are assisting retailers in gaining real-time insights on inventory, shoppers, employees, and the retail environment through an extensive understanding of the retail sector, artificial intelligence (AI), and computer vision-based solutions.
- In 2020, Intel India launched INAI, an applied artificial intelligence research center in Hyderabad, in collaboration with multiple entities, i.e. Government of Telangana, the International Institute of Information Technology, Hyderabad (IIIT-H), and the Public Health Foundation of India (PHFI). INAI is a program that uses artificial intelligence to address population-scale problems in the Indian setting, with an emphasis on identifying and addressing difficulties in the healthcare and smart mobility segments through strong ecosystem engagement.
M&As
- In Oct 2020, Intel acquired SigOpt, a San Francisco-based firm building a platform for optimizing AI software models. The terms of the transaction, which is scheduled to conclude this quarter, have not been disclosed, but Intel said this would utilize SigOpt’s technology across its hardware products to speed, amplify, and expand AI software tools for developers. Following the acquisition, SigOpt’s team, including Clark and Hayes, would join Intel’s machine learning performance business. SigOpt’s software innovations, according to Intel, would complement its existing AI software portfolio, which includes OpenVINO, a toolkit introduced in 2018 to enable developers to speed AI inference on edge and cloud devices.
- In 2020, Intel bought Israel-based Cnvrg.io as part of its current acquisition frenzy. The acquisition is intended to improve the company’s machine learning and artificial intelligence operations. The business, which was launched in 2016, provides a platform for data scientists to create and execute machine learning models, which can be used to train, conduct comparisons, and make suggestions, among other things. Cnvrg, which was co-founded by Yochay Ettun and Leah Forkosh Kolben, was valued at about $17 million in its most recent financing.
- In 2019, Intel Corporation announced the $2 billion acquisition of Habana Labs, an Israel-based provider of programmable deep learning accelerators for data centers. The merger expands Intel’s artificial intelligence (AI) portfolio and accelerates its efforts in the young, rapidly developing AI silicon industry, which Intel estimates to be worth more than $25 billion by 2024. Habana would continue to operate as a standalone business unit, managed by its present management team. Habana would report to Intel’s Data Platforms Group, which houses the company’s extensive portfolio of data center-class AI technology. This merger provides Habana with access to Intel AI capabilities, including large resources created over the previous three years with deep expertise in AI software, algorithms, and research, which would assist Habana in scaling and accelerating.
5. Amazon
Amazon is a global technology firm headquartered in the United States that specializes in e-commerce, cloud computing, digital streaming, and artificial intelligence. At Amazon, artificial intelligence (AI) is the branch of computer science dedicated to tackling cognitive issues often associated with human intelligence, such as problem-solving, learning, and pattern recognition.
For Amazon, AI is one of the most critical technologies it utilizes to develop on behalf of its customers. It enables them to automate elements of the fulfillment and delivery network and serves as the foundation for Alexa’s ability to assist users to play music, check the news and weather, switch on the lights, order a pizza or a cab, and more easily by using their voice. Amazon believes that artificial intelligence will fundamentally enhance the way it provides customers with ease, cheap costs, and a wide range of options.
Products & Technologies
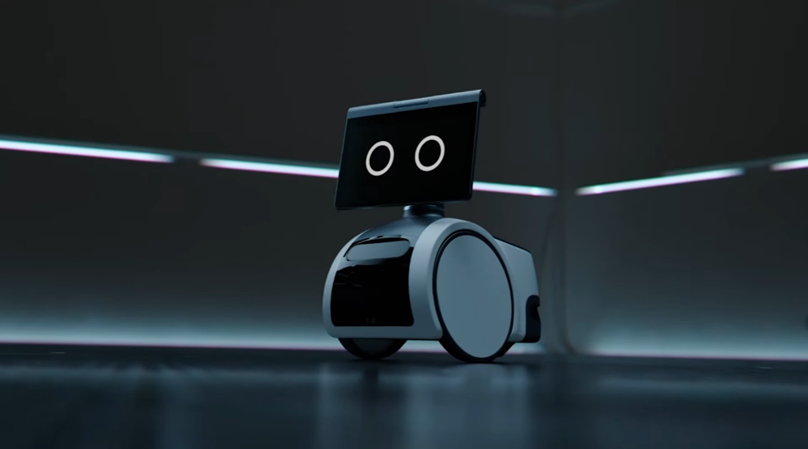
Amazon Astro – In 2021, Amazon introduced Astro, a canine-like domestic robot. The Amazon Astro is a modern autonomous robot in the Wall-E style from Amazon that combines Alexa and AI capabilities with wheels. The Astro is a robot pet with a periscope camera and live stream, as well as Ring Protect Pro support and other capabilities. Astro will have its own functions, such as beatbox and rest on demand, and will be more than simply Alexa on wheels.
SageMaker Data Wrangler – Amazon unveiled SageMaker Data Wrangler, a new AWS service meant to accelerate data preparation for machine learning and AI applications, in 2020. The SageMaker Data Wrangler decreases the time it takes to gather and process data for machine learning (ML) from weeks to minutes. With SageMaker Data Wrangler, one can ease data preparation and feature engineering and complete each stage of the data preparation workflow, including data selection, cleaning, exploration, and visualization, from a single visual interface.
Amazon Kendra – In 2020, Amazon announced the public availability of Amazon Kendra which is an AI and machine learning-powered, user-friendly corporate search tool. Amazon introduced a preview version of Amazon Kendra at the end of 2019. Amazon Kendra enables enterprises to index structured and unstructured data stored in various backends such as file systems, apps, intranets, and relational databases. All data is secured in-flight using HTTPS and may be encrypted at rest using AWS Key Management Service (KMS).
Amazon CodeGuru – In Jun 2020, Amazon announced CodeGuru, an AI-powered developer tool that gives recommendations for enhancing code quality. It was initially announced during the company’s Amazon Web Services (AWS) re:Invent 2019 conference in Las Vegas. Amazon CodeGuru is a developer tool that makes intelligent recommendations to enhance code quality and identify the costliest lines of code in an app. CodeGuru Reviewer uses machine learning and automated reasoning to detect important flaws, security vulnerabilities, and difficult-to-find errors during application development and makes recommendations to enhance code quality.
Collaborations
- In Feb 2021, Amazon and the National Science Foundation announced a collaboration to promote computational research focusing on fairness in AI, intending to contribute to trustworthy AI systems that are easily accepted and implemented to address society’s major concerns. Specific topics of interest include but are not limited to, explainability, transparency, accountability, inclusivity, potential adverse biases (including social biases) and effects, fairness objectives, mitigation strategies, algorithmic advances, fairness validation, participatory design, and advances in broad accessibility and utility. Funded initiatives will promote greater adoption of AI systems, allowing the United States to benefit from the potential of AI technology. Although Amazon is providing partial financing for this initiative, it will not be involved in the selection of proposals for the award.
- In Oct 2021, Amazon and MIT collaborated to develop the Science Hub to support research, education, and outreach activities in areas of mutual interest. The SCC at MIT will manage the hub, which will focus on artificial intelligence (AI) and robotics in its initial year. The relationship with Amazon will enable activities at MIT such as yearly grants for graduate and postdoctoral researchers, events to expedite and make AI and robotics research more accessible, and stand-up research projects directed by faculty members.
- In Apr 2021, Amazon Web Services (AWS) partnered with CAR to accelerate the deployment of artificial intelligence and machine learning in Canadian healthcare. AWS offers over 200 services, including a strong bench in artificial intelligence. CAR’s relationship with AWS aims to promote the convergence of technology and healthcare provision for radiologists through education and exposure to industry-leading cloud services.
- In 2020, Amazon and Columbia Engineering announced new cooperation to establish the Columbia Center of Artificial Intelligence Technology, with Amazon investing $5 million over the next five years ($1 million per year) to promote AI research, education, and outreach projects. Amazon funding will aid a wide range of Columbia programs, including two-year fellowships awarded yearly to Ph.D. students enrolled in the Engineering School; research projects headed by Columbia faculty members in partnership with post-doctoral researchers, undergraduate and graduate students, and research staff; and assistance for collaborative research events and activities that expedite AI research and make it more accessible in the NYC area.
M&As
- In 2020, Amazon acquired Zoox, a self-driving firm launched in 2014 that has raised about $1 billion in financing and wants to build autonomous driving technologies, including vehicles, to provide a full-stack solution for ride-hailing. Zoox will continue to operate as a separate entity, and the general corporate objective will remain unchanged, according to the announcement. According to Financial Time, the acquisition was worth $1.2 billion. Zoox’s goal is to create a purpose-built self-driving passenger vehicle from the ground up, as well as the software and AI to support its autonomous driving capabilities. The Zoox acquisition appears to be intended exclusively at assisting the firm in bringing their vision of autonomous ride-hailing to reality, rather than Amazon’s logistical capabilities for package delivery. However, Zoox’s ground-up technology, which involves the development of zero-emission vehicles designed particularly for autonomous use, may readily adapt to Amazon’s operations.
- In 2019, Amazon acquired Canvas Technology, a robotics firm that powers autonomous cars in industrial environments. The company’s technology effectively equates to driverless automobiles for warehouses. Canvas Technology employs spatial artificial intelligence and cutting-edge cameras to assist cars in autonomously navigating through places with many moving elements, such as people on foot and running machinery. Canvas was then directed by Jonathan McQueen, who had previously worked at Qualcomm for six years. In 2017, the firm secured $15 million in Series A financing.
- In 2017, Amazon (AWS) acquired Harvest.ai, a San Diego security firm, for approximately $20 million. Harvest.ai has built technologies that can assist businesses in detecting and preventing targeted attacks on their data. The firm uses machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) to learn and recognize when an unauthorized individual attempt to steal intellectual property or other vital data from corporate servers.
6. Baidu
Baidu is a Chinese-language Internet search company. Through links on its website, the company provides a Chinese language search platform that allows users to locate information online, such as webpages, news, photos, documents, and multimedia files. It was founded in 2000 as a search engine platform, and in 2010 it was an early adopter of artificial intelligence to help with content discovery on the internet.
Baidu is one of the few companies in the world that provides a full AI stack, which includes an infrastructure comprised of AI chips, a deep learning framework, core AI capabilities such as natural language processing, speech recognition, knowledge graph, computer vision, and augmented reality, as well as an open AI platform to facilitate widespread application and use.
Products & Technologies
Kunlun II – In 2021, Baidu launched its second-generation AI chip Kunlun (Kunlun II). The second-generation AI chip aids devices in processing enormous volumes of data and enhances computing power multifold. It has two to three times the processing capability of the previous generation and is equipped with Baidu’s second-generation XPU architecture. Kunlun II may be used in a variety of applications, including cloud, terminal, and edge computing, enabling high-performance computer clusters, biocomputing, intelligent transportation, and autonomous driving. It may also be optimized for AI technologies such as voice, NLP, and images. The first generation Kunlun chip was released in 2018.

Robocar – Baidu showcased a two-seater ‘Robocar’ idea at its annual Baidu World 2021 conference. The future, AI-powered car is without a steering wheel as well as gas and brake pedals, but it is large enough for a passenger to stretch out and take a nap. It could do a U-turn, change routes if the passenger changed the destination, and avoid collisions in real-time. The car will be a crucial component of Baidu’s transition from a mostly online corporation to a technology company that builds self-driving electric vehicles (EVs) utilizing artificial intelligence.

Baidu Brain 7.0 – In 2021, Baidu unveiled the newest edition of its open AI platform, named Baidu Brain 7.0. Baidu Brain 7.0 improves the integration of multiple information sources and deep learning, including language understanding and reasoning, by leveraging a number of integrated technologies to enable output across formats (language, voice, and visual).

Collaborations
- In 2021, Baidu and China Huaneng Group Co. signed a memorandum of understanding (MoU) to drive the intelligent transformation of the energy industry. Baidu will employ its expertise in AI-powered new infrastructure to assist Huaneng in closely integrating the digital economy with the energy and power industries, which will improve efficiency and user experience. The two businesses will collaborate to create a next-generation automated and intelligent financial shared services platform, as well as to apply AI and big data technologies to the energy and power sectors.
- In 2020, Baidu and Intel announced new artificial intelligence (AI) cooperation, demonstrating technologies that potentially disrupt a variety of industries. Baidu Cloud is using Intel CPUs and a neural network as part of a new financial services solution for prominent Chinese banks. In the shipping industry, it tries to assist enterprises in monitoring trucks in real-time by enhancing the efficiency of edge devices to enhance shipping operations and report back to the central office on outstanding events.
- In Sep 2021, Baidu and China Gas signed a strategic cooperation agreement to push digital and intelligent transformation in the energy and power sectors through innovative solutions built on the Baidu AI Cloud. The companies will also look into business opportunities that will help them reach a peak in carbon emissions and, eventually, carbon neutrality. Baidu will accelerate China Gas’ move to the cloud and use its AI capabilities to build customized applications such as smart monitoring, smart scheduling, gas usage prediction, and smart customer services in the first stage of their partnership, valued at RMB 936 million yuan.
- In Jan 2021, Baidu entered the electric vehicle market in collaboration with Geely, a Chinese automaker. Baidu stated that it would provide intelligent driving capabilities for vehicles designed and manufactured by Geely, the parent company of several well-known brands such as Volvo and Lotus. They will collaborate closely in the development of intelligent vehicles based on Geely’s recent Sustainable Experience Architecture (SEA) research, which is the world’s first open-source electric vehicle platform. Baidu will be in charge of design, R&D, production, and sales, and will rely on its artificial intelligence and technology DNA.
M&As
- In 2020, Baidu signed formal agreements with JOYY Inc. According to the agreements, Baidu will acquire JOYY’s domestic video-based entertainment live streaming business in China-YY Live, which includes the YY mobile app, YY.com website, and PC YY, among other things-for an estimated US$3.6 billion in cash, subject to certain modifications. The deal is subject to certain conditions and is presently scheduled to close in the first half of 2021.
- In 2017, Baidu acquired xPerception, a computer vision startup based in the United States. Following the acquisition, the xPerception team will join Baidu’s AI research team to work on technology that uses sensors and cameras to detect objects and plan pathways. This technology, known as SLAM (simultaneous localization and mapping), is used in self-driving cars and virtual and augmented reality. xPerception is yet another U.S. anchor for the company, which has been investing heavily in its Silicon Valley AI Lab.
- In 2017, Baidu expanded its artificial intelligence drive when it announced the acquisition of Raven Tech, a Chinese firm that created an AI voice assistant platform. Baidu has acknowledged acquiring the startup’s technology, product, and 60-person staff. Baidu did not disclose how much it paid for Raven Tech, a Microsoft Venture Accelerator, and Y Combinator alumni and has received $18 million from investors like DCM Ventures and Zhenfund. This acquisition is noteworthy since it includes a startup from the United States. It may also hold the key to Baidu’s future initiatives in autonomous driving and augmented reality.
- In 2017, Baidu purchase Kitt.ai to continue its drive into artificial intelligence, especially to help it carve out a niche as a platform for developers looking to build chatbots and other services using natural language technology. Kitt.ai has created a framework for building and powering chatbots and voice-based services across numerous platforms and devices.
7. Meta
Meta is developing a long-term business in which the role of Meta AI is incomprehensible. Meta is rapidly expanding its business by learning about its users and packaging their information for advertising. It is currently using artificial intelligence to map the world’s population density. According to Meta’s most recent announcement, its all-new machine learning technologies are quicker and more efficient than those introduced in 2016. Its AI is built on an autonomous translation mechanism. Every month, the Applied Machine Learning team assists 800 million consumers in finding preferred translated items in their news feed.
According to Kevin Lee, Technical Program Manager, Facebook, “If you’ve logged into Facebook, it’s very likely you’ve used some type of AI system we’ve been developing.”
Products & Technologies
Automatic AI-Based Translation System – Meta’s AI experts are directly competing with Google to create the most robust online global communication system. Facebook’s applied machine learning team has developed its own autonomous AI-based translation system to allow Facebook users from various countries to interpret messages that appear in their News Feeds.
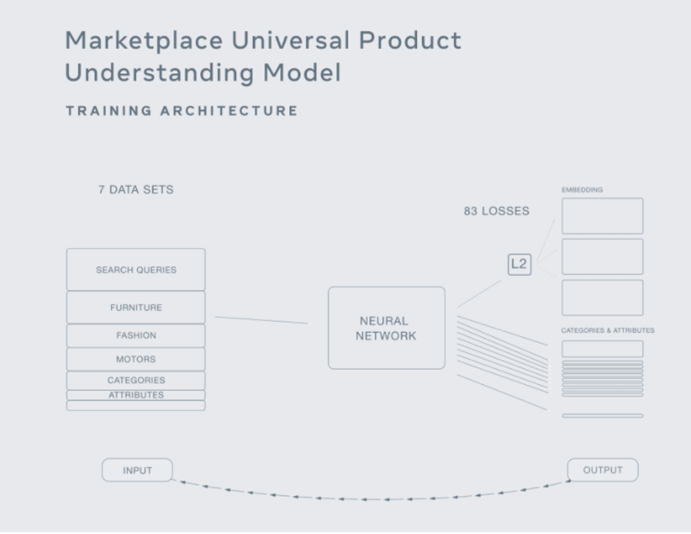
Universal Product Recognition Model (GrokNet) – Meta developed a “universal product identification model” in 2020 that utilizes artificial intelligence to recognize consumer items ranging from furniture to fast fashion to fast automobiles. According to the business, product identification is the first of a spate of AI-powered improvements coming to its e-commerce platforms in the near future. These eventually incorporated AI, augmented reality, and even digital assistants to create a “social-first” shopping experience. GrokNet, the company’s latest product recognition technology, can recognize tens of thousands of different features in a picture. These might range from specific brands to color and size. GrokNet was trained on a massive collection of over 100 million pictures, the vast bulk of which was obtained from Marketplace.
3D Product Images, Rotating View – In 2020, Meta launched Rotating View, a cutting-edge 3D-like picture capability that lets anybody with a camera on their phone shoot multi-dimensional panoramic views of their Marketplace items. This tool enables any seller with a camera phone to convert standard 2D video into a 3D-like interactive experience. The firm has begun testing this capability for iOS Sellers on Marketplace.
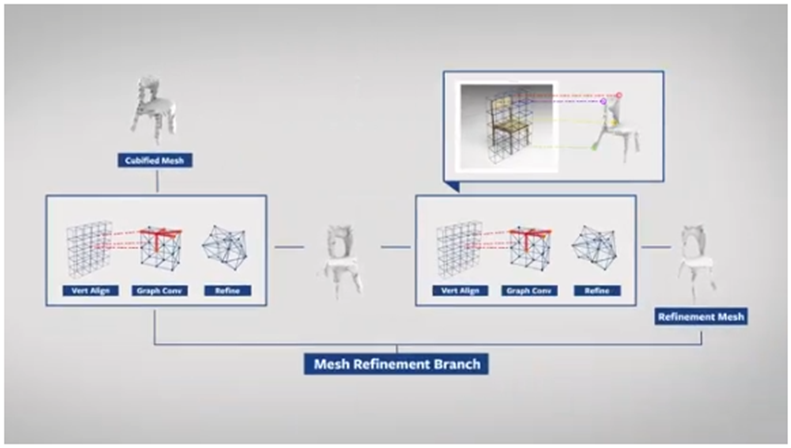
Mesh R-CNN – It is a unique, cutting-edge approach for predicting the most accurate 3D forms in various real-world 2D pictures. This method, which uses the general Mask R-CNN framework for object instance segmentation, can detect complex objects such as chair legs or overlapping furniture.
Collaborations
In 2021, Facebook AI Research (FAIR) partnered with Matterport, the spatial data business, introducing the digital transformation of the built environment to make the world’s most extensive dataset of 3D interior places available solely for academic, non-commercial operation. The Habitat-Matterport 3D Exploration Dataset (HM3D) is a first-of-its-kind collection of high-resolution Matterport digital halves of domestic, marketable, and communal areas created exactly from real-world settings. HM3D will play an important part in advancing embodied AI exploration, which aims to educate robots and virtual AI aides on how to understand and interact with the complexity of the physical terrain.
Researchers may use it in confluence with FAIR’s Habitat simulator to train embodied agents at scales, similar to home robots and AI sidekicks. HM3D is a critical step in aiding these agents in navigating real-world situations and better understanding the variations of spaces similar as bedrooms, bathrooms, kitchens, and corridors, as well as the numerous layouts of those apartments within each structure. It can also help robots recognize how particulars in apartments are generally arranged so that instructions are appropriately interpreted.
In 2018, the tech giant and the Department of Radiology at New York University School of Medicine launched fastMRI, a new joint research initiative that would study the use of artificial intelligence (AI) to improve magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans up to ten times quicker. If this initiative is successful, it will make MRI technology more accessible to more individuals, therefore increasing access to this critical diagnostic tool. Using artificial intelligence, it may be feasible to collect fewer data and therefore scan quicker, while retaining or even increasing the information richness of magnetic resonance pictures. The idea is to train artificial neural networks to detect the underlying structure of the pictures in order to fill in the gaps left by the faster scan. The imaging data collection utilized in the research was gathered entirely by NYU School of Medicine and includes roughly 3 million magnetic resonance images of the knee, brain, and liver.
M&As
- In 2019, Meta (Formerly Facebook) bought Deeptide Ltd. for $40 million. Deeptide was behind Atlas ML and the curator of “Papers With Code,” a free and open repository for machine learning papers and code.
- In 2018, Meta (Formerly Facebook) acquired Bloomsbury AI for between $23 and $30 million. The latter’s primary product is an API called Cape, which allows developers to add question-and-answer capability to websites and other publications. This acquisition will allow the company’s personnel and technology to focus on combating false news and other content challenges. The company intended to enlist the Bloomsbury AI team to assist it in developing technology to combat false news on the network and other elements of its apparent moderation problem.
8. Apple
In recent years, as machine learning underpins various functions in Apple’s products, Apple’s interaction with the AI community has grown. Apple integrates hardware and software across all devices, allowing researchers and engineers to work more efficiently to improve the user experience while protecting personal data. The individuals who work here in machine learning and AI are creating extraordinary experiences in every Apple device, allowing millions of consumers to accomplish things they never thought possible. Apple has also developed an AI/ML residency program and is already taking applications for the class of 2022.
Products & Technologies
No-Code AI platform – Apple researchers developed a no-code AI framework (Trinity) for complicated geographical information in 2021. The platform enables machine learning researchers and non-technical geospatial professionals to tackle diverse issues by experimenting with domain-specific signals and information. It tailors complicated Spatio-temporal datasets to suit conventional deep learning models–in this example, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)–and formulates diverse tasks, such as semantic segmentation, in a standard fashion. Standardizing, model development, and deployment facilitate rapid prototyping and rapid experimentation and decrease time to production.
Apple’s Siri – Siri is an AI-enabled assistant accessible on all Apple devices and promises to help consumers complete daily activities more swiftly. The cognitive assistant was developed in collaboration with EPFL, a Swiss institute of technology, as part of the SRI-led Cognitive Assistant that Learns and Organizes (CALO) project, which is part of DARPA’s Personalized Assistant that Learns (PAL) program, the largest-known AI project in US history. Siri is based on massively parallel machine learning techniques integrating speech recognition and natural language processing (NLP). Speech recognition is converting human speech into its written counterpart, whereas NLP algorithms attempt to interpret the intent of what users are saying. At the 2020 Worldwide Developers Conference (WWDC), Yael Garten, Director of Siri Data Science and Engineering, stated that Siri processed 25 billion queries each month.
Smart HDR and Deep Fusion Photos – It is Apple’s machine learning-powered image processing technologies that are accessible in the company’s most recent products. Apple launched its Smart HDR picture feature with the launching of the iPhone 11 in 2018. After a year, the firm revealed an improvement to the Smart HDR photo-taking mode and a new image processing technology dubbed Deep Fusion. The firm announced the release of its new application machine learning-powered by the A13 Bionic chip’s neural engine. Overall, the influence of camera quality on the smartphone industry looks to be a significant breakthrough.
In 2020, Apple stated that iOS, iPadOS, and macOS would include various new features and upgrades based on machine learning and AI concepts. These various features and updates include:
Facial Recognition For HomeKit: This HomeKit includes intelligent cameras that will utilize photographs tagged on the phone to identify who is knocking on the door and even proclaim the individual by name to let people know who it is.
Native Sleep Tracking For Apple Watch: Apple Watch uses machine learning to detect motions and determine when a person is asleep. The same technology detects whether individuals are dancing, walking, running, and so on.
Handwashing: The Apple Watch also has a new function that allows it to track one’s hand-washing habits. The sound of hand-washing will start a countdown in the watch, which will assist in keeping track of the time.
App Library Suggestions: The app library layout now includes a new feature that uses on-device intelligence to display the user’s applications that they are likely to install next.
Translate App: Because of on-device machine learning, this app can function offline. It identifies the language being spoken and instantly translates conversations.
Sound Alerts: The newly revealed iOS 14 has a new function that allows the phone to listen to sounds including doorbells, sirens, dogs barking, and infants crying.
Collaborations
- In 2018, Apple and IBM announced new cooperation focused on mobile AI. The partnership sought to connect IBM’s Watson platform with Apple’s Core ML framework in order to create a new development tool platform that would allow iOS designers to better use machine learning and artificial intelligence in their apps. The current deal builds on the businesses’ previous relationship, which they struck around four years ago with the goal of developing corporate apps for Apple’s devices, including as in the healthcare and construction industries.
- In 2017, Apple collaborated with the Partnership on AI. Apple joined Google, Amazon, Microsoft, Facebook, and IBM, as well as six new corporate and charity trustees, to solidify the Partnership’s position as the leading industry AI research organization.
M&As
- In 2020, Apple paid approximately $50 million for Vilynx, a Spain-based AI video firm. This acquisition will allow Apple to better utilize Vilynx’s technology in a number of apps. According to the media, Siri, search, Photos, and other Apple-reliant applications, as well as Apple TV, Music, and News, to mention a few, will be transformed by Vilynx’s technology. The acquisition will also help Apple improve its AI skills, with up to 50 engineers and data scientists arriving from Vilynx, and the firm will become one of Apple’s major AI research centers in Europe.
- In 2020, Apple invested $200 million for Xnor.ai, a Seattle firm focusing on low-power, edge-based artificial intelligence capabilities. The deal is similar to Apple’s high-profile acquisition of Seattle AI firm Turi in 2016. According to the agreement, Xnor’s AI-enabled picture identification technologies might become standard features in future iPhones and cameras. The purchase of Xnor.ai is a significant victory for the Allen Institute for Artificial Intelligence, or AI2, which was founded by late Microsoft co-founder Paul Allen to further AI research. Apple would likely appreciate the fact that Xnor.ai’s technologies can protect AI data on mobile devices rather than transmitting it to the cloud.
- Apple paid about $200 million for the AI startup Lattice Data, a specialist in unstructured ‘black data.’ Lattice Data gives a brief graphic regarding the technology that they specialize in, and Apple has added about 20 engineers as a result of this acquisition.
9. Qualcomm
Qualcomm is the world’s top pioneer in wireless technology. Their work is behind and inside the inventions that greatly benefit billions of people every day across numerous sectors. Qualcomm AI is revolutionizing industries by speeding the worldwide commercialization of artificial intelligence. Qualcomm’s technological innovations are not only driving power-efficient AI but also paving the way for 5G, the cornerstone for an intelligently linked future. The convergence of these two technological platforms, driven by Qualcomm, will scale intelligence to trillions of linked items.
Products & Technologies
Qualcomm Snapdragon 778G – Qualcomm Snapdragon 778G was announced in 2021 during Qualcomm’s 5G Snapdragon Summit. The new system-on-chip (SoC), which falls between the Snapdragon 750G and Snapdragon 780G, is designed to deliver a superior multimedia experience with a whole new configuration. The Snapdragon 778G SoC succeeds the Snapdragon 768G, which was introduced in May 2020. The new device is built on 6nm technology, which might result in significant processing and power efficiency gains over the Snapdragon 768G SoC. Qualcomm claims that the Snapdragon 778G may outperform its predecessor in terms of artificial intelligence (AI). The Snapdragon 778G SoC would be publicly available in the second quarter of 2021.
Qualcomm Snapdragon 888 Plus – Qualcomm Snapdragon 888 Plus SoC was revealed for flagship phones at MWC 2021. The new processor is a minor upgrade to the Snapdragon 888 SoC, with an increased Qualcomm Kryo 680 CPU Prime core clock speed of up to 3.0 GHz and a 6th-generation Qualcomm AI Engine with up to 32 TOPS (Tera Operations Per Second) AI performance, which the company claims is a more than 20% improvement. Aside from that, the new Snapdragon 888 Plus SoC is nearly identical to its sibling, which was released in December, and the new model is expected to power new flagships launching in the second half of 2021.
Collaborations
- In 2020, Qualcomm Technologies and Microsoft partnered to give a unified artificial intelligence (AI) and machine literacy (ML) development experience. The effectiveness provided by this flawless development and deployment will profit companies employing Microsoft’s Azure and AI results, similar to the Azure IoT platform, as well as Qualcomm Technologies’ IoT processors and AI conclusion products. Qualcomm Technologies’ presence in the mobile ecosystem enables them to produce tackle-accelerated conclusion capabilities ranging from ultra-low power edge AI results to high-performance AI inferencing on the pall via the Qualcomm Cloud AI 100, using marketable 5G deployments.
- In 2020, Altek stated that it will maintain its long-standing strategic partnership with Qualcomm Technologies. The new QCS610 and QCS410 SoCs take Altek’s Edge Vision AI series, which includes an AI camera and an AI box, to the next level by providing clients with new experiences through very efficient AI inferencing across various edge vision AI applications. Altek Corporation released a Qualcomm QCS610-based camera reference design hardware development kit in Q3 2020.
- In 2017, Qualcomm Technologies, Inc. and SenseTime Group started working on AI and ML for future mobile and IoT devices. This collaboration relied on both businesses’ AI experience by combining SenseTime’s machine learning models and algorithms with Qualcomm Snapdragon premium and high-tier platforms, which provide powerful heterogeneous computing capabilities for client-based AI. The businesses anticipated that on-device AI will grow in popularity and development in areas such as novel vision and camera-based image processing.
M&As
- In March 2021, Qualcomm Technologies acquired NUVIA for $1.4 billion before working capital and other adjustments. The NUVIA purchase expands on Qualcomm Technologies’ Snapdragon technological leadership, offering step-function increases in CPU performance and power efficiency to meet the needs of next-generation 5G computing.
- In 2017, Qualcomm acquired Scyfer, a machine learning firm located in the Netherlands. Scyfer has worked on artificial intelligence for firms in manufacturing, health care, and finance. Qualcomm, in addition to acquiring Scyfer, outlined its “future vision,” which envisions a world in which AI makes gadgets, automobiles, and machines more intelligent. This acquisition aided Qualcomm Technologies’ AI research and development efforts.
10. Huawei
A global leader in information and communications technology (ICT) infrastructure and smart products. Huawei presented real-time examples of the application of AI in the industry at CEBIT 2018 in Hannover, Germany, including smart manufacturing processes to assist businesses in reducing waste and boost production capacity.
Products & Technologies
HUAWEI CLOUD Agent – HUAWEI CLOUD AI is built on the cloud, with AI at its heart. It blends new technologies such as cloud, big data, and AI with industry procedures and expert knowledge via a single platform and architecture to deliver integrated and collaborative intelligent services and exploit the value of data. It assists the government and businesses in upgrading smartly and gaining a competitive advantage. ModelArts is a one-stop-shop for AI development for developers. For machine learning and deep learning, it offers enormous data pre-processing and semi-automatic annotation, large-scale distributed training, automated model creation, and end-side-cloud model deployment capabilities.
Huawei iMaster NAIE – The iMaster NAIE creates a cloud-based data lake and AI training platform, as well as an AI inference framework in the control unit and each NE device. The AUTIN solution, which is part of Huawei’s service domain, enables network design, building, maintenance, and optimization of automated and intelligent services throughout the whole process. NAIE is a network enabler for intelligent autonomous driving that offers basic AI data management and model training services for the service, wireless, fixed network, core network, and data center domains. The trained model may be applied to inference analysis in a variety of disciplines, assisting each domain in effectively realizing automation and intelligence.
Collaborations
- In 2020, Huawei, UvA, and VU Amsterdam collaborated to establish a research lab for artificial intelligence (DREAMS Lab). Huawei put in about €3.5 million. This collaboration intended to deliver the next generation of search technology while considering Europe’s many languages and cultures. The lab’s aim is to guarantee that the next generation of search technology is pervasive, accurate, adaptable, relevant, intelligent, compassionate, and safe.
- In 2019, Huawei and the UNESCO Regional Office for Eastern Africa collaborated at the HUAWEI CONNECT Summit in Shanghai, China, to improve digital skills and the use of Artificial Intelligence (AI). This partnership aided in the training of university and college faculty members from Eastern Africa Regional nations who are in their early careers and eager to develop and incorporate AI into their teaching courses as part of their regular course. At the end of the course, there was an online certification exam, and those who passed got a Huawei HCIA-AI certification, allowing them to become qualified AI experts.
- In 2019, Huawei and Baidu launched a collaboration to investigate the artificial intelligence (AI) industry. This collaboration between the Chinese technological behemoths will aid in the development of a fundamental technical foundation to fuel the local AI sector. Huawei Kirin will collaborate with Baidu’s open-source deep-learning platform PaddlePaddle to establish a learning platform based on chipsets created in-house.
M&As
In 2019, Huawei acquired Vocord, a Russian face recognition company for $50 million along with patents, equipment, and hiring most of the related team. In 2016, Vocord’s face recognition algorithm was named the best in the world. At that time, Vocord, whose algorithm is inspired by deep neural networks, was able to correctly identify 75.127% of the faces amid 1 million distractors.
Conclusion
While a lot of companies and startups are researching AI and machine learning, these are the top AI companies that are collaborating with startups and making AI accessible to all. A detailed study of these companies along with their patent innovation portfolio in AI will foreshadow how AI technology will change the future world.
We at GreyB are eager to see what the future with AI will look like and are keen to keep digging into the top AI companies. Want to stay updated? Subscribe to our newsletter and join over 500 technoids for market moves, technology advancements, and industry insights.
Authored By: Vipin Singh, Market Research
Next Read: How research trends in Artificial Intelligence look like?







